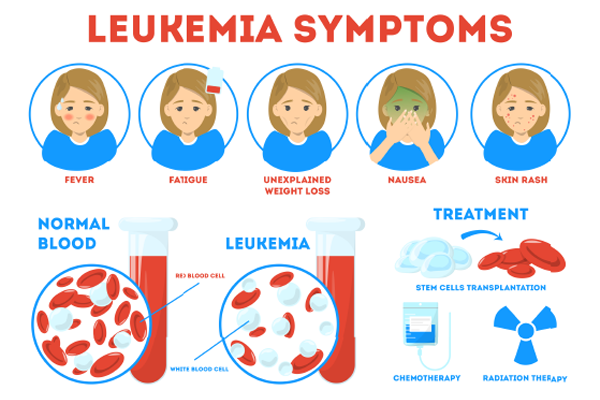
Blood cancer is often called the “silent enemy” because its early symptoms can be vague and easy to overlook. For women juggling work, family, and personal commitments, these warning signs may be brushed aside as stress, hormonal changes, or just part of daily life. However, recognising the blood cancer symptoms in females early can be life-saving. Awareness is the first step toward a timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
Recognising symptoms of blood cancer in female patients can be life-saving, as early intervention improves prognosis significantly. Here are ten early signs of blood cancer in women that should never be ignored.
Synopsis
10 Early Signs of Blood Cancer in Women
1. Unexplained Fatigue and Weakness
Fatigue is one of the most common yet overlooked blood cancer symptoms in females. Unlike normal tiredness, cancer-related fatigue is persistent and does not improve with rest. This occurs because cancerous cells interfere with the production of healthy red blood cells, leading to anemia. Women, especially those managing multiple responsibilities, often dismiss fatigue as a result of a busy lifestyle. However, if extreme tiredness persists for weeks, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
2. Frequent Infections
Blood cancers, particularly leukemia and lymphoma, weaken the immune system by reducing the production of white blood cells, making women more susceptible to infections. Persistent colds, respiratory infections, urinary tract infections, and slow-healing wounds could indicate an underlying issue. If you find yourself frequently ill without a clear cause, it may be time to undergo a medical evaluation.
3. Unexplained Weight Loss
Unexpected weight loss without changes in diet or exercise can be a warning sign of blood cancer. Cancer cells consume a significant amount of energy, leading to unintentional weight loss. In addition, certain blood cancers trigger metabolic changes that cause loss of appetite. If you have lost more than 5% of your body weight in six months without trying, seek medical advice.
4. Persistent Fever or Night Sweats
Unexplained fever and night sweats are common early symptoms of blood cancer in female patients, particularly those with lymphoma and leukemia. These fevers are usually low-grade but persistent, and they are not linked to an infection. Night sweats can be so severe that they drench bed sheets and disrupt sleep. If you experience frequent fevers and excessive sweating at night without any apparent infection, consult a doctor for further evaluation.
5. Easy Bruising and Bleeding
Blood cancers affect the bone marrow's ability to produce platelets, which help with blood clotting. As a result, women may notice unexplained bruising, frequent nosebleeds, prolonged bleeding from minor cuts, or heavy menstrual bleeding. If you experience unusual bleeding or bruising without a clear cause, it is essential to undergo blood tests to check platelet levels.
6. Swollen Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped glands that help fight infections. When affected by lymphoma or leukemia, these nodes can become enlarged, forming painless lumps in the neck, underarms, or groin. While swollen lymph nodes are often associated with common infections, persistent or growing lumps that do not resolve in a few weeks should be examined by a doctor.
7. Bone and Joint Pain
Bone and joint pain, especially in the back, hips, or ribs, can indicate blood cancer. Leukemia and multiple myeloma commonly affect the bone marrow, leading to bone destruction and discomfort. If you experience persistent or worsening pain in these areas without injury or exertion, it is advisable to seek medical attention.
8. Persistent Shortness of Breath
Breathlessness, even during mild activity, can be a symptom of blood cancer-related anemia. When red blood cell production declines, oxygen delivery to tissues is compromised, causing shortness of breath. If you find yourself gasping for air or feeling breathless without exertion, it is crucial to have your blood counts checked.
9. Skin Rashes or Itching
Certain types of blood cancer, particularly lymphoma, can cause persistent itching or rashes. This occurs due to the release of cytokines, which trigger inflammatory responses in the skin. If you develop unexplained rashes or severe itching that does not respond to usual treatments, it could be a sign of an underlying hematologic malignancy.
10. Abdominal Discomfort and Fullness
Some blood cancers cause enlargement of the spleen or liver, leading to a sensation of fullness, bloating, or discomfort in the abdomen. Women may notice they feel full after eating small amounts of food or experience pain in the left upper side of the abdomen. If such symptoms persist, it is important to undergo imaging tests to evaluate the size of internal organs.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Health
While medical treatment is essential, adopting a healthy lifestyle can support your recovery and overall well-being. Here are some lifestyle changes to consider:
-
Balanced Diet: Consume a nutrient-rich diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains to support your immune system.
-
Regular Exercise: Engage in moderate physical activity to boost energy levels and reduce fatigue.
-
Stress Management: Practice meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to manage stress and anxiety.
-
Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Eliminating harmful substances can improve your overall health and help in better treatment outcomes.
-
Adequate Rest: Ensure you get enough sleep to support the healing process.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing blood cancer involves several tests, including:
-
Complete Blood Count (CBC): Identifies abnormalities in red and white blood cell levels.
-
Bone Marrow Biopsy: Determines the presence of cancerous cells in the bone marrow.
-
Imaging Tests (CT, MRI, PET scans): Help assess the spread of the disease.
-
Flow Cytometry: Analyses blood cells to classify different types of blood cancer.
Treatment Options
Treatment for blood cancer varies based on the type and stage of the disease. Common treatments include:
-
Chemotherapy: Uses powerful drugs to kill cancerous cells.
-
Radiation Therapy: Targets and destroys cancer cells using high-energy beams.
-
Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific genetic mutations in cancer cells.
-
Bone Marrow Transplant: Replaces diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells.
-
Immunotherapy: Boosts the body's immune system to fight cancer effectively.
Blood Cancer Symptoms in Women
|
Symptom |
Possible Cause |
|
Unexplained fatigue |
Reduced red blood cell production (anemia) |
|
Frequent infections |
Weakened immune system due to low white blood cells |
|
Unexplained weight loss |
Cancer metabolism affecting appetite |
|
Persistent fever or night sweats |
Immune system response to cancerous cells |
|
Easy bruising and bleeding |
Low platelet count |
|
Swollen lymph node |
Lymphoma or leukemia affecting lymphatic system |
|
Bone and joint pain |
Cancerous cells in bone marrow |
|
Persistent shortness of breath |
Low red blood cells reducing oxygen delivery |
|
Skin rashes or itching |
Cytokine release from lymphoma |
|
Abdominal discomfort and fullness |
Enlarged spleen or liver |
Conclusion
Recognising the blood cancer symptoms in females early can make all the difference in successful treatment and recovery. If you or someone you know is experiencing persistent or unexplained symptoms, seeking medical guidance from an experienced specialist is essential.
At Manipal Hospital Dwarka, we offer comprehensive diagnostic and treatment options for blood cancer, ensuring that every patient receives specialised care tailored to their needs. Our expert oncologists, advanced facilities, and patient-centred approach help individuals navigate their journey toward better health. If you suspect any concerning symptoms, don’t delay—schedule a consultation with our specialists today. Early detection saves lives!
FAQ's
Early signs include persistent fatigue, frequent infections, unexplained weight loss, and swollen lymph nodes.
Doctors use blood tests, bone marrow biopsies, and imaging scans to diagnose blood cancer.
Yes, treatment options include chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy, and bone marrow transplants.
While most cases are not inherited, some genetic factors can increase the risk.
If you experience multiple persistent symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation.





















 7 Min Read
7 Min Read