Did You Know that India Leads the World in Mouth Cancer Cases?
India reports the highest number of oral cancer cases globally. This condition affects different parts of the oral cavity, such as the lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, and throat. Major risk factors include smoking or chewing tobacco as well as betel quid, excessive alcohol intake, poor oral hygiene, and infections like human papillomavirus (HPV).
In 2020 alone, India documented around 135,929 new cases of oral cancer. Alarmingly, between 60% and 80% of these are identified at later stages. This data underscores the necessity for increased awareness as well as prompt diagnosis and interventions for oral cancer.
Synopsis
Understanding Mouth/Oral Cancer
Mouth cancer is one of the most common types of head and neck cancers. It typically affects people over the age of 40. Men are more likely to develop it than women. The disease can appear in various areas, including the lips, tongue, tonsils, roof of the mouth, the floor of the mouth, and the throat.
Oral cancer begins in the squamous cells that line the mouth. When these cells undergo genetic mutations, they begin to grow abnormally and uncontrollably, forming malignant tumours.
What Can Increase the Risk of Mouth Cancer?
Several everyday habits and health factors can raise the chances of developing mouth or oral cancer. Here are some of the most common ones:
- Tobacco Use
Whether it's smoking cigarettes, using cigars, or chewing tobacco, all forms can be harmful. Cigarettes and tobacco usually have chemicals like nicotine and other carcinogens. These harmful agents significantly contribute to health issues, including mouth cancer.
- Alcohol Consumption
Drinking alcohol, especially heavily or regularly, can irritate the tissues inside your mouth. When combined with tobacco, the risk becomes much higher, as the two substances can work together to harm healthy cells.
- HPV Infection
The human papillomavirus (HPV) can affect parts of the mouth and throat, especially the area at the back, like the base of the tongue and the tonsils. Certain types of HPV, particularly HPV-16, are now known to cause oropharyngeal cancers
- Too Much Sun Exposure
Spending a lot of time in the sun without lip protection can increase the risk of lip cancer, particularly in people with lighter skin. This type of cancer is usually related to long-term sun damage.
- Poor Oral Hygiene
Not taking care of your teeth and gums doesn’t just lead to dental problems. It can also make the mouth more vulnerable to cancer, especially if combined with smoking or drinking.
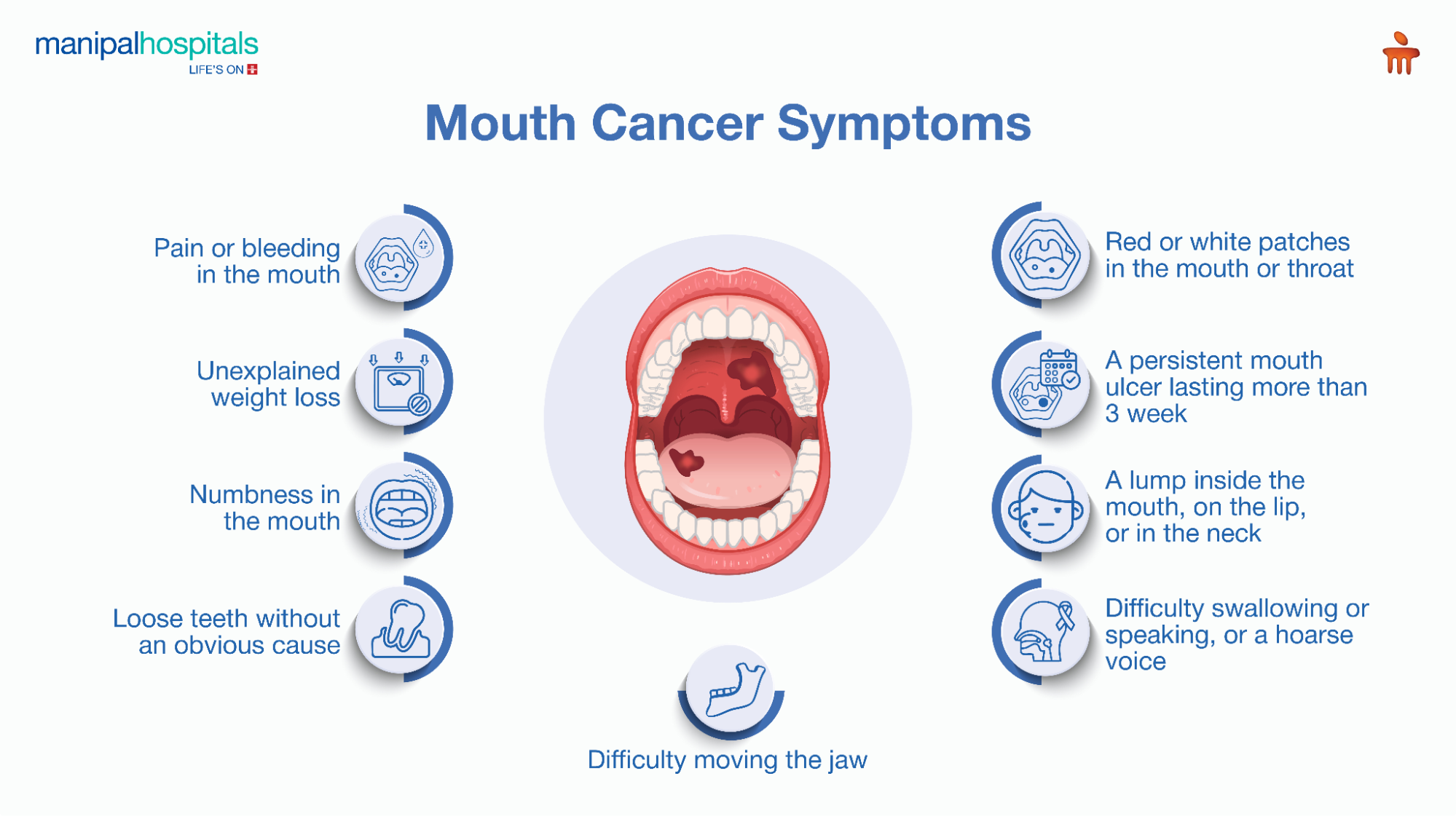
Signs and Symptoms of Mouth Cancer
-
White or red patches inside the mouth or throat.
-
Non-healing mouth ulcers for more than 3 weeks.
-
Lumps in the mouth, neck, or lips.
-
Bleeding or pain in the mouth.
-
Trouble swallowing or speaking.
-
Hoarseness of voice
-
Sudden, unexplained weight loss.
-
Numbness in the mouth.
-
Loosening of teeth without a dental cause.
-
Restricted jaw movement
Diagnosis of Mouth Cancer
The doctor will start by checking your mouth, throat, tongue, and neck to look for suspicious areas. Biopsy is advised in case any suspicious growths or lesions are found. This is done to determine if the cancer is present. Once detected, imaging or screening tests are done to determine the extent and stage of cancer. Some of these tests are X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, PET scans, or Endoscopy.
Staging of Mouth Cancer
Oral cancer is classified into four stages:
Stage 1: The tumour is 2 cm or smaller and hasn’t spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Stage 2: Tumour size is between 2 cm and 4 cm, without lymph node involvement.
Stage 3: Tumour may be larger than 4 cm, or it may have reached one nearby lymph node but not distant sites.
Stage 4: The cancer has spread extensively, possibly to surrounding tissue, involving multiple lymph nodes, or other organs.
Mouth Cancer Treatment
The treatment plan depends on the size, location, stage, and type of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Common treatments include:
-
Surgery: For early-stage cancers, removing the tumour and possibly affected lymph nodes can be effective.
-
Chemotherapy: Uses anti-cancer drugs. These drugs target and kill cancer cells throughout the body. These may be used before surgery or radiotherapy (to shrink the tumour and make it easy to treat), after surgery, alongside radiotherapy, or in recurrent cancer cases.
-
Radiation Therapy: High-energy radiation beams destroy cancer cells. This is often used for precise targeting in head and neck cancers, minimising the damage to adjacent tissues.
-
Targeted Therapy: These drugs block specific molecules that cancer cells rely on to grow and survive. They may also make cancer cells more responsive to radiation.
-
Immunotherapy: By strengthening the immune system’s response, this newer treatment helps the body fight cancer more effectively, particularly in advanced or resistant cases.
Conclusion
Mouth cancer can affect different regions of the oral cavity, such as the lips, tongue, gums, and throat. If you notice warning signs like non-healing mouth ulcers, unusual patches, lumps, difficulty speaking or swallowing, or unexpected weight loss, don’t delay seeking medical help. Early detection significantly improves the chances of successful treatment.
At Manipal Hospitals, Goa, our team of skilled oncologists and head and neck specialists are equipped to provide accurate diagnoses and advanced treatments for mouth cancer.
FAQ's
Yes, particularly when diagnosed early. Early-stage treatment often leads to complete recovery. Advanced cases are harder to treat, but therapies can still help manage the disease and improve the patient's quality of life.
Most mouth cancers are squamous cell carcinomas. They tend to progress at a moderate to fast pace. The progression depends on the tumour location and type.
You can lower your risk by avoiding tobacco, limiting alcohol, getting vaccinated for HPV, protecting your lips from excessive sun exposure, and visiting your dentist regularly for checkups.
Usually, pain is not an early symptom. Pain tends to develop as the cancer progresses. However, persistent discomfort should never be ignored. Consult your doctor or dentist if symptoms arise.
You can schedule your visit by calling us or heading to our official website.
Visit: https://www.manipalhospitals.com/goa
Contact:1800 102 5555





















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read