Cholera is a potentially fatal disease caused by consuming food or water tainted with the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. It spreads swiftly in areas lacking proper sanitation and clean water facilities. Understanding how to prevent cholera and recognising early symptoms can help save lives, particularly during outbreaks or in high-risk regions.
This article outlines the top 10 essential measures to prevent cholera, discusses its symptoms, causes, treatment, and the important role of us being a highly trusted multi-speciality hospital in Delhi in managing the condition effectively.
Synopsis
What Triggers Cholera?
Knowing what causes cholera is key to stopping its spread. The infection arises from ingesting contaminated water or food. Common transmission sources include:
-
Polluted drinking water
-
Undercooked seafood (especially shellfish)
-
Raw fruits and vegetables cleaned with unsafe water
-
Poor sanitation and improper sewage disposal
Once inside the body, the bacterium releases toxins that lead to acute watery diarrhoea and severe dehydration.
Symptoms of Cholera
Being able to identify the symptoms of cholera early allows for timely treatment. Signs and symptoms typically develop between a few hours to five days after infection. Common features of cholera include:
-
Frequent watery diarrhoea (often pale or “rice-water” in appearance)
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Fast heartbeat
-
Dry mouth and tongue
-
Muscle cramps
-
Intense thirst
-
Shock due to fluid loss in advanced stages
Prompt medical assistance is crucial, especially for vulnerable individuals such as children and the elderly.
Top 10 Preventive Measures of Cholera
Below are the most effective cholera prevention strategies:
1. Consume Clean Drinking Water
Always drink water that is boiled, filtered, treated with chlorine, or bottled. Avoid drinking tap water or using ice made from unclean sources.
2. Maintain Good Hand Hygiene
Wash hands thoroughly with soap and safe water:
-
Before handling food or eating
-
After using the lavatory
-
After coming into contact with infected individuals
Use a hand sanitiser containing alcohol when soap and water aren’t available.
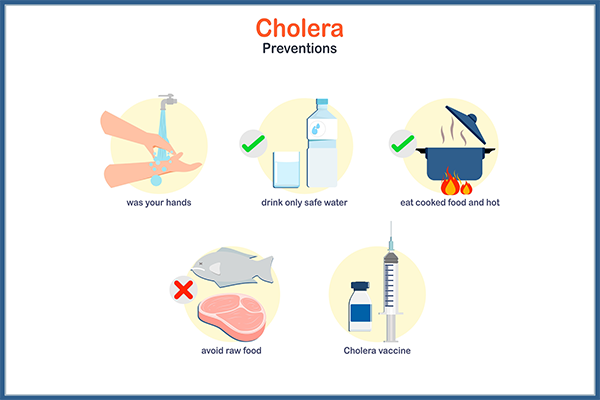
3. Stick to Well-Cooked Meal
Avoid raw or partially cooked seafood and meats. Ensure your food is cooked completely and served hot. This is one of the most important cholera prevention techniques.
4. Clean Fruits and Vegetables Properly
Wash produce with clean water before eating. If possible, peel fruits before consumption to reduce exposure to contaminants.
5. Use Proper Sanitation Facilities
Using clean toilets or latrines helps stop the spread of cholera. Avoid defecating in open areas, particularly near water bodies.
6. Dispose of Waste Safely
Ensure household waste is disposed of in a sanitary manner. Keep rubbish bins sealed and away from water supplies.
7. Disinfect Surfaces Regularly
Clean cooking utensils, kitchen counters, and bathroom surfaces often with disinfectants like bleach to prevent bacterial transmission.
8. Store Food and Water Securely
Keep food and water covered in clean containers to prevent exposure to flies, dust, or dirty hands.
9. Vaccinate When Required
For individuals living in or travelling to areas with known outbreaks, consider oral vaccines like Dukoral or Shanchol. These provide added protection, though they should be used alongside other preventive methods.
10. Seek Prompt Medical Attention
If you experience signs of cholera, such as sudden diarrhoea and vomiting, get medical help straight away. Healthcare brands like us are well-equipped to handle cholera cases with expert care.
How Can We Prevent Cholera Outbreaks?
In addition to individual actions, governments and communities must invest in:
-
Clean water infrastructure
-
Efficient sewage systems
-
Health education programmes
-
Rapid response to reported cholera cases
Public awareness and preparedness are vital. At Manipal Hospital, we often participate in such community initiatives, working towards creating a cholera-free environment.
More Reads: Assessing The Risk Of Infectious Diseases In Flooded Areas
Cholera Treatment Options
Despite being highly infectious, cholera is manageable with quick and appropriate treatment. The main focus is on restoring fluids and electrolytes. Common cholera treatment methods include:
-
Oral Rehydration Solutions (ORS): A balanced mix of water, salt, and sugar to prevent dehydration.
-
Intravenous (IV) Fluids: Used for patients who are critically dehydrated or cannot consume ORS.
-
Antibiotic Therapy: Prescribed in more serious cases to shorten the duration of diarrhoea and reduce fluid loss.
-
Zinc Supplements: Particularly helpful in young children to enhance recovery.
We offer round-the-clock care, including IV fluid management, lab testing, and intensive care, ensuring the best possible outcome for patients affected by cholera.
Conclusion
Cholera is preventable and treatable with the right knowledge and timely action. Practising proper hygiene, using clean water, eating cooked food, and seeking early medical care are the cornerstones of cholera prevention. By understanding how we can prevent cholera and recognising the signs and symptoms of cholera, individuals and communities can reduce the risk significantly.
If you or a loved one shows any symptoms of cholera disease, consult your nearest healthcare provider immediately. For expert diagnosis, treatment, and preventive care, Manipal Hospital Delhi is a trusted name in combating infectious diseases. Their commitment to patient safety, advanced medical facilities, and community health education makes them a leader in managing outbreaks like cholera.
FAQ's
Cholera is caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae, which spreads through contaminated food or water. It is often linked to poor sanitation, unclean drinking water, and inadequate hygiene practices. Outbreaks commonly occur in areas lacking proper sewage and water treatment systems.
Early symptoms of cholera include the sudden onset of watery diarrhoea, vomiting, muscle cramps, and signs of dehydration such as dry mouth, sunken eyes, and low blood pressure. Immediate medical care is essential to prevent complications. Hospitals like ours provide rapid and effective treatment for such cases.
Cholera prevention involves drinking safe water, practising good hand hygiene, consuming fully cooked food, and using clean sanitation facilities. Proper food storage and vaccination in high-risk areas also help reduce the risk.
Yes, oral cholera vaccines such as Shanchol and Dukoral are available and recommended for people travelling to or living in high-risk regions. While not 100% effective, they offer significant protection when combined with good hygiene practices.
Cholera treatment focuses on rapid rehydration using oral rehydration salts (ORS) or intravenous fluids. In severe cases, antibiotics may be prescribed. We are equipped with skilled doctors and advanced facilities to manage cholera efficiently and prevent complications.





















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read