Kidney health plays a vital role in maintaining overall well-being, yet kidney disorders often progress silently. Among the most commonly diagnosed conditions are acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease. While both affect kidney function, their causes, progression, treatment approaches, and long-term outcomes differ significantly. Understanding these differences can help patients seek timely care and prevent irreversible damage.
This blog explains chronic kidney disease, compares it with acute kidney injury, discusses types of chronic kidney disease, outlines acute kidney injury treatment, and highlights available chronic kidney disease treatment options.
Synopsis
- What Is Chronic Kidney Disease?
- What Is Acute Kidney Injury?
- Acute vs Chronic Kidney Disease: Overview
- Key Differences Between Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease
- Types of Chronic Kidney Disease
- Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease
- Acute Kidney Injury Treatment
- Chronic Kidney Disease Treatment
- Lifestyle Management in Chronic Kidney Disease
- Complications of Untreated Chronic Kidney Disease
- When to See a Nephrologist
- Conclusion
What Is Chronic Kidney Disease?
Chronic kidney disease is a long-term condition characterised by a gradual and irreversible loss of kidney function over months or years. In chronic kidney disease, the kidneys progressively lose their ability to filter waste, regulate electrolytes, and maintain fluid balance.
Most patients with chronic kidney disease remain asymptomatic in early stages, making regular screening essential. According to our nephrologists in Patiala, delayed diagnosis is one of the most common challenges in managing chronic kidney disease effectively.
What Is Acute Kidney Injury?
Acute kidney injury (AKI) refers to a sudden decline in kidney function occurring over hours or days. Unlike chronic kidney disease, acute kidney injury is often reversible if identified and treated promptly.
Common Causes of Acute Kidney Injury
-
Severe dehydration
-
Infections or sepsis
-
Sudden blood loss
-
Drug toxicity
Prompt acute kidney injury treatment can restore kidney function completely in many cases.
Acute vs Chronic Kidney Disease: Overview
Understanding how acute kidney injury differs from chronic kidney disease is essential for accurate diagnosis and management.
|
Feature |
Acute Kidney Injury |
Chronic Kidney Disease |
|
Onset |
Sudden |
Gradual |
|
Duration |
Short-term |
Long-term |
|
Reversibility |
Often reversible |
Usually irreversible |
|
Progression |
Rapid |
Slow |
|
Treatment focus |
Immediate recovery |
Long-term management |
Key Differences Between Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease
1. Onset and Progression
-
Acute kidney injury develops rapidly and requires urgent acute kidney injury treatment.
-
Chronic kidney disease progresses slowly, often over years, before symptoms appear.
2. Symptoms
-
Acute kidney injury may cause sudden reduced urine output and swelling.
-
Chronic kidney disease may initially be silent, later causing fatigue, swelling, and appetite loss.
3. Long-Term Impact
-
Acute kidney injury may resolve completely.
-
Chronic kidney disease often leads to permanent kidney damage if unmanaged.
Early identification by our nephrologists in Patiala helps prevent complications in both conditions.
Types of Chronic Kidney Disease
Understanding the types of chronic kidney disease helps tailor treatment strategies.
Major Types of Chronic Kidney Disease
-
Diabetic nephropathy
-
Hypertensive nephropathy
-
Glomerulonephritis
-
Polycystic kidney disease
-
Chronic interstitial nephritis
Each of these types of chronic kidney disease progresses differently and requires individualised care. Accurate classification of types of chronic kidney disease improves long-term outcomes, as emphasised by our nephrologists in Patiala.
Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease
Diagnosis of chronic kidney disease involves a combination of:
-
Blood tests (creatinine, eGFR)
-
Urine tests (protein levels)
-
Imaging studies
-
Kidney biopsy (in select cases)
Early diagnosis allows timely chronic kidney disease treatment and slows disease progression.
Acute Kidney Injury Treatment
Acute kidney injury treatment focuses on correcting the underlying cause and supporting kidney recovery.
Core Components of Acute Kidney Injury Treatment
-
Fluid and electrolyte correction
-
Treating infections
-
Stopping nephrotoxic medications
-
Temporary dialysis if required
With appropriate acute kidney injury treatment, many patients regain normal kidney function.
Chronic Kidney Disease Treatment
Unlike acute conditions, chronic kidney disease treatment aims to slow progression and manage complications.
Key Goals of Chronic Kidney Disease Treatment
-
Control blood pressure
-
Manage blood sugar
-
Reduce proteinuria
-
Correct anaemia and mineral imbalance
Effective chronic kidney disease treatment often requires long-term lifestyle changes and medication adherence. According to our nephrologists in Patiala, patient education plays a critical role in treatment success.
Lifestyle Management in Chronic Kidney Disease
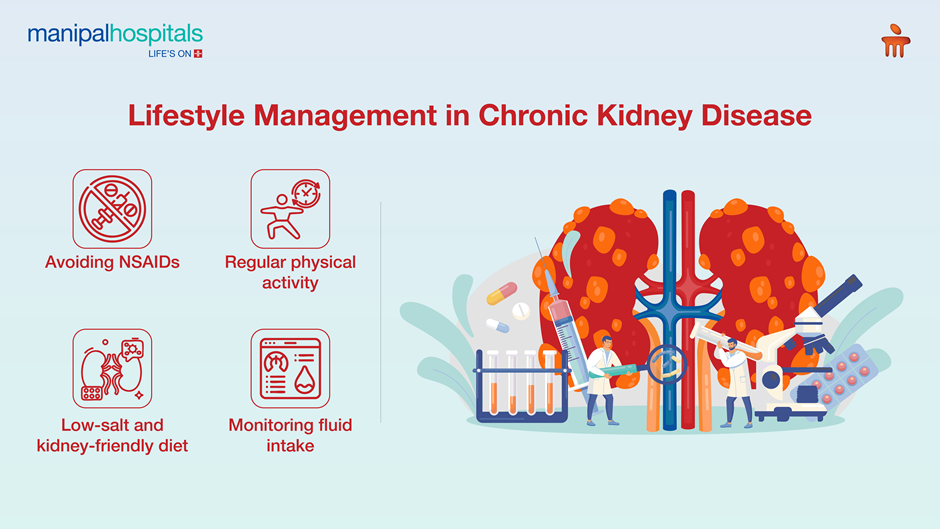
Lifestyle modification is a cornerstone of chronic kidney disease treatment.
Recommended Lifestyle Measures
-
Low-salt and kidney-friendly diet - A low-salt, kidney-friendly diet helps control blood pressure, reduce fluid retention, and minimise stress on the kidneys. Patients with chronic kidney disease are often advised to limit sodium, manage protein intake, and regulate potassium and phosphorus levels based on disease stage.
-
Regular physical activity - Engaging in regular physical activity improves cardiovascular health, helps maintain a healthy weight, and enhances insulin sensitivity, all of which are important in chronic kidney disease management.
-
Avoiding NSAIDs - Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can significantly worsen kidney function by reducing blood flow to the kidneys. In patients with chronic kidney disease, regular or unsupervised use of NSAIDs increases the risk of further kidney damage.
-
Monitoring fluid intake - Monitoring fluid intake is essential to prevent both dehydration and fluid overload in chronic kidney disease. Depending on disease stage and urine output, patients may need to adjust daily fluid consumption.
Such measures significantly improve the quality of life in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Complications of Untreated Chronic Kidney Disease
Without appropriate chronic kidney disease treatment, complications may include:
-
Cardiovascular disease
-
Electrolyte imbalance
-
Bone disorders
-
End-stage kidney disease
Preventing these complications is a key focus for our nephrologists in Patiala.
When to See a Nephrologist
Patients should consult a specialist if they experience:
-
Persistent swelling
-
Reduced urine output
-
Abnormal blood or urine tests
Timely referral helps manage both acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease effectively.
Conclusion
Both acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease require timely diagnosis and appropriate management, but their treatment goals differ significantly. While acute kidney injury treatment focuses on recovery, chronic kidney disease treatment emphasises long-term control and complication prevention. Understanding the types of chronic kidney disease, recognising early symptoms, and seeking expert care can make a profound difference in outcomes.
FAQ's
Acute kidney injury is sudden and often reversible, while chronic kidney disease is gradual and usually permanent.
No, chronic kidney disease cannot be cured, but proper chronic kidney disease treatment can slow progression.
Common types of chronic kidney disease include diabetic nephropathy, hypertensive kidney disease, and glomerulonephritis.
Early acute kidney injury treatment is highly effective and often restores kidney function.
Dialysis is considered in advanced stages when chronic kidney disease severely impairs kidney function.





















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read