The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism by producing hormones that control various bodily functions. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid becomes overactive, producing excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. This condition speeds up metabolism, leading to various physical and emotional symptoms. If left untreated, it can cause severe complications. Fortunately, hyperthyroidism treatment options are available to help manage and control the condition effectively.
Synopsis
- How Does the Thyroid Work?
- Hyperthyroidism Causes
- Signs and Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
- How is Hyperthyroidism Diagnosed?
- Hyperthyroidism Treatment Options
- Lifestyle and Dietary Changes: Hyperthyroidism What to Eat
- Complications if Hyperthyroidism is Left Untreated
- Living with Hyperthyroidism: Coping Strategies
- Quick Reference Table: Hyperthyroidism Overview
- Conclusion
How Does the Thyroid Work?
Located at the front of the neck, the thyroid gland produces hormones like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which influence metabolism, heart rate, and energy levels. In hyperthyroidism, excess thyroid hormones accelerate these processes, causing symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and nervousness.
Hyperthyroidism Causes
Understanding the hyperthyroidism causes is crucial for effective treatment. Several factors can lead to an overactive thyroid:
-
Graves’ Disease: The most common cause, an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the thyroid, causing excessive hormone production.
-
Thyroid Nodules: Lumps in the thyroid that increase hormone secretion.
-
Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid, often due to infections or autoimmune conditions.
-
Excessive Iodine Intake: High iodine levels from diet or medications can trigger overproduction of thyroid hormones.
-
Medications and Other Factors: Certain drugs and genetic predisposition can contribute to hyperthyroidism.
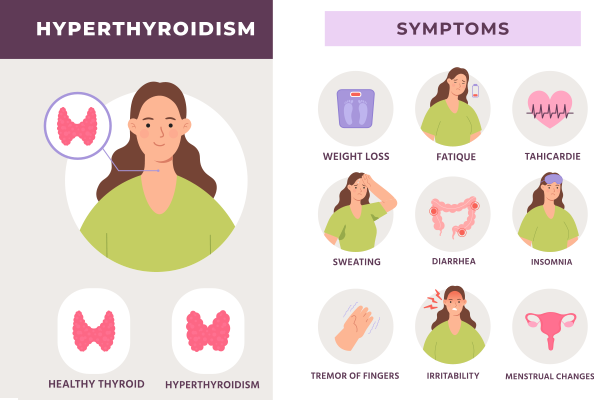
Signs and Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism affects multiple body systems, leading to a wide range of symptoms. The most common signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism include:
-
Unintentional weight loss
-
Rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
-
Increased appetite
-
Nervousness, anxiety, or irritability
-
Excessive sweating
-
Tremors (shaking hands or fingers)
-
Fatigue and muscle weakness
-
Difficulty sleeping
-
Frequent bowel movements
-
Thinning hair
-
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism in Women
Women with hyperthyroidism may experience additional symptoms, such as:
-
Increased risk of osteoporosis due to hormone imbalance
-
Fertility issues
-
Hair thinning and brittle nails
How is Hyperthyroidism Diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose hyperthyroidism through a combination of:
-
Blood Tests: Checking levels of TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), T3, and T4.
-
Imaging Tests: Ultrasound of thyroid scans to examine the gland.
-
Physical Examination: Checking for an enlarged thyroid (goitre) or eye changes.
Hyperthyroidism Treatment Options
There are multiple hyperthyroidism treatment approaches, depending on the severity of the condition.
1. Medications
Anti-thyroid drugs, such as Methimazole and Propylthiouracil, help reduce hormone production. These medications are often the first line of treatment and are effective for many patients.
2. Radioactive Iodine Therapy
This treatment involves ingesting radioactive iodine, which selectively destroys overactive thyroid cells. It is a highly effective, permanent solution but may lead to hypothyroidism, requiring lifelong hormone replacement therapy.
3. Surgery (Thyroidectomy)
For severe cases, surgical removal of the thyroid may be necessary. This procedure is usually recommended when other treatments fail or if a patient has a large goitre.
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes: Hyperthyroidism What to Eat
A well-balanced diet can support thyroid health and improve symptoms. Here’s what to consider:
Foods to Eat:
-
Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cabbage, and cauliflower may help slow thyroid hormone production.
-
Dairy Products: Calcium and vitamin D-rich foods can combat osteoporosis risk.
-
Protein Sources: Lean meats, eggs, and beans support muscle strength.
-
Fruits and Nuts: Berries, almonds, and walnuts provide essential nutrients.
Foods to Avoid:
-
High Iodine Foods: Seaweed, fish, and iodised salt can worsen symptoms.
-
Caffeine and Sugar: Can increase nervousness and heart rate.
-
Soy Products: May interfere with thyroid medications.
Complications if Hyperthyroidism is Left Untreated
If not managed properly, hyperthyroidism can lead to serious complications:
-
Thyroid Storm: A life-threatening condition with severe symptoms like fever, rapid heartbeat, and confusion.
-
Heart Problems: Increased risk of high blood pressure, heart failure, and arrhythmia.
-
Osteoporosis: Excess thyroid hormones can weaken bones, increasing fracture risks.
Living with Hyperthyroidism: Coping Strategies
Regular Monitoring: Routine check-ups to assess hormone levels.
-
Stress Management: Practices like yoga and meditation can help manage anxiety.
-
Adequate Rest: Ensuring proper sleep to combat fatigue.
-
Joining Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges can be beneficial.
Quick Reference Table: Hyperthyroidism Overview
|
Aspect |
Details |
|
Definition |
An overactive thyroid gland produces excess hormones. |
|
Common Causes |
Graves’ disease, thyroid nodules, and excessive iodine intake. |
|
Symptoms |
Weight loss, rapid heartbeat, tremors, anxiety, and sweating |
|
Symptoms in Women |
Irregular periods, fertility issues, and osteoporosis risk. |
|
Diagnosis |
Blood tests, imaging, and physical examination. |
|
Treatment Options |
Medications, radioactive iodine therapy, and surgery. |
|
Diet Recommendations |
Eat dairy, proteins, and cruciferous vegetables; avoid iodine-rich foods. |
|
Complications |
Thyroid storm, heart issues, osteoporosis. |
Conclusion
While hyperthyroidism can be challenging, timely diagnosis and appropriate hyperthyroidism treatment can help individuals lead a healthy life. By understanding the hyperthyroidism causes, recognising symptoms early, and making lifestyle changes, patients can effectively manage the condition.
For expert diagnosis and treatment of hyperthyroidism, consult the specialists at Manipal Hospitals Baner. Our experienced endocrinologist provides personalised care, ensuring optimal thyroid health. Book an appointment today to take control of your well-being.
FAQ's
While treatments can effectively control hyperthyroidism, some cases require lifelong management. In some instances, treatments like radioactive iodine therapy can permanently resolve the condition, leading to hypothyroidism that requires medication.
Medication typically starts working within a few weeks, but full stabilisation of thyroid hormone levels can take several months. Radioactive iodine therapy may take a few months to show complete results.
Untreated hyperthyroidism can lead to severe complications, including heart disease, osteoporosis, and a life-threatening condition called thyroid storm.
Yes, hyperthyroidism is more common in women, especially those with autoimmune conditions like Graves’ disease






















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read