Although the thyroid is a small gland, it plays a powerful role in an individual’s overall health. The gland produces hormones that help regulate metabolism and energy production and even affect mood. When the thyroid does not function correctly, it can cause a variety of symptoms that might affect everyday living. In India, about 42 million people suffer from thyroid diseases.
In this blog, we’ll explore common thyroid disorders, thyroid symptoms, how the thyroid impacts different body systems, and available thyroid treatments, including options for thyroid cancer and colloid cysts.
Synopsis
Understanding the Thyroid Gland
The thyroid is a tiny gland situated on the front of your neck, directly behind the Adam's apple. It measures two inches in length. Despite its small size, it controls vital functions through the release of hormones like T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine). Women are more prone to suffer thyroid problems, particularly during or after pregnancy and menopause.
Thyroid Symptoms
Thyroid dysfunction typically manifests in one of two ways:
Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
-
Anxiety and irritability
-
Rapid and irregular heartbeat
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Sweating and sensitivity to heat
-
Fatigue and muscle weakness
-
Difficulty sleeping
Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
-
Weight gain
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Depression
-
Sensitivity to cold
-
Memory problems
-
Muscle cramps and joint pain
-
Dry skin and hair
Effects of the Thyroid on the Body
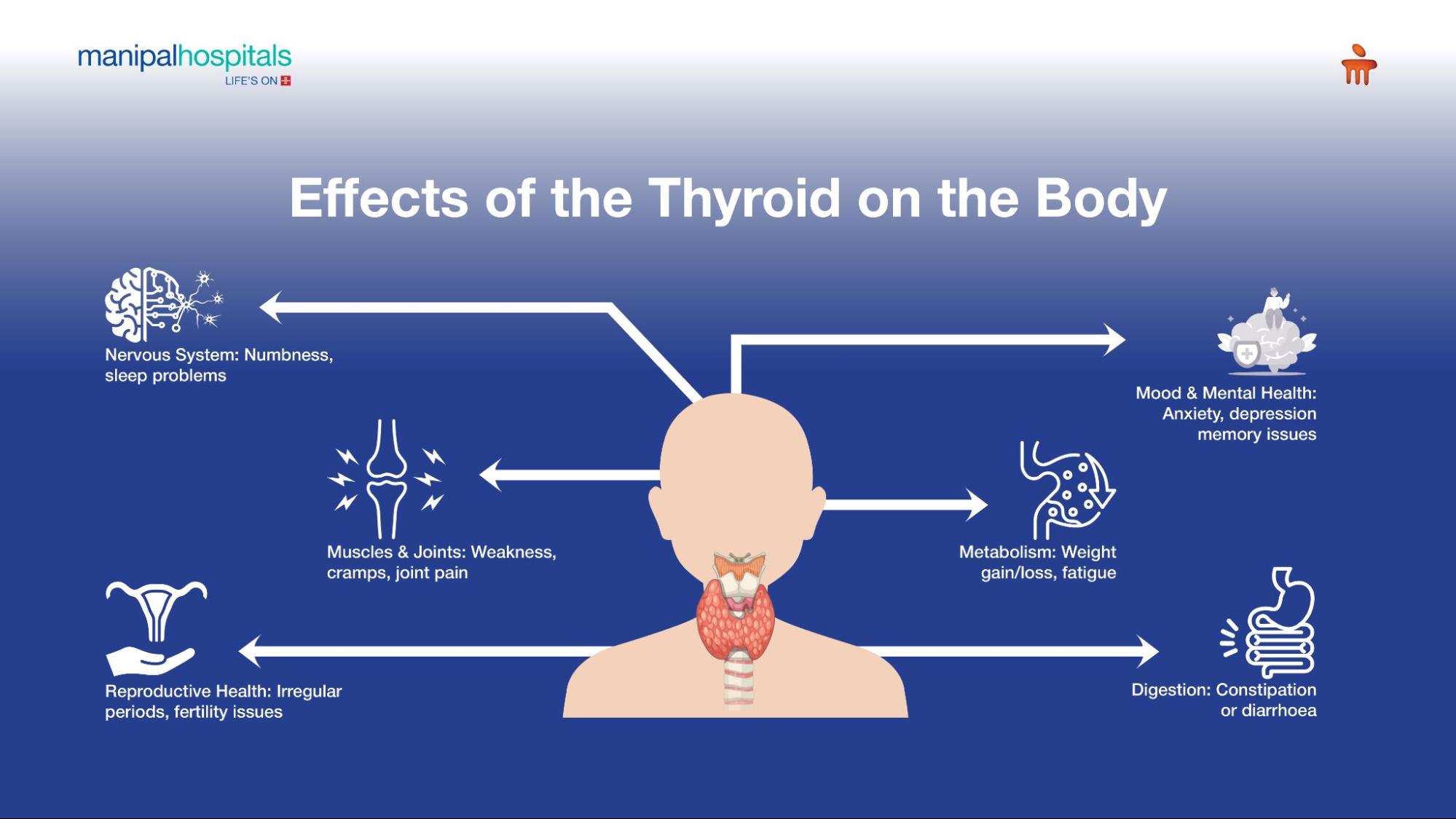
Metabolism
Thyroid hormones, primarily T3 and T4, are responsible for controlling metabolism. The hormones help convert the food into energy. In individuals with hypothyroidism, the metabolism slows down, causing symptoms like sluggishness, weight gain, and difficulty losing weight. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism accelerates the metabolism, resulting in inadvertent weight loss, elevated heart rate, and anxiety.
Energy Levels
Thyroid hormones also affect how energy is used in the body. Therefore, any disruptions to its functioning could make you feel drained or exhausted even after adequate rest. Hypothyroidism leads to continuous weariness, mental confusion, and muscular weakness. In contrast, hyperthyroidism can cause restlessness, difficulty sleeping, and being active even if tired.
Mood and Mental Health
The thyroid gland has a profound effect on the individual’s mood and emotional well-being. Hypothyroidism is associated with sadness, irritability, and motivational issues. An overactive thyroid leads to mood fluctuations, anxiety, and uneasiness. Since thyroid hormones influence neurotransmitter function, any imbalance may cause mental health struggles.
Digestive system
Thyroid dysfunction impacts the body's ability to digest food. Hyperthyroidism can lead to digestive problems, such as vomiting, diarrhoea, difficulty swallowing, lactose intolerance, weight loss, and liver problems. When there is too little thyroid hormone produced, it causes low stomach acid, constipation, gallstones, anaemia, poor absorption, and bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine.
Reproductive system
Thyroid hormones play a vital role in the female reproductive system by supporting the metabolism and development of ovarian, uterine, and placental tissues. They significantly influence the menstrual cycle, ovulation, and fertility. An imbalance, whether too much or too little, can lead to irregular, heavy, or absent menstrual periods. Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can interfere with ovulation, making it harder to conceive. In cases of hypothyroidism, elevated prolactin levels may further suppress ovulation. During pregnancy, thyroid dysfunction can pose risks such as miscarriage, preeclampsia, low birth weight, and premature birth.
Nervous system
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in cognitive development and various other aspects of nervous system function. It is accountable for the development and operation of both the central and peripheral nervous systems. In hypothyroidism, the way the nerve sends signals to the brain, spinal cord, or body changes, leading to peripheral neuropathy. However, both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are responsible for psychiatric symptoms such as depression, anxiety, memory loss, or even psychosis.
Musculoskeletal system
Thyroid hormones have a key role in muscle growth, regeneration, and function. Dysfunctioning of the thyroid gland can lead to myopathy or muscle weakness. In patients with hypothyroidism, they experience weakness and cramps closest to the centre of the body, especially in the thighs and shoulders.
Thyroid Treatment
Thyroid therapy is dependent on the kind and severity of the illness. Hypothyroidism is typically managed with daily hormone replacement therapy, while hyperthyroidism may require Anti-thyroid medications, Radioactive Iodine Therapy, or Surgery.
Thyroid cancer treatment often involves surgical removal of the gland, followed by Radioactive Iodine and long-term Hormone Therapy. Additional treatments may be used based on the cancer type and stage.
For colloid cyst thyroid treatment, small cysts are usually monitored, while larger or symptomatic ones may need aspiration, alcohol injection, or surgery. Early detection and personalised care are essential for effective thyroid management.
Conclusion
The thyroid gland influences most of our body functions, be it reproductive health, metabolism, or the nervous system. Any imbalance in their functioning can hurt our health. Recognising the signs early and taking treatment can help improve our overall well-being.
If you are experiencing symptoms of thyroid dysfunction or need guidance from an expert doctor, visit the Internal Medicine Department of Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur.
FAQ's
Hyperthyroidism can be caused by several factors, such as Graves' disease, thyroiditis, toxic nodules, excess TSH secretion, excess iodine intake, or taking excess thyroid hormone.
Papillary thyroid cancer, follicular or Hurthle cell cancer, medullary thyroid cancer, and anaplastic thyroid cancer are some of the types of thyroid cancer. Among them, papillary thyroid cancer is the most common type of thyroid cancer.
There is a complicated link between thyroid function, metabolism, and weight gain. Hypothyroidism is associated with decreased metabolism, which may lead to weight gain. Most of the weight gain is a result of excess salt and fluid retention. The symptom can be avoided by taking thyroid hormone replacement.
Hyperthyroidism, as well as hypothyroidism, can affect the individual’s sleep. Hypothyroidism causes excessive daytime sleepiness, whereas hyperthyroidism may lead to insomnia. If the sleep disturbances are left untreated, they cause mood changes, fatigue, and decreased productivity.
You can schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur, by contacting us or visiting our website.
Visit: https://www.manipalhospitals.com/mukundapur/specialities/internal-medicine/
Contact no: 033 6907 0001





















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read