Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic condition affecting millions globally, including a growing number in India. Understanding what type 2 diabetes is, recognising type 2 diabetes symptoms early, learning the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and adopting effective type 2 diabetes treatment and diet plans are crucial for managing this condition successfully. With the expert guidance of our endocrinologist in Jaipur, patients receive personalised care tailored to their unique health needs to lead fulfilling lives.
Synopsis
- What is Type 2 Diabetes?
- Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms: Recognising the Signs
- Difference Between Type 1 and 2 Diabetes
- Causes and Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes
- Type 2 Diabetes Treatment: Multimodal Approach
- Type 2 Diabetes Diet: Key Nutritional Guidelines
- Living Well with Type 2 Diabetes: The Role of Experts in Jaipur
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a long-term health condition where the body either resists the effects of insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar, or does not produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into cells, where it is used for energy. When this process is disrupted, glucose accumulates in the blood, causing high blood sugar levels or hyperglycemia.
Our endocrinologists in Jaipur explain that type 2 diabetes develops gradually and is largely influenced by lifestyle factors and genetics. It often begins with insulin resistance, where muscle, fat, and liver cells do not respond properly to insulin. Over time, insulin production declines, worsening blood sugar control.
Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms: Recognising the Signs
Type 2 diabetes symptoms often develop slowly and can be subtle at first, which means many people remain undiagnosed for years. Key symptoms to watch for include:
-
Increased thirst and dry mouth
-
Frequent urination, especially waking at night
-
Increased hunger despite eating
-
Unexplained weight loss or gradual weight gain
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Slow healing of cuts and wounds
-
Frequent infections, such as gum, skin, or urinary infections
-
Numbness or tingling sensations, particularly in the hands and feet
-
Darkened skin patches, especially around the neck or underarms (acanthosis nigricans)
If these signs are noticed, consulting our endocrinologists in Jaipur immediately can ensure early diagnosis and intervention.
Difference Between Type 1 and 2 Diabetes
Clarifying the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes is important for understanding treatment approaches:
-
Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. It usually presents early in life and requires lifelong insulin therapy.
-
Type 2 Diabetes: A metabolic disorder mostly linked to insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency, commonly occurring in adults but increasingly seen in younger populations due to lifestyle changes. It is managed with lifestyle modifications, oral medications, and sometimes insulin.
Our endocrinologists in Jaipur emphasise that while type 1 diabetes requires insulin replacement from diagnosis, type 2 diabetes management begins with lifestyle changes and may escalate to medicines or insulin as needed.
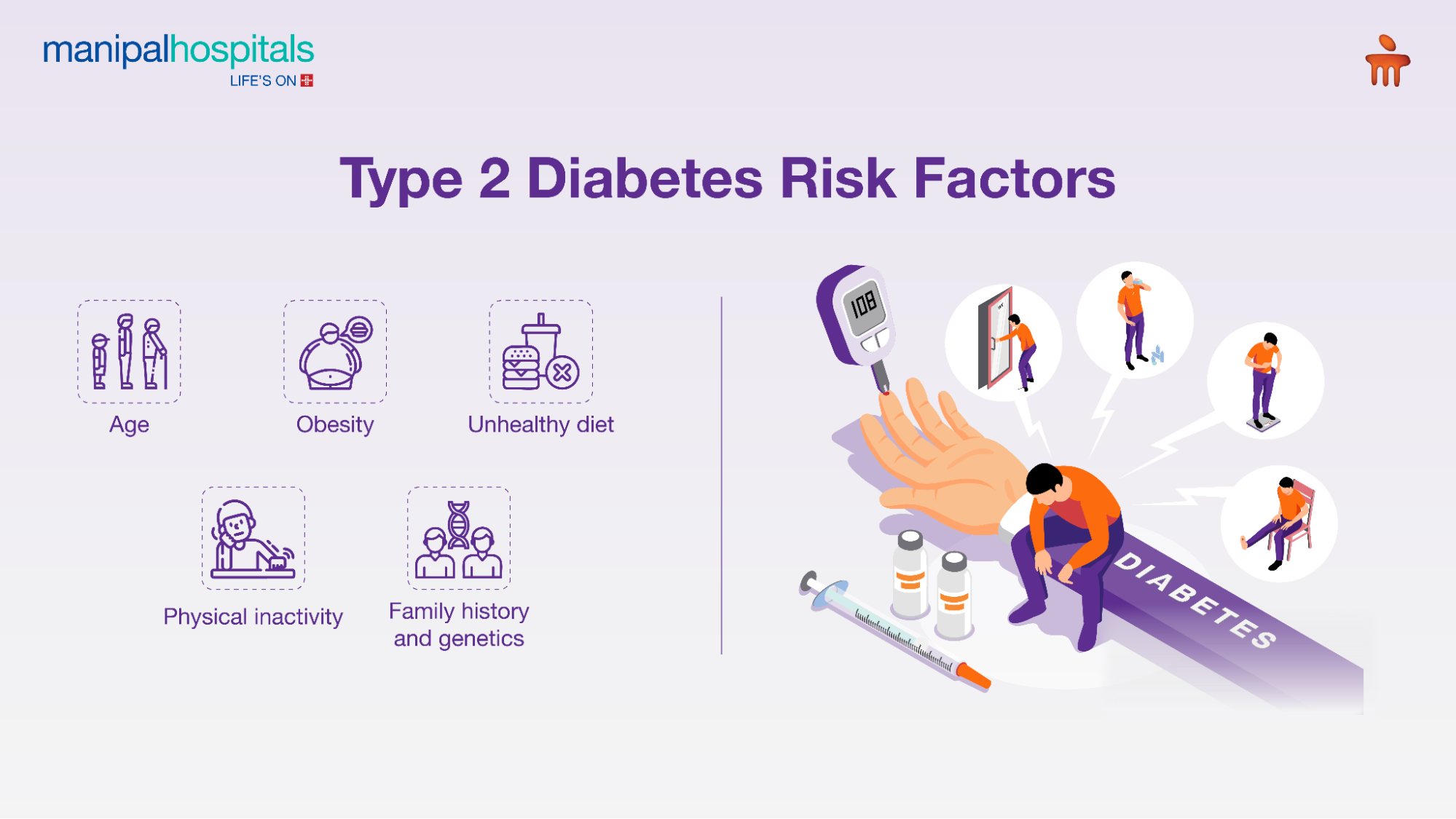
Causes and Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes arises from a complex interplay of genetics and lifestyle factors that impair insulin sensitivity and secretion. Common causes include:
-
Obesity and excess abdominal fat: Fat cells interfere with insulin action.
-
Physical inactivity: Lack of exercise contributes to insulin resistance.
-
Unhealthy diet: A Diet high in sugars and saturated fats increases risk.
-
Family history and genetics: Having a parent or sibling with diabetes raises susceptibility.
-
Age: Risk increases after 45 years, though younger people are increasingly affected.
-
Ethnic background: South Asians, including Indians, have a higher risk.
-
Other medical conditions: Hypertension, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and a history of gestational diabetes are linked to higher diabetes risk.
Pinpointing these causes helps our experts in Jaipur to create targeted intervention strategies.
Type 2 Diabetes Treatment: Multimodal Approach
Treating type 2 diabetes effectively involves a blend of lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring:
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Losing even a modest amount of weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise significantly improves insulin sensitivity.
-
Medications: When lifestyle changes alone are insufficient, our endocrinology experts in Jaipur may prescribe medication
-
Insulin Therapy: Reserved for advanced or uncontrolled cases where pancreatic function declines significantly.
Regular blood sugar monitoring and attending scheduled follow-ups with our endocrinologists in Jaipur are vital components of ongoing care.
Type 2 Diabetes Diet: Key Nutritional Guidelines
A healthy type 2 diabetes diet forms the cornerstone of managing blood sugar levels. Our nutrition specialists collaborate with our endocrinologists in Jaipur to create individualised meal plans. General recommendations include:
-
Balanced Macronutrients: Include moderate carbohydrates with low glycemic index, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
-
Fibre-Rich Foods: Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes improve blood sugar control and digestion.
-
Portion Control: Avoid overeating by managing meal sizes and timing.
-
Limit Sugars and Refined Carbs: Reduce sugary beverages, sweets, and processed snacks.
-
Regular Meal Schedule: Eating at consistent intervals stabilises glucose levels.
-
Hydration: Plenty of water and avoiding sugary drinks.
A type 2 diabetes diet, combined with physical activity, empowers patients to control their condition better and reduce complications.
Living Well with Type 2 Diabetes: The Role of Experts in Jaipur
Managing type 2 diabetes is a lifelong commitment that extends beyond medications and diet. Our diabetes and endocrinology experts in Jaipur provide comprehensive care that includes emotional support, education, and guidance on lifestyle modifications.
They work closely with patients to set realistic goals, monitor for complications like cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and kidney problems, and adjust treatment plans as needed. Patient empowerment and active participation in care lead to better outcomes.
Learn More: Diabetes: Types, Risks, Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention
FAQ's
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition where the body either resists insulin or doesn’t produce enough of it, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, unexplained weight changes, and slow-healing wounds.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease causing insulin deficiency requiring insulin therapy from diagnosis, while type 2 involves insulin resistance and relative deficiency managed initially by lifestyle changes and oral medications.
Treatment begins with lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, and may escalate to medications such as metformin, other oral drugs, or insulin therapy based on individual needs.
A type 2 diabetes diet emphasises balanced meals with fibre-rich foods, controlled carbohydrates, lean proteins, healthy fats, and avoidance of refined sugars and processed foods.





















 7 Min Read
7 Min Read