Dementia is a challenging disease to cope with for individuals suffering from it and those who care for them. It stands as a leading cause of disability and dependency among older people globally, affecting an estimated 55 million individuals. Providing care for dementia patients can be emotionally taxing and frustrating for caregivers and may cause early caregiver burnout. Therefore, a complete understanding of dementia is pivotal for optimal care. This blog post provides a concise yet insightful overview of dementia.
Synopsis
Understanding Dementia
Dementia (from the Latin “demens,” meaning “devoid of the mind”), or Major Neurocognitive disorder as it is named nowadays, is a multifaceted condition characterised by cognitive deterioration from a previously higher level of functioning that includes memory impairment, decreased speech output, disturbance in planning, execution, and decision-making abilities that affect daily tasks. While commonly linked with older age, it’s important to note that dementia isn’t an inevitable consequence of ageing. Rather, it can stem from multiple diseases that gradually affect the brain and destroy brain cells or neurons, impairing cognitive function. The underlying pathology often involves the accumulation of abnormal proteins in the neurons, such as tau proteins and amyloid plaques. Despite its prevalence, dementia goes undiagnosed.
The following factors are the most common causes of dementia:
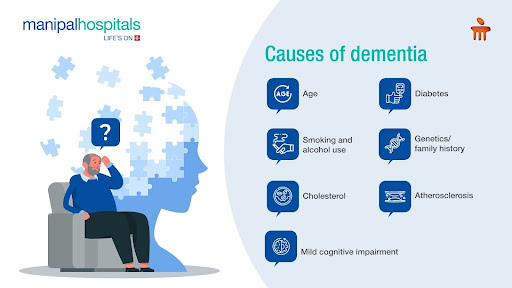
-
Age: Dementia is a chronic condition in which brain cell damage happens over several years. Therefore, the symptoms intensify with advancing age.
-
Genetics/family history: Alzheimer's disease is known to be caused by changes occurring in genes like Amyloid precursor protein (APP) and Presenilin 1 or 2 (PSEN 1 and 2).
-
Smoking and alcohol use: Smokers are more likely to develop atherosclerosis and other vascular diseases, which may be the root reasons for the elevated risk of dementia. Studies have also found that drinking large amounts of alcohol appears to increase the risk of dementia.
-
Atherosclerosis: Atherosclerosis is a significant risk factor for vascular dementia because it interferes with the delivery of blood to the brain cells and can lead to stroke. Studies have found a relationship between the two conditions.
-
Cholesterol: High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) appear to significantly increase a person's risk of developing vascular dementia.
-
Diabetes: It is associated with a higher chance of atherosclerosis and stroke, both of which are contributing factors to vascular dementia.
-
Mild cognitive impairment: Although mild cognitive impairment does not always result in dementia, those who have it do have a notably higher risk of the disease than the general population.
Types of Dementia Disease
-
Alzheimer's disease: The definitive cause of Alzheimer's disease is unknown, but scientists have found that mutations in the above-mentioned genes may cause the disease.
-
Vascular dementia: Damage to the arteries that carry blood to the brain is the cause of this type of dementia. Persons with a previous history of strokes are at increased risk of developing vascular dementia.
-
Lewy body dementia: Lewy bodies are protein aggregates that accumulate in various parts of the brain. It is seen in patients with Parkinson’s disease or Lewy body disease.
-
Frontotemporal dementia: This set of disorders is marked by the degeneration of neurons and their connections within the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. This dementia is characterised by personality, behaviour, and language problems.
-
Mixed dementia: Individuals diagnosed with mixed dementia may exhibit symptoms associated with Alzheimer's disease, and vascular and other forms of dementia.
-
Reversible Dementia: This form of dementia is reversible and can be cured with proper treatment. This includes hypothyroidism, vitamin B12 deficiency, chronic alcoholism, multiple sclerosis, HIV, head injury etc.
-
Pseudodementia: Persons with major depressive illness may have cognitive deficits that may mimic depression, seen more commonly in elderly patients.
Advanced treatment for dementia
These are strategies to effectively manage symptoms:
-
Cholinesterase inhibitors: These medications function by enhancing the levels of a neurotransmitter, Acetylcholine associated with memory and cognitive function. They consist of Donepezil, Rivastigmine, and Galantamine. While their primary use is for Alzheimer's disease treatment, these medications may also be recommended for other types of dementia.
-
Memantine: Memantine functions by modulating the activity of glutamate, another neurotransmitter crucial for brain functions like learning and memory.
-
Other medicines: Additional medications may be necessary to treat associated symptoms and underlying conditions. Patients may require treatment for depression, agitation, insomnia, hypothyroidism, and vitamin deficiency.
Book an appointment with our best Neurologist in Mukundapur to learn more about the advanced dementia treatment options.
Dementia Therapies
-
Occupational therapy: An occupational therapist can demonstrate methods to enhance the safety of your home environment and instruct you on adaptive strategies.
-
Changes to the environment: Minimising clutter and reducing noise levels can enhance the ability of individuals with dementia to concentrate and carry out tasks.
-
Simpler tasks: Establishing a structured routine can alleviate confusion for individuals with dementia.
Conclusion
Dementia presents a considerable health concern that can be efficiently treated through prompt interventions. Identifying dementia symptoms and implementing an essential lifestyle to facilitate medical care can mitigate the risk of complications. For mapping the effective dementia treatment, consider visiting our Neurology Hospital in Mukundapur. Check out our blog page for more updates about the advancements in neurology.
FAQ's
As time progresses, the underlying disease responsible for dementia extends its impact to other regions of the brain. This results in additional symptoms as a greater portion of the brain becomes impaired in its functioning. Previously affected areas of the brain experience greater damage.
Signs and symptoms of dementia include:
-
Memory loss.
-
Difficulty concentrating.
-
Having trouble finding the right word or keeping up with conversation.
-
Being confused about time and place.
-
Mood changes.
Dementia is distinct from the typical ageing process. It involves a disturbance in cognitive functions such as thinking, remembering, learning, reasoning, and behavioural abilities, to the extent that it disrupts an individual's quality of life and daily activities.
To schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, contact us or visit our website.
Preventing dementia can be challenging, as its causes are often unclear. However, individuals with dementia resulting from a stroke may potentially have reduced their risk of heart disease and stroke.
Increasing evidence suggests that engaging in physical exercise can serve as a protective measure against dementia, particularly when coupled with a nutritious diet and the management of cardiovascular risk factors.



















 4 Min Read
4 Min Read















