Are you ignoring the subtle signs your lungs are trying to send? Could that mild wheeze or breathlessness be something far more serious than you think? In most cases, these small signs are the body’s way of warning us of something complex. In India, the prevalence of lung infections, particularly pneumonia, bronchitis, and severe acute respiratory infections, is rising. According to India's National Health Portal, respiratory infections accounted for more than 41 million cases and over 3000 fatalities in 20181.
In this blog, we'll discuss what lung infections are and how identifying their early signs can help you take preventative measures and act more quickly.
Synopsis
Understanding Lung Infections—What Are They and How Do They Occur?
Lung infection(s), or pulmonary infection(s), are one of the most common medical conditions. It usually happens when a microorganism, such as a virus, bacteria, or fungus, comes in contact with the lungs and causes inflammation. It can also occur due to inhalation of harmful substances like chemicals, pollutants, or allergens, or aspiration. The condition can be mild or severe. Although most cases resolve on their own, severe lung infections may require hospitalization and improved treatments.
Some conditions that cause infections in the lungs include influenza, pertussis (whooping cough), croup, pneumonia, bronchitis, tuberculosis, COVID-19, and other coronaviruses.
How Are Lung Infections Diagnosed and Treated?
Diagnosis for lung infections is usually based on medical and family history and your symptoms. Doctors ask about your job, travel history, lifestyle, and if you were exposed to animals. Any suspicion may further suggest diagnostic tests for confirmation. Common ways of diagnosing lung infection can include:
-
Imaging tests: These include chest X-rays or computer tomography (CT) scans to find abnormalities in the lungs.
-
Blood tests: Increased white blood cells (WBCs) could indicate inflammation caused by a respiratory infection
-
Sputum Test: It analyses a sample of mucus (phlegm) that is coughed up from the lungs to identify infections or other conditions affecting the respiratory tract.
-
Pulmonary Function Tests: PFTs are a group of tests used to assess how well your lungs are functioning.
-
Bronchoscopy: By using a thin, flexible camera attached tube, airways and surrounding tissues are assessed. It is mostly used to confirm the diagnosis in severe cases.
Additional tests, like allergy tests (e.g., tuberculin skin test) and other microbiological tests, are done to diagnose particular infections, namely tuberculosis or other fungal infections.
Treatments for Lung Infections
Common methods doctors often perform to treat lung infections include:
-
Medications: These include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, or over-the-counter medications.
-
Oxygen Therapy: In serious conditions like pneumonia or ARDS, where blood oxygen levels drop (hypoxaemia), supplemental oxygen helps restore proper oxygenation and support breathing.
-
Nebulisation/Inhalation: For conditions like bronchitis, nebulisers or inhalers help reduce inflammation by administering medications directly to the lungs.
-
Rest: Adequate rest helps your body build up its immune system to fight infections. Therefore, drink warm water or fluids, and try saltwater gargling to soothe sore throats and reduce inflammation
-
Surgery: In severe cases like infection resistance, lung abscess, etc., surgical intervention may be required.
In some cases, pulmonary rehabilitation may be recommended for individuals recovering from chronic respiratory infections to improve lung function and support overall recovery.
Lung Infections – Early Symptoms You Should Look Out For
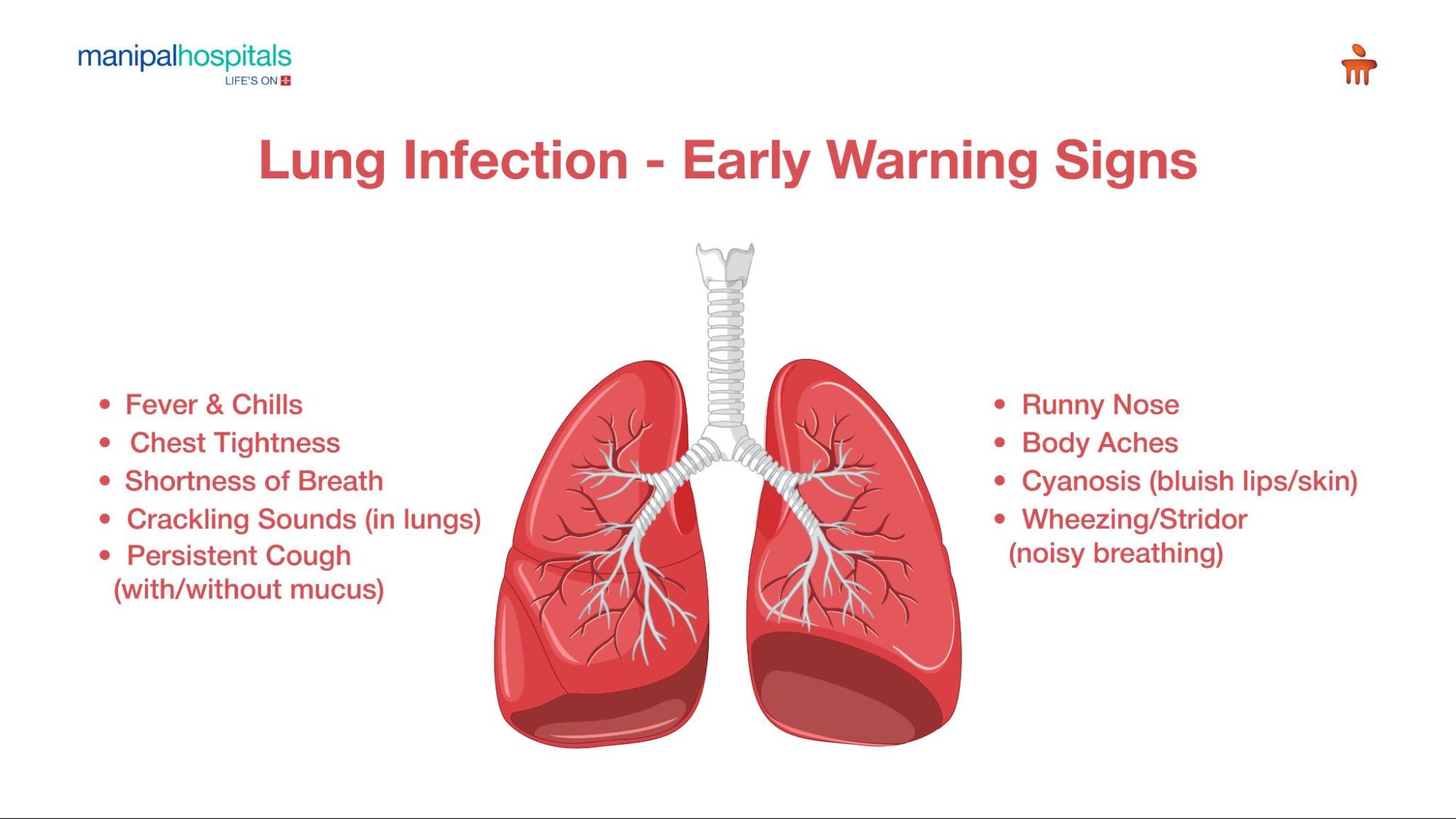
Symptoms of lung infections can differ depending on the type, cause, severity, and patient condition. Symptoms can be similar to getting a cold or the flu. However, they often linger for a longer time and do not go away quickly. Common symptoms of respiratory infections one should look for include:
a. Severe Cough with Mucus Production: Think mucus along with a severe cough is a symptom seen in conditions like bronchitis or pneumonia. They can appear clear, white, green, or yellowish grey. Even after other symptoms subside, the symptoms can stick around for several weeks.
b. Fever: In cases like respiratory infections caused by bacteria, high-temperature fever can be a symptom. It is often accompanied by other symptoms, like chills, sweating, fatigue, dehydration, muscle aches, and more.
Chest Tightness: A feeling of tightness in the chest could be due to conditions like pneumonia or bronchitis, causing inflammation and infections.
c. Runny nose: Commonly seen in conditions like bronchitis
Shortness of Breath: Difficulty in breathing is another symptom observed in respiratory infections. Immediate care is necessary if the symptom is exhibited.
d. Crackling / /Rattling sounds: Bibasilar crackles are abnormal crackling sounds heard from lower lung regions. This can happen due to fluid or mucus accumulation in the lungs caused by respiratory infections.
e. Wheezing or Stridor: Both produce high-pitched sounds during a respiratory infection. Wheezing is seen in conditions like allergies, and it is produced when you exhale. It could indicate narrow airways or inflammation. Stridor may occur due to airway blockage and is a common symptom seen in respiratory infections.
f. Cyanosis: Decreased oxygen in the bloodstream, which transforms the skin, lips, or nails into blue.
Body ache: Called myalgia, you may experience muscle and back aches. The symptom is commonly seen in respiratory infections.
Other symptoms include fatigue, haemoptysis (coughing up blood), delirium, nausea and vomiting, a faster heart or pulse rate, lightheadedness, rapid breathing, dehydration, and many more. If you experience mild to moderate symptoms and they do not go away after two weeks, you may need to seek immediate attention from a specialist.
Conclusion
It is a concern that respiratory infections are continuing to be the leading cause of death worldwide. While treatments have advanced, challenges like lung barriers limit the effectiveness of inhalation drug delivery. Nanoparticles offer a promising way to overcome these obstacles and improve outcomes2. Additionally, new strategies using monoclonal antibodies are being explored for viruses like RSV, aiding in the development of more effective vaccines and therapies.
At Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur, we prioritise delivering expert care for individuals diagnosed with respiratory infections. If you or your loved ones suspect any symptoms that may indicate a respiratory infection, we encourage you to consult our pulmonologists as soon as possible.
FAQ's
Look for symptoms like a persistent cough with or without mucus, fever, shortness of breath, weakness, fatigue, chest pain, chills, and body aches. Wheezing or coarse breath sounds may also occur. Since these symptoms can mimic other lung conditions, you must consult a pulmonologist for an accurate diagnosis.
Yes, many lung infections, such as tuberculosis, pneumonia, and bronchitis, are contagious and spread through coughing, sneezing, or close contact.
An untreated lung infection causes the pleural layer of the lungs to swell, leading to a sharp pain while breathing. In some cases, the pleural cavity gets filled with fluid, causing pleural effusion and worsening of lung infection.
You must contact your doctor if you develop:
-
Fever more than 102°F for more than three days
-
Persistent cough with mucus
-
Chest pain or tightness
You can schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur, by contacting us or visiting our website.
Visit: https://www.manipalhospitals.com/mukundapur/specialities/pulmonology-respiratory-sleep-medicine/
Contact no: 033 6907 0001





















 7 Min Read
7 Min Read