
The liver is one of the body’s most essential organs, playing a central role in metabolism, regulating red blood cells (RBC), glucose synthesis and storage, and eliminating waste products from the body. Unfortunately, liver diseases are responsible for approximately two million deaths annually, accounting for around 4% of all deaths globally. The high mortality rate is largely due to complications from cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and acute hepatitis. To reduce the burden of liver diseases, liver function tests (LFTs), which are a series of blood tests, are often recommended. These tests measure substances produced by the liver, and abnormal levels—either high or low—can indicate the presence of various liver conditions. In this blog post, we will discuss the types, purpose, and interpretation of liver function tests to help you better understand your liver health.
Synopsis
What is a liver function test?
Liver function tests are blood tests to measure various substances produced by your liver, providing insights into your liver’s health and function. LFTs measure several substances from a blood sample, including enzymes, proteins, and byproducts. These tests help understand how your liver is functioning and avoid developing any long-term complications, making it crucial to get the test done periodically.
The liver function test procedure includes drawing a small amount of blood from your arm's vein by the healthcare provider and sending it to the laboratory. Abnormally high and low levels of various liver substances are measured in the lab, and the levels of different enzymes and proteins are compared. Any discrepancies in the results can help your doctor diagnose the underlying liver disease.
Why is a liver function test done?
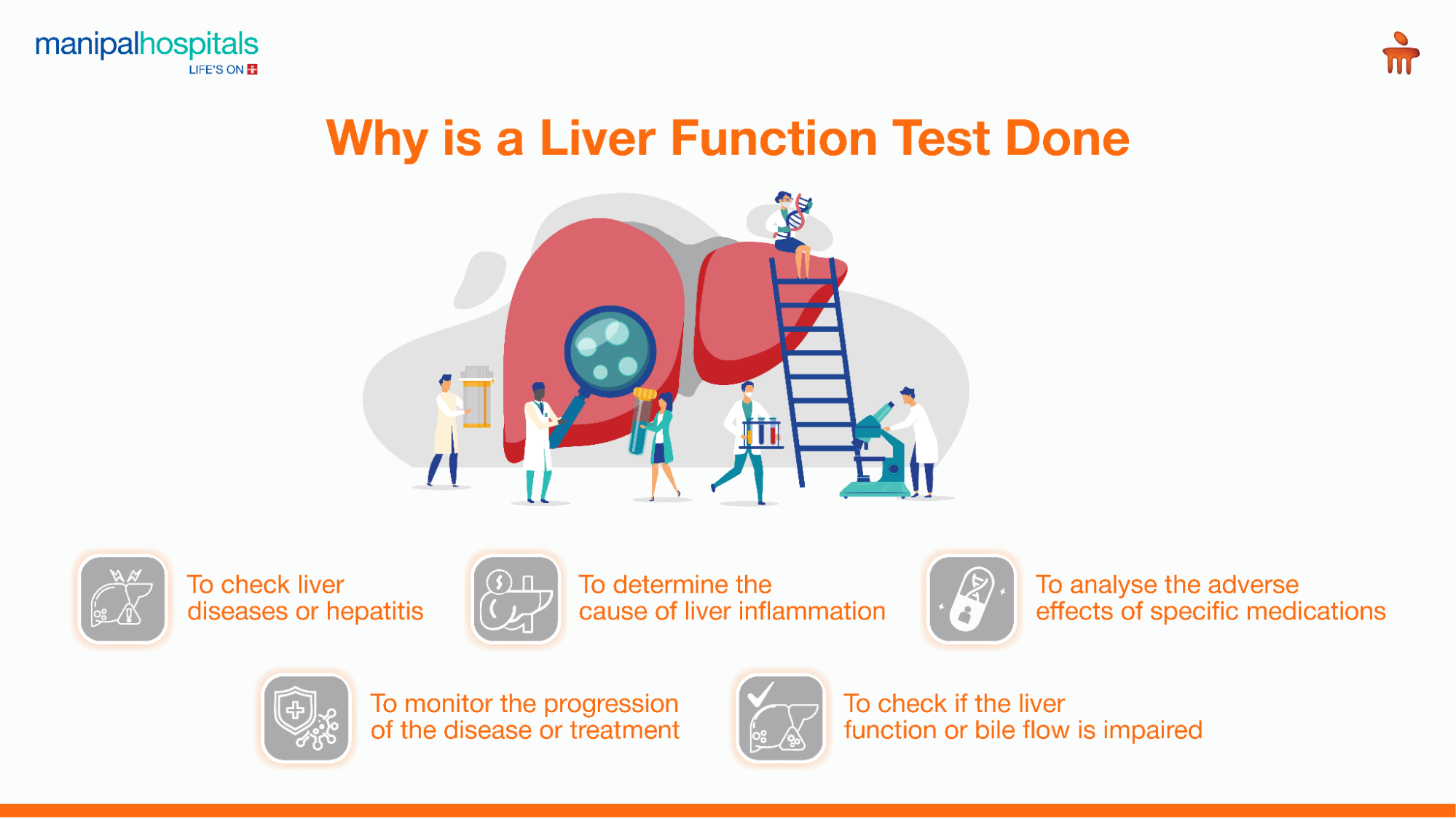
A liver function blood test is done to:
-
Check the test result values to determine if the individual has hepatitis or other liver disease. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment and disease management.
-
To monitor the progression of the disease or to check if the treatment is working. This helps make necessary modifications to therapy and prevent complications.
-
Analyse the effects of specific medications that could adversely harm the liver.
-
To determine if the liver inflammation is caused by alcoholic or non-alcoholic factors.
-
To analyse whether the problem lies in the liver itself or the bile ducts.
-
To check if the liver function or bile flow is impaired.
An LFT test might help diagnose fatty liver disease, hepatitis (toxic, autoimmune, or viral), hemochromatosis, Wilson’s disease, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, primary biliary cholangitis, liver cirrhosis, or cancer.
Types of Liver Function Tests
-
Liver enzyme tests: These tests may include alkaline phosphatase (ALP), alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) estimation. These enzymes are necessary to speed up chemical reactions within the body. High levels indicate liver injury, damage, or inflammation.
-
Total protein test: The test measures the level of protein in your blood, especially albumin. A low level indicates your liver isn’t functioning properly.
-
Bilirubin test: It is the measure of a waste product the liver releases into bile. Bilirubin is obtained when the liver breaks down old red blood cells; a higher bilirubin level indicates the liver’s inability to process and clear waste products.
-
Lactate dehydrogenase test: An enzyme found in many tissues, including the liver.
-
Prothrombin time tests: They measure the duration of time your blood takes to clot.
Interpretation of liver function tests
LFT test interpretation is important as the report often compares the values obtained with a normal range. However, you must remember that the normal range for a substance can vary with gender, body size, and different laboratories. Generally, the normal ranges for a liver substance are:
-
Alanine transaminase (ALT): 0 to 45 IU/L.
-
Aspartate transaminase (AST): 0 to 35 IU/L.
-
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP): 30 to 120 IU/L.
-
Gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT): 0 to 30 IU/L.
-
Bilirubin: 2 to 17 micromoles/L.
-
Prothrombin time (PT): 10.9 to 12.5 seconds.
-
Albumin: 40 to 60 g/L.
-
Total proteins: 3 to 8.0 g/dL
Elevated AST and ALT levels are indicators of liver injury, as these enzymes are released into the bloodstream when the liver is stressed. If both enzymes show equal elevation, there is a possibility of nonalcoholic injury, often caused by infections or toxins. In alcoholic liver injury, the AST levels are twice the level of ALT.
Are liver function blood tests accurate?
Even though LFT blood tests do not always point to a specific liver disease, they guide the healthcare provider to make the right diagnostic and treatment decisions. In addition to LFTs, the individual may have to undergo other blood tests, imaging studies, or a liver biopsy for disease confirmation.
Conclusion
Liver function tests often provide key insights into your liver’s health, helping detect issues early and resulting in better treatment outcomes. Understanding the importance of these tests is crucial to ensuring optimal liver functioning. Book your liver function test today at Manipal Hospitals, where our team of medical experts will provide you with the right guidance, resolve your queries, and offer comprehensive care.
FAQ's
Many illnesses can cause liver impairment, but the majority of them are caused by lifestyle choices, including drinking alcohol, being overweight, or getting viral infections.
If you have signs of liver illness such as jaundice, nausea and vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, dark urine, light stool, or exhaustion, you may require liver function testing. It is also indicated for people who have a history of liver illness or alcoholism, have been exposed to the hepatitis virus, or are taking medications that may harm their liver.
You may need to fast for at least 10 to 12 hours prior to the test.
The risks connected with the LFT test are negligible. Some patients may suffer little pain or bruising where the needle was put, although these symptoms subside quickly.
Lifestyle changes can support liver function and reduce the risk of damage. These include eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, limiting alcohol, avoiding toxins, and exercising regularly. Also, get vaccinated for hepatitis A and B, practice hygiene to prevent infections, and use medications responsibly.
You can schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals by contacting us or visiting our website.
Visit: https://www.manipalhospitals.com/specialities/pathology/
Contact no: 1800 102 5555






















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read










