Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) remains a leading health concern worldwide, affecting millions and often necessitating interventions to restore proper blood flow to the heart. When diagnosed with significant blockages in the heart's arteries, patients and their families often face a critical decision: whether to undergo angioplasty or coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery. Both procedures aim to alleviate symptoms, prevent heart attacks, and improve long-term outcomes, but they differ significantly in their approach, recovery, and suitability for various conditions. Understanding the difference between angioplasty and bypass is crucial for making an informed choice.
At Manipal Hospitals, our dedicated team of the best cardiologists in Patiala is committed to guiding you through this complex decision, ensuring you receive the most appropriate and effective care. This comprehensive guide will delve into angioplasty vs bypass surgery, helping you understand which option might be right for your unique situation.
Synopsis
- Understanding Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
- Angioplasty: A Minimally Invasive Solution
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery: A Comprehensive Revascularisation
- Angioplasty vs. Bypass: Key Differences and Decision Factors
- Life After the Procedure: Recovery and Lifestyle
- Care Essentials: Do's and Don'ts
- Why Choose Manipal Hospitals Patiala?
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
CAD occurs when the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque (atherosclerosis). This narrowing reduces blood flow, leading to symptoms like chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, and in severe cases, a heart attack. The choice between angioplasty and bypass surgery depends largely on the severity, number, and location of these blockages, as well as the patient's overall health.
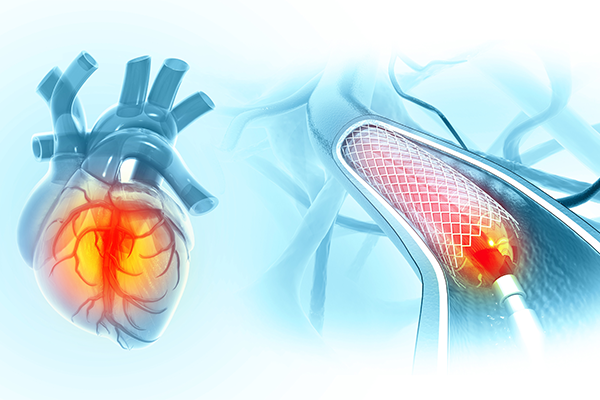
Angioplasty: A Minimally Invasive Solution
Angioplasty, often performed as Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI), is a minimally invasive procedure designed to open narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. It is typically performed by a skilled cardiologist in Patiala.
How Angioplasty Works:
-
A thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, usually in the wrist or groin, and guided to the blocked coronary artery.
-
A tiny balloon at the tip of the catheter is inflated to compress the plaque against the artery walls, widening the artery.
-
In most cases, a small mesh tube called a stent is then deployed. The stent remains permanently in the artery, acting as a scaffold to keep it open and reduce the chance of re-narrowing. Modern stents are often coated with medication to further prevent blockages.
-
Laser angioplasty is a specialised form where a laser is used to vaporise plaque buildup, particularly effective for certain types of blockages that are difficult to treat with traditional balloons.
Advantages of Angioplasty:
-
Minimally Invasive: Involves only a small incision, leading to less pain and scarring.
-
Quicker Recovery: Patients often return home within 1-2 days and resume normal activities sooner.
-
Lower Initial Risk: Generally associated with fewer immediate complications compared to open-heart surgery.
-
High Success Rate: Studies show that angioplasty successfully opens blocked arteries in over 95% of cases, providing significant relief from symptoms.
Considerations:
-
It may not be suitable for very complex, long, or multiple blockages.
-
Risk of restenosis (re-narrowing of the artery), though greatly reduced with drug-eluting stents.
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery: A Comprehensive Revascularisation
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) surgery, commonly known as bypass surgery, is a major open-heart procedure that involves creating new pathways for blood to flow around blocked coronary arteries.
How Bypass Surgery Works:
-
A surgeon makes an incision in the chest to access the heart.
-
Healthy blood vessels (grafts) are taken from other parts of the body, such as the leg (saphenous vein), chest wall (internal mammary artery), or arm (radial artery).
-
These grafts are then attached to the coronary artery above and below the blockage, effectively bypassing the narrowed section and restoring blood flow.
Advantages of Bypass Surgery:
-
Comprehensive Treatment: Highly effective for patients with multiple, severe, or complex blockages that are not amenable to angioplasty.
-
Long-Term Durability: Often provides excellent long-term relief of symptoms and improved survival rates, particularly in patients with multi-vessel disease. Over 90% of patients experience significant symptom relief for 10-15 years or more.
-
Reduced Need for Repeat Procedures: Due to its comprehensive nature, it may reduce the likelihood of needing future interventions compared to angioplasty for certain patient groups.
Considerations:
-
More Invasive: Involves open-heart surgery, leading to a longer hospital stay (typically 5-7 days) and recovery period (several weeks to months).
-
Higher Initial Risk: Carries a greater risk of complications compared to angioplasty, though overall success rates are very high at our leading cardiac centres like Manipal Hospitals.
-
Requires general anaesthesia and involves a longer operating time.
Angioplasty vs. Bypass: Key Differences and Decision Factors
The decision between angioplasty vs bypass is a complex one, tailored to each patient. Our expert cardiologists at Manipal Hospital Patiala consider several factors:
The difference between angioplasty and bypass can be summarised as:
-
Number and Severity of Blockages:
-
Angioplasty: Often preferred for one or two discrete blockages.
-
Bypass: Generally recommended for multiple severe blockages (e.g., three-vessel disease) or very complex, diffuse blockages.
-
-
Location of Blockages:
-
Angioplasty: Less ideal for blockages in critical areas like the left main coronary artery in some cases.
-
Bypass: Often the gold standard for left main coronary artery disease or extensive multi-vessel disease.
-
-
Patient's Overall Health:
-
Angioplasty: May be preferred for older patients or those with multiple co-morbidities where open-heart surgery poses a higher risk.
-
Bypass: Suitable for patients who can tolerate major surgery, offering robust long-term benefits.
-
-
Long-Term Outcomes: While both procedures significantly improve quality of life, long-term studies often show superior outcomes with CABG for certain high-risk patient groups with complex CAD. However, for many patients, angioplasty provides comparable results with a quicker recovery.
-
Urgency: Angioplasty is often the first-line treatment for acute heart attacks due to its rapid ability to open blocked arteries.
Life After the Procedure: Recovery and Lifestyle
Regardless of whether you undergo angioplasty or bypass surgery, successful recovery and long-term health depend significantly on lifestyle changes.
-
Cardiac Rehabilitation: A structured program of exercise, education, and counselling is vital. Participants in cardiac rehab programs can reduce their risk of future cardiac events by up to 25-30%.
-
Medication Adherence: Taking prescribed medications consistently is crucial to prevent further plaque buildup and managing associated conditions.
-
Healthy Lifestyle:
-
Diet: Following a heart-healthy diet is paramount. After angioplasty or bypass, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium is recommended. This diet after angioplasty (and bypass) helps prevent disease progression.
-
Regular Exercise: As advised by your doctor, incorporate regular physical activity.
-
Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is the single most impactful lifestyle change for heart health.
-
Stress Management: Techniques like yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can significantly benefit cardiovascular health.
-
Care Essentials: Do's and Don'ts
-
Do: Follow your cardiologist's post-procedure instructions diligently.
-
Do: Attend all follow-up appointments and cardiac rehabilitation sessions.
-
Do: Adopt a heart-healthy diet and maintain an active lifestyle.
-
Do: Manage stress through relaxation techniques.
-
Don't: Miss your prescribed medications without consulting your doctor.
-
Don't: Ignore new or worsening symptoms; seek immediate medical attention.
-
Don't: Engage in strenuous activities too soon after surgery (especially bypass) without medical clearance.
-
Don't: Resume smoking; it severely compromises your heart health.
Why Choose Manipal Hospitals Patiala?
At Manipal Hospitals, we understand the complexities of heart health. Our state-of-the-art cardiology department is equipped with advanced diagnostic tools and treatment facilities. Our team includes some of the best cardiologists in Patiala, offering unparalleled expertise in both interventional cardiology (angioplasty) and cardiac surgery (bypass). We pride ourselves on a patient-centric approach, ensuring thorough evaluation, clear communication, and personalised treatment plans, resulting in excellent patient outcomes and a high success rate.
FAQ's
Recovery from angioplasty is typically quick. Most patients are discharged within 1-2 days and can resume light activities within a week. Full recovery and return to normal routine usually take about 1-2 weeks, depending on individual health.
Patients undergoing bypass surgery typically stay in the hospital for about 5-7 days, including time in the intensive care unit. Full recovery at home can take 6-12 weeks, with a gradual return to normal activities.
While angioplasty with stent placement is highly effective, it's not always a permanent solution. Stents can re-narrow (restenosis) over time, though modern drug-eluting stents have significantly reduced this risk. Lifestyle changes and medication are crucial for long-term success.
Yes, it is possible. Sometimes, a patient might undergo angioplasty for one blockage and later require bypass surgery for other, more complex blockages, or vice versa, based on the progression of their disease and clinical presentation.
A heart-healthy diet is essential. This includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins (fish, poultry, legumes), and healthy fats (avocado, nuts). Limit saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sugars. Our dietitians can provide personalised guidance on a suitable diet after angioplasty or bypass.
If you are experiencing symptoms of heart disease or have been diagnosed with coronary artery blockages, it's crucial to seek timely medical advice. Book an appointment with our expert cardiologists at Manipal Hospitals Patiala today to discuss the best treatment option for your heart health.





















 8 Min Read
8 Min Read




.png)