Many women experience pelvic pain, heavy periods, or a feeling of fullness in the lower abdomen—symptoms often dismissed as “normal.” However, these can be signs of uterine fibroids—a common but often misunderstood condition.
Although benign, these uterine fibroids remain a major source of morbidity in women of reproductive age, affecting 68.6% of them. Almost 30% of women with uterine fibroids present with severe symptoms, including abnormal bleeding, infertility, iron-deficiency anaemia, and pelvic pain, intervening a necessity.
In this blog, we will discuss the uterine fibroid symptoms, causes, types, and treatment options available to help women take charge of their reproductive health.
Consult one of the best Gynaecologists in Mukundapur, Kolkata at the Manipal Hospitals for expert suggestions, early diagnosis, proper care and effective treatments.
Synopsis
What Are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus. They often appear during the reproductive years of women when they can get pregnant and give birth. These fibroids can vary in size and symptoms. While not usually life-threatening, fibroids can cause significant discomfort and affect quality of life.
What Causes Uterine Fibroids?
The exact cause of fibroids is unknown. Several risk factors for fibroid growth are:
-
Hormonal Changes: Oestrogen and progesterone—the hormones that regulate your menstrual cycle—can promote fibroid growth.
-
Genetics: If your mother or sister had fibroids, you may be more likely to have them.
-
Age: Fibroids are more commonly seen in women aged 30 to 50.
-
Obesity: Being overweight increases your risk of developing fibroids.
-
Lifestyle Factors: A diet low in fruits and high in red meat may contribute to fibroids.
Understanding what causes uterine fibroids can help women seek early care and avoid complications.
Types of Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are classified based on where they grow:
-
Intramural Fibroids: Found within the muscular wall of the uterus.
-
Subserosal Fibroids: Project outside the uterus.
-
Submucosal Fibroids: Grow into the inner cavity and may affect fertility.
-
Pedunculated Fibroids: Attached to the uterus by a stalk-like structure.
Knowing the types of uterine fibroids can help doctors decide the best approach to treatment.
Common Uterine Fibroids Symptoms
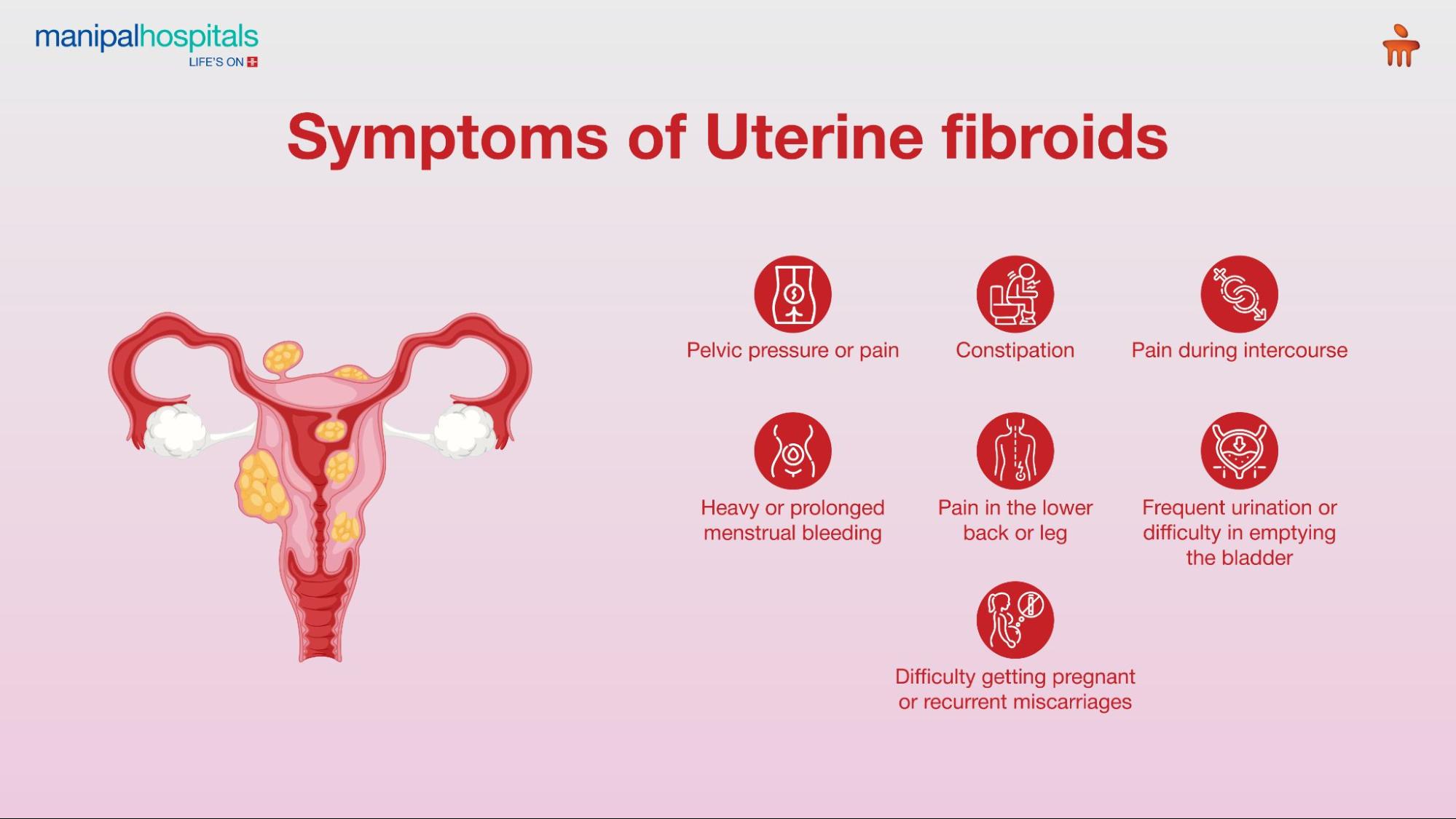
While some women may have no noticeable issues, others experience symptoms that can disrupt daily life. Common uterine fibroid symptoms include:
-
Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
-
Frequent urination or difficulty in emptying the bladder
-
Constipation
-
Pain during intercourse
-
Lower back or leg pain
-
Difficulty getting pregnant or recurrent miscarriages
If you notice these symptoms, especially if they worsen over time, it’s important to consult a gynaecologist.
How Are Uterine Fibroids Diagnosed?
Your doctor usually starts with a pelvic exam and may also recommend:
-
Ultrasound: To visualise the size and location of fibroids.
-
MRI Scan: Offers a detailed view, especially for large or multiple fibroids.
-
Hysterosonography: A saline-infusion ultrasound for submucosal fibroids.
-
Hysteroscopy: A thin, lighted tube is inserted into the uterus to check for growths.
-
Blood tests: These are conducted to rule out anaemia caused by heavy bleeding.
Early diagnosis ensures better outcomes with uterine fibroid treatment.
Uterine Fibroids Treatment Options
Treatment depends on your symptoms, age, fibroid size, and whether you plan to have children. Common uterine fibroid treatment options include:
1. Watchful Waiting
If fibroids are not causing symptoms, regular monitoring is all that’s needed.
2. Medications
-
Hormonal therapy to shrink fibroids
-
Pain relievers for symptom relief
-
Medications to reduce heavy bleeding
3. Non-Surgical Procedures
-
Uterine Artery Embolisation: It blocks the blood supply to fibroids.
-
MRI-Guided Focused Ultrasound: Destroys fibroid tissue using sound waves.
4. Surgical Treatments
-
Myomectomy: Removes fibroids while preserving the uterus - often preferred for younger women who wish to conceive
-
Hysterectomy: Complete removal of the uterus - usually considered for severe cases or when childbearing is not desired
Your doctor will help you choose the best option based on your needs and lifestyle.
Check Out More of Our Blogs: Does Stress Affect Your Period? Understanding the Science Behind Hormones and Cycles
Conclusion
Uterine fibroids are common, especially during the reproductive years. While not usually dangerous, they can impact physical comfort, fertility, and emotional well-being. Recognising uterine fibroid symptoms early, understanding your risk, and exploring treatment options can lead to better outcomes.
At Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur, our experts from the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology provide comprehensive care, from diagnosis to advanced uterine fibroid treatment, tailored to your health goals.
FAQ's
Uterine fibroids are almost always non-cancerous. In very rare cases, they can become cancerous. Regular monitoring and checkups help detect unusual changes early, and timely treatment can reduce the risk.
Yes, some uterine fibroids can interfere with fertility. Particularly, those inside the uterus (submucosal) may block the fallopian tubes, disrupt implantation ,or increase the risk of miscarriages.
Surgery is not always needed. Some fibroids cause mild or no symptoms; those can be managed with medication or noninvasive options. In contrast, large painful fibroids that may affect fertility will require surgical removal.
Mostly, fibroids shrink after menopause. This is because they grow in response to hormones. When hormone levels drop after menopause, fibroids mostly shrink naturally.
You can call us directly or visit our website to schedule a consultation with a gynaecologist.





















 4 Min Read
4 Min Read