Managing diabetes during pregnancy is crucial for both the mother's health and the baby’s development. Pregnancy brings a lot of changes to the body, and for women with diabetes, these changes can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels. Whether you have pre-existing diabetes (type 1 or type 2) or develop gestational diabetes, effective management is essential to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
In this blog, we will explore the causes, risks, and methods of managing diabetes during pregnancy, as well as the important role of healthcare professionals in guiding the management process.
Synopsis
Understanding Diabetes and Pregnancy
Types of Diabetes in Pregnancy
-
Pre-existing Diabetes: If you have diabetes before becoming pregnant, it’s important to work with your healthcare provider to manage your condition. Pre-existing diabetes can be type 1 or type 2, both of which involve issues with insulin production or sensitivity.
-
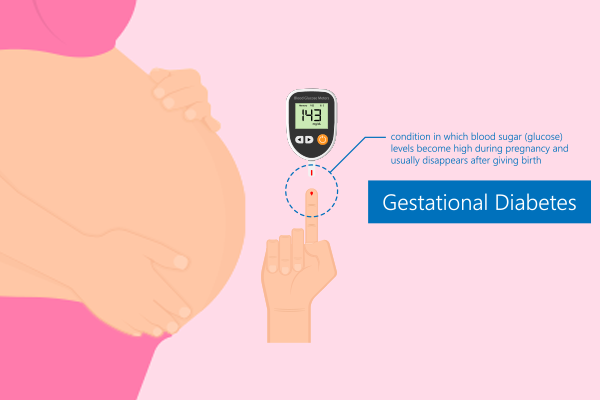
Gestational Diabetes: Gestational diabetes (GD) is a form of diabetes that develops during pregnancy and usually goes away after childbirth. It occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands during pregnancy, causing blood sugar levels to rise.
Gestational diabetes is more common in women who are overweight, have a family history of diabetes, or are over the age of 25. However, it can affect any pregnant woman.
More Reads: Glycemic Index: How It Affects Blood Sugar & Diabetes Management
Risks of Untreated Diabetes During Pregnancy
If diabetes is not well managed during pregnancy, it can lead to a range of complications for both the mother and the baby, including:
For the Mother:
-
Increased risk of developing high blood pressure and pre-eclampsia.
-
Higher likelihood of needing a caesarean section.
-
Postpartum bleeding and infection.
-
Increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes after pregnancy.
For the Baby:
-
Macrosomia: The baby may grow too large, making delivery difficult and increasing the risk of birth injuries.
-
Premature birth: The baby may be born prematurely due to high blood sugar levels.
-
Hypoglycaemia: Babies born to mothers with diabetes may experience low blood sugar shortly after birth.
-
Respiratory issues: Babies born early may have trouble breathing.
-
Increased risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes later in life.
More Reads: A To Z Expert Tips By Doctors To Follow During Pregnancy
Managing Diabetes During Pregnancy
Effective management of diabetes during pregnancy involves a combination of careful monitoring, lifestyle adjustments, and medication. Here are key strategies for managing diabetes:
1. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly
Frequent blood sugar monitoring is crucial for managing diabetes during pregnancy effectively. This allows you to understand how different foods, activities, and medications affect your blood sugar levels.
-
Pre-pregnancy: If you have pre-existing diabetes, it’s important to get your blood sugar levels under control before pregnancy. This will reduce the risk of complications.
-
During pregnancy: Your healthcare provider will likely recommend monitoring your blood sugar levels several times a day. This includes testing before and after meals, as well as during the night if necessary.
2. Adopt a Healthy, Balanced Diet
A healthy diet plays a critical role in managing diabetes during pregnancy. It’s important to eat nutritious meals that help keep blood sugar levels stable. Here are some dietary guidelines:
-
Carbohydrate Control: Focus on complex carbohydrates that release glucose more slowly, such as whole grains, vegetables, and legumes.
-
Healthy Fats: Include sources of healthy fats like avocados, nuts, and seeds. These fats are beneficial for both you and your baby.
-
Protein: Protein-rich foods, such as lean meats, eggs, and plant-based sources like beans and lentils, help maintain blood sugar control.
-
Portion Control: Eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day helps to prevent large spikes in blood sugar levels.
It’s advisable to work with a dietitian who specializes in managing diabetes to develop a meal plan that suits your individual needs.
More Reads: Home Remedies to Stop Vomiting During Pregnancy
3. Exercise Regularly
Exercise is beneficial for both controlling blood sugar and improving overall health during pregnancy. However, you should consult with your healthcare provider before starting or continuing any exercise regimen during pregnancy.
-
Moderate exercise such as walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga can help control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
-
Aim for 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week, but always listen to your body. Avoid any high-impact or risky exercises, especially as your pregnancy progresses.
4. Medication and Insulin Therapy
For some women with pre-existing diabetes or gestational diabetes, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to control blood sugar levels. In such cases, medication or insulin therapy may be necessary.
-
Insulin: If your blood sugar levels are not well-controlled with diet and exercise, insulin injections may be prescribed to help regulate blood sugar.
-
Oral Medications: For gestational diabetes, your healthcare provider may consider oral medications like metformin or other prescribed drugs. However, insulin is more commonly used during pregnancy due to its proven safety.
5. Keep Regular Check-ups with Your Healthcare Provider
Regular visits to your healthcare provider are essential to monitor your health and ensure the proper management of diabetes during pregnancy. These appointments typically include:
-
Blood Pressure Monitoring: High blood pressure is a common complication for women with diabetes during pregnancy. It’s important to monitor blood pressure regularly.
-
Ultrasound and Growth Monitoring: Regular ultrasounds can help track your baby’s growth and detect potential complications, such as macrosomia.
-
Urine Tests: Your healthcare provider may conduct urine tests to check for signs of protein, which could indicate pre-eclampsia.
6. Managing Stress
Stress can impact your blood sugar levels, so managing stress is an important part of managing diabetes during pregnancy. Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or prenatal yoga. Ensuring adequate sleep is also crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Postpartum Care
After childbirth, women who had gestational diabetes should continue to monitor their blood sugar levels, as they are at higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes in the future. It’s also important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular physical activity, to reduce the risk of diabetes in the future.
Top Tips for Managing Diabetes During Pregnancy
|
Tip |
Explanation |
|
Eat Small, Balanced Meals |
Instead of large meals, eat smaller meals more frequently to help maintain steady blood sugar levels. |
|
Monitor Your Blood Sugar Regularly |
Regular monitoring is key to understanding how your body responds to food, exercise, and medications. |
|
Exercise Regularly |
Engage in moderate exercise like walking or swimming to help control blood sugar levels. Always consult your doctor before starting an exercise routine. |
|
Plan Your Diet Wisely |
Include a variety of healthy foods: lean proteins, whole grains, and vegetables. Limit processed foods and sugar intake. |
|
Take Your Medications as Prescribed |
If insulin or other medications are prescribed, make sure to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions precisely. |
|
Stay Hydrated |
Drink plenty of water to help your kidneys filter out excess sugar through urine. |
|
Attend All Prenatal Appointments |
Regular check-ups allow your doctor to monitor both your health and your baby's development, making adjustments to your care plan if necessary. |
|
Reduce Stress |
Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation to help control stress, which can affect blood sugar levels. |
|
Get Enough Sleep |
Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night to help regulate your blood sugar levels and promote overall well-being. |
Conclusion
Managing diabetes during pregnancy requires a proactive approach, involving regular blood sugar monitoring, dietary adjustments, physical activity, and appropriate medication. With the right care and attention, it is possible to have a healthy pregnancy and reduce the risk of complications for both mother and baby. Always work closely with your healthcare team, including an obstetrician, diabetes & endocrinologist, and dietitian, to create a personalised plan for managing your diabetes.
If you are experiencing any signs or symptoms of diabetes during pregnancy, don’t hesitate to consult your healthcare provider. For women with diabetes, getting the right medical support and making lifestyle adjustments can help ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy.
For personalised care and support during pregnancy, visit Manipal Hospitals. Their expert team provides comprehensive care for women with diabetes, ensuring both mother and baby receive the best possible treatment throughout the pregnancy journey.
FAQ's
A pregnancy diabetes test, also known as the gestational diabetes test, is usually performed between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. It measures how your body handles sugar and is used to diagnose gestational diabetes.
Yes, gestational diabetes usually resolves after delivery. However, women who experience it are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
To reduce the risk of diabetes during pregnancy, maintain a healthy weight before pregnancy, eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and attend prenatal check-ups.
You can manage blood sugar levels by following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and monitoring your blood sugar frequently. If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, your doctor may suggest oral medication.
Uncontrolled diabetes during pregnancy can lead to complications such as high birth weight (macrosomia), preterm birth, low blood sugar in the baby after birth, and increased risk of pre-eclampsia for the mother.





















 7 Min Read
7 Min Read