A woman who has undergone treatment for breast cancer or who has a congenital breast abnormality may opt for Breast Reconstruction Surgery. It is performed to reconstruct the form and appearance of the breast. A 2021 report revealed that less than 1% of women in India undergo breast reconstruction after a Mastectomy (surgical removal of the breast).1
Breast Reconstruction Surgery is not the same as Breast Plastic Surgery. In Breast Reconstruction Surgery, breast shape and size are restored. Whereas, in Breast Plastic Surgery, the aim is to improve the appearance by increasing or decreasing the size. In both procedures, breast implants are usually used to form the new shape of the breast.
Although Breast Reconstruction Surgery is generally considered a safe procedure, like any other surgery, it may carry certain risks. This blog explores the procedure and types of Breast Reconstruction Surgery, focusing on its possible risks and complications.
Synopsis
What is Breast Reconstruction Surgery?
Breast Reconstruction is a surgical procedure designed to recreate a breast after the removal of all or part of the breast. The goal is to restore a breast with a size and shape similar to the original. In some cases, multiple surgeries may be required to achieve the desired outcome. Breast Reconstruction plays an important role in the overall treatment approach for breast cancer. However, the decision to undergo the procedure is entirely up to the patient.
Types of Breast Reconstruction Surgery
Implant Reconstruction
This method of Breast Reconstruction utilises a breast implant to restore the shape and volume of the breast following a Mastectomy or surgical removal of the breast.
Most implants are made of silicone, while some consist of a combination of silicone and saline (salt water).
Flap Reconstruction
In Flap Reconstruction, the surgeon uses tissue from your body (autologous tissue) to create a new breast. This tissue is typically taken from the lower abdomen (belly) but can also be sourced from the thigh, back, or buttocks.
Following are the types of Flap Reconstruction:
-
Tissue Flaps: Pedicle flaps and free flaps are the types of tissue flaps usually used for Breast Reconstruction Surgery. In Pedicle Flap Surgery, tissue is moved to the chest while keeping most blood vessels intact. Some vessels are cut, but others remain connected. The tissue is then reshaped to form the new breast.
In Free Flap Surgery, tissue and blood vessels are moved to the chest. The surgeon disconnects the tissue from its original blood supply and reattaches it to new vessels. This procedure usually takes longer than Pedicle Flap Surgery.
-
DIEP Flap: The DIEP Flap procedure involves transferring skin, fat, and blood vessels from the lower abdomen without removing the underlying abdominal muscle.
-
TRAM Flap: In this procedure, skin, fat, blood vessels, and muscle are removed from the lower abdomen.
-
SIEA Flap: The SIEA free flap is the least invasive microsurgical Breast Reconstruction, using shallower abdominal blood vessels. However, not everyone has suitable SIEA vessels for this procedure.
-
TUG Flap: The TUG flap uses tissue from the thigh and includes muscle along with skin and fat.
-
PAP Flap: Tissue from the inner and back thigh is used to create a breast without transplanting muscle.
Risks Associated With Breast Reconstruction
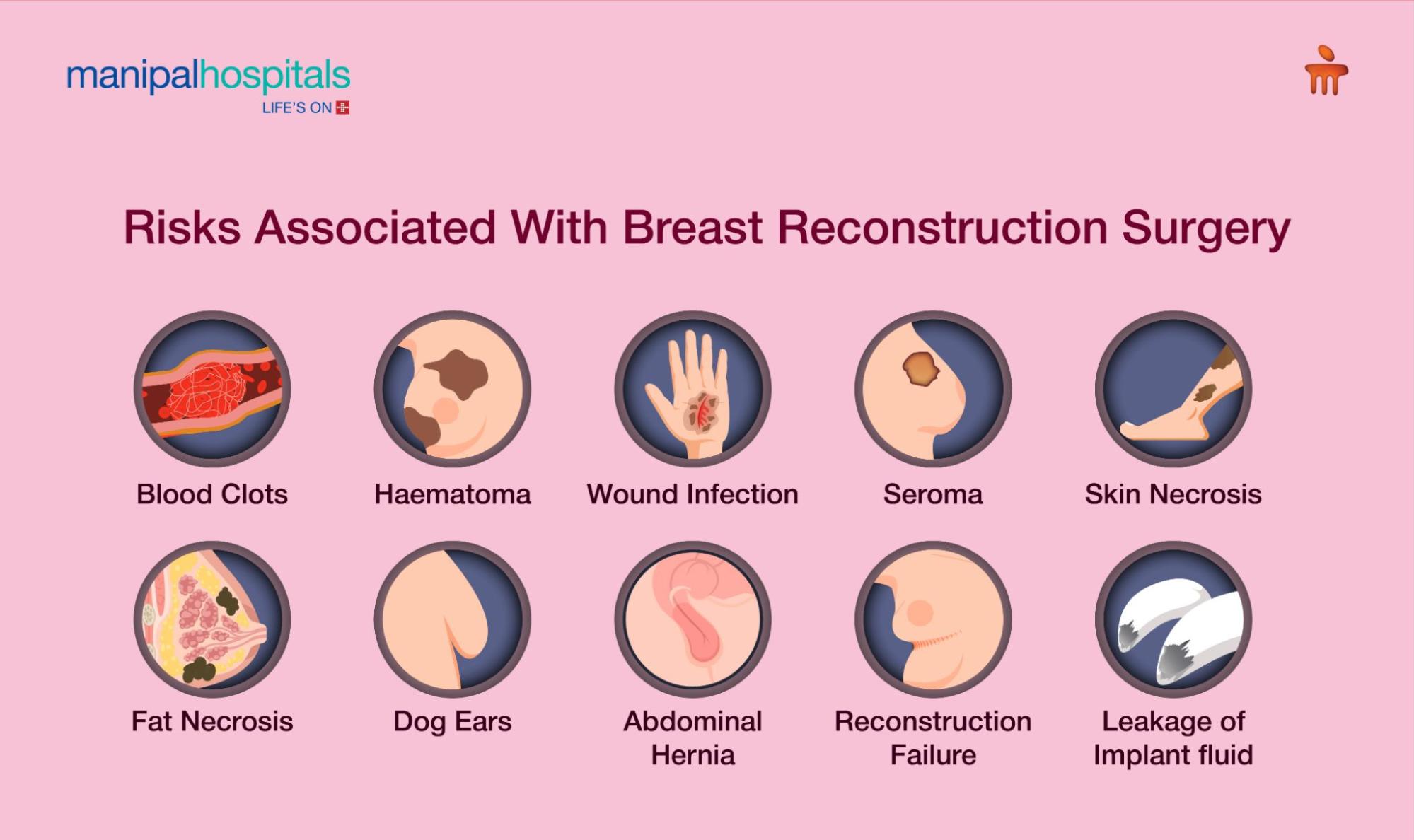
Some complications may occur after Breast Reconstruction Surgery. Your surgeon will discuss all possible risks with you beforehand.
-
Haematoma: A breast haematoma is a buildup of blood within the breast tissue, often occurring after injuries or procedures. It may cause pain, swelling, and, in rare cases, infection or delayed wound healing. While not usually life-threatening, proper treatment is important to prevent complications.
-
Wound infection: Infection is a risk after Breast Reconstruction, but it usually clears with rest and antibiotics within a week. Symptoms include fever, breast redness, wound discharge, chills, or feeling unwell. If you notice these signs, contact your 24-hour advice line immediately.
-
Seroma: After Breast Cancer Surgery, fluid can build up where tissue was removed, forming a seroma. Although it is harmless, it may cause discomfort and slow recovery. Seromas often go away on their own, but sometimes need drainage.
-
Skin necrosis: Skin flap necrosis is a rare complication of Flap Reconstruction caused by poor blood flow or surgical trauma. Treatment may include trimming dead tissue, wound care, and antibiotics. In severe cases, surgery may be needed to remove the affected area.
-
Fat necrosis: Fat necrosis can occur if the fatty tissue lacks sufficient blood supply, forming a hard lump of dead fat cells weeks after surgery. In rare cases, it may lead to infection or fluid leakage. If the area feels hard or you have concerns, contact your surgeon or nurse.
-
Dog ears: Dog ears are small folds of excess skin and fat that can form at the incision ends after DIEP Flap Breast Reconstruction. While harmless, they may affect appearance and cause minor discomfort. Small dog ears often improve over time, but some may require a minor procedure or Liposuction under local anaesthesia, typically six months after surgery.
-
Abdominal hernia: After DIEP or TRAM Flap Reconstruction, there is a small risk of an abdominal wall hernia, a weakness or hole in the muscle that allows underlying structures to push through.
-
Reconstructive failure: Reconstructive failure occurs when a Breast Reconstruction doesn’t heal properly, leading to implant or tissue removal without immediate replacement. This can be distressing, so surgeons should discuss risks and secondary reconstruction options with patients.
-
Leakage of implant fluid: Implant leakage can occur if a rupture allows fluid to seep into surrounding tissue, sometimes causing lymph gland swelling. Signs include lumps, pain, or changes in breast shape. If a leak occurs, the implant must be removed and replaced. Contact your doctor if you notice any of these symptoms.
Conclusion
Breast Reconstruction Surgery is usually performed after a Mastectomy for breast cancer. It is not considered a Breast Cosmetic Procedure, however, it can restore the shape and function of the breast. Breast Reconstruction Surgery may carry certain risks like any other procedure. Some of the common risks and complications include blood clots, haematoma, infection, necrosis, hernia, reconstruction failure, and more. Your doctor will discuss potential risks and complications before the surgery. If you need more guidance regarding Breast Reconstruction Surgery, visit Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur.
FAQ's
Recovery time after Breast Reconstruction Surgery varies by procedure. Most women feel better within weeks and resume normal activities in a few months.
Routine mammograms aren’t needed after Breast Reconstruction Surgery following a Mastectomy. However, if any concerns arise during an exam, diagnostic imaging like a mammogram, ultrasound, or MRI may be recommended.
The breast implants have a long in vivo life and usually do not require removal.
Breast Reconstruction Surgery can be done at the time of a Mastectomy or Lumpectomy, or delayed for months or years. Immediate reconstruction avoids extra surgery and ensures the patient doesn’t go without a breast mound.
You can schedule an appointment with a plastic surgeon at Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur, by contacting us or visiting our website.
Visit: https://www.manipalhospitals.com/mukundapur/specialities/plastic-and-cosmetic-surgery/
Contact no: 033 6907 0001





















 7 Min Read
7 Min Read