Sustaining a bone fracture can be a life-altering moment. One slip, fall, or accident can suddenly pause your daily routine, bringing pain, discomfort, and uncertainty. Questions about healing time, mobility, and precautions are common. Effective fracture management, especially in the early stages, plays a crucial role in ensuring complete recovery and preventing long-term complications.
At Manipal Hospital Jaipur, our orthopaedic specialists reassure patients every day that fractures, when treated correctly, heal extremely well. With timely medical care, proper immobilisation, balanced nutrition, and guided rehabilitation, more than 95% of fractures heal completely, allowing patients to return to normal, active lives.
This guide serves as your step-by-step roadmap to recovery, explaining fracture management, fracture types, and the stages of fracture healing from injury to full strength.
Synopsis
- Initial Fracture Management: Laying the Foundation for Healing
- Reduction: Aligning the Bone
- Immobilisation and Surgical Support
- Understanding the Fracture Healing Stages
- Nutrition: Fuel for Faster Bone Healing
- Home Care Essentials: Do’s and Don’ts After a Fracture
- Rehabilitation and Physiotherapy: Regaining Strength and Confidence
- Conclusion: Healing Happens Best Together
Initial Fracture Management: Laying the Foundation for Healing
The first few hours and days after a fracture are critical. Proper early fracture management directly affects how well and how quickly the bone heals.
Accurate Diagnosis
At Manipal Hospital Jaipur, orthopaedic doctors begin with a detailed clinical examination supported by advanced imaging:
-
X-rays to identify the fracture location and alignment
-
CT scans or MRI for complex fractures involving joints, spine, or soft tissues
Accurate diagnosis also helps determine the types of fractures, such as simple fractures, compound fractures, stress fractures, or comminuted fractures.
Reduction: Aligning the Bone
If the broken bone ends are misaligned, doctors perform a reduction:
-
Closed reduction - realigning the bone without surgery
-
Open reduction - surgical correction for unstable or severe fractures
Correct alignment is essential for restoring normal function.
Immobilisation and Surgical Support
Once aligned, the bone must be stabilised:
-
Casts or splints for simple, stable fractures
-
Surgical fixation using plates, screws, rods, or pins for complex injuries
Surgical stabilisation often allows earlier movement of nearby joints and better outcomes in long-term fracture management.
Understanding the Fracture Healing Stages
Bone healing is a natural biological process that occurs in well-defined fracture healing stages. While most fractures heal within 6–8 weeks, complete recovery may take longer depending on age, overall health, and fracture severity.
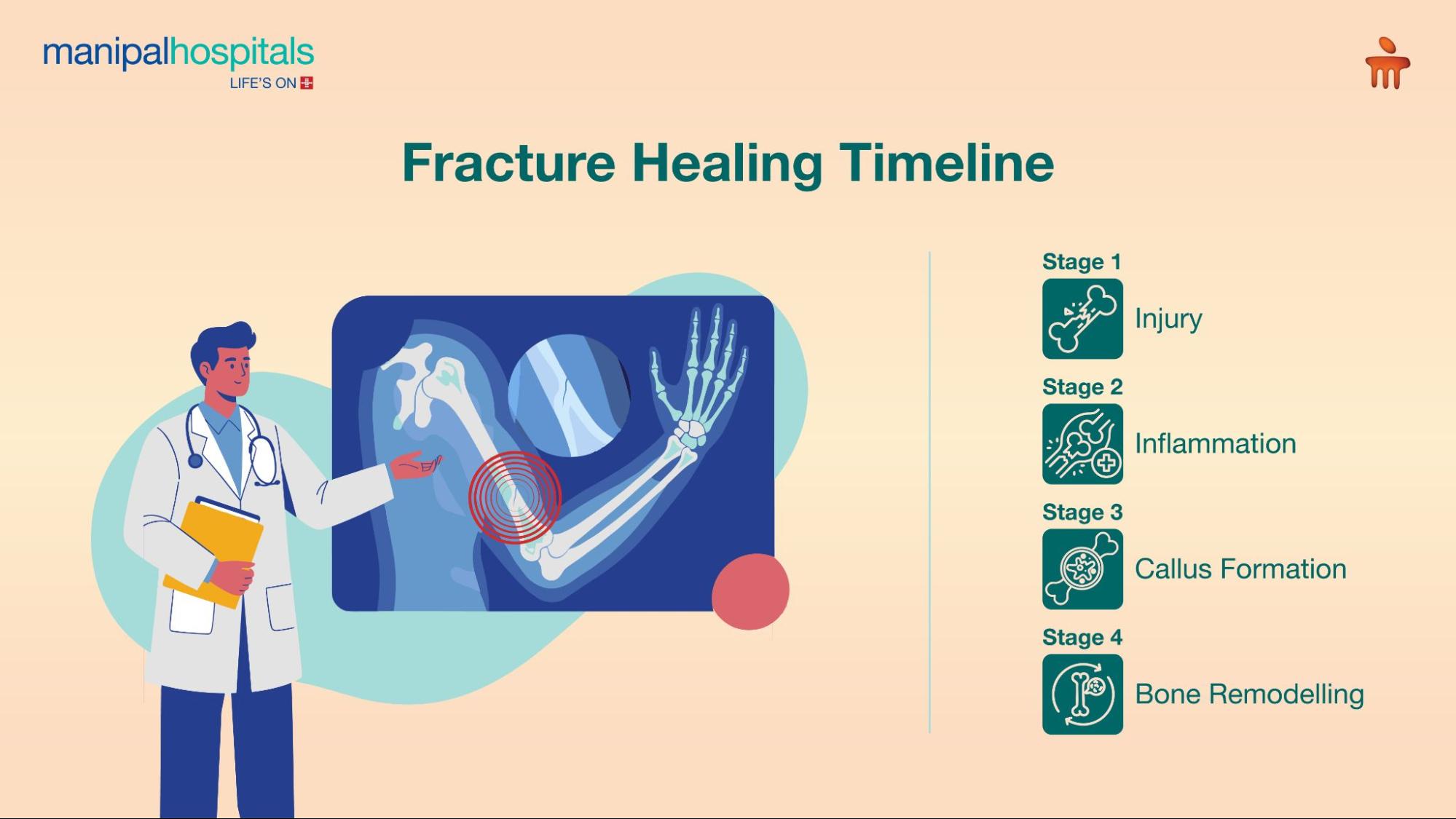
Stage 1: Inflammatory Phase (First Few Days)
-
Pain, swelling, and bruising are common
-
Blood clots form around the fracture site
This phase marks the body’s immediate healing response.
Stage 2: Reparative Phase (2–6 Weeks)
-
A soft callus forms around the fracture
-
The callus gradually hardens as new bone develops
During this stage, the bone begins to knit together.
Stage 3: Remodelling Phase (Months to a Year)
-
The new bone reshapes and strengthens
-
Bone regains near-normal structure and durability
Following medical advice during this phase ensures long-term strength and alignment.
Nutrition: Fuel for Faster Bone Healing
Good nutrition is a vital part of complete fracture management. At Manipal Hospital Jaipur, patients are encouraged to follow a bone-friendly diet.
Key Nutrients for Bone Repair
-
Protein - supports tissue repair
-
Sources: milk, yoghurt, eggs, pulses, fish, lean meat
-
-
Calcium - essential for bone strength
-
Sources: dairy products, ragi, sesame seeds, leafy greens
-
-
Vitamin D - improves calcium absorption
-
Sources: sunlight, fortified milk, egg yolk, fatty fish
-
-
Vitamin C - supports collagen formation
-
Sources: oranges, amla, guava, tomatoes
-
Adequate hydration further supports healing.
Home Care Essentials: Do’s and Don’ts After a Fracture
Proper home care prevents complications and supports a smoother recovery.
Do’s
-
Elevate the injured limb to reduce swelling
-
Apply ice packs around (not directly on) the cast
-
Keep the cast clean and completely dry
-
Move fingers or toes regularly
-
Follow weight-bearing instructions carefully
Don’ts
-
Do not insert objects into the cast
-
Do not ignore increasing pain or numbness
-
Do not loosen or remove the cast yourself
-
Do not smoke, as it delays bone healing
If you notice severe pain, colour changes, or a foul smell from the cast, seek medical attention immediately.
Rehabilitation and Physiotherapy: Regaining Strength and Confidence
Once healing is stable, rehabilitation begins—an essential part of successful fracture management.
At Manipal Hospital Jaipur, physiotherapists design personalised programmes to:
-
Restore joint mobility
-
Strengthen weakened muscles
-
Improve balance and coordination
-
Prevent stiffness and long-term disability
-
Enable safe return to work, daily activities, and sports
Studies show that patients who follow physiotherapy recover up to 50% faster with better functional outcomes.
Conclusion: Healing Happens Best Together
Recovering from a fracture requires patience, consistency, and expert care. With proper fracture management, healthy nutrition, and structured rehabilitation, most patients regain full strength and independence.
At Manipal Hospital Jaipur, our orthopaedic team supports you at every stage—from emergency care and surgery to physiotherapy and long-term recovery—ensuring you heal stronger and safer.
If you or a loved one has suffered a fracture, book an appointment with our orthopaedic specialists at Manipal Hospital Jaipur for comprehensive and compassionate care.
Disclaimer - This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Please consult a qualified orthopaedic specialist for diagnosis and treatment.
FAQ's
Most fractures heal in 6–8 weeks, but full recovery may take several months, depending on fracture type and age.
Common types include simple fractures, compound fractures, stress fractures, and comminuted fractures.
You cannot rush healing, but proper nutrition, avoiding smoking, and following fracture management guidelines help support faster recovery.
Limited movement weakens muscles and stiffens joints. Physiotherapy helps restore normal function.
Severe pain, swelling, numbness, fever, or foul smell from the cast requires immediate medical attention.





















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read