Every day movement depends on the smooth functioning of our joints, whether it’s bending your elbow, kneeling, or simply walking. But sometimes, a small fluid-filled sac called a bursa becomes inflamed, leading to a painful condition known as bursitis.
Bursitis can affect anyone, from athletes to people with desk jobs, and though it’s not life-threatening, it can greatly interfere with daily comfort and mobility. Let’s explore the causes, symptoms, and recovery tips to help you understand and manage this condition better.
Synopsis
What Is Bursitis?
Bursitis occurs when a bursa, a small, jelly-like sac that cushions your joints, becomes inflamed or irritated. These bursae are located between bones and soft tissues, acting like shock absorbers to reduce friction during movement.
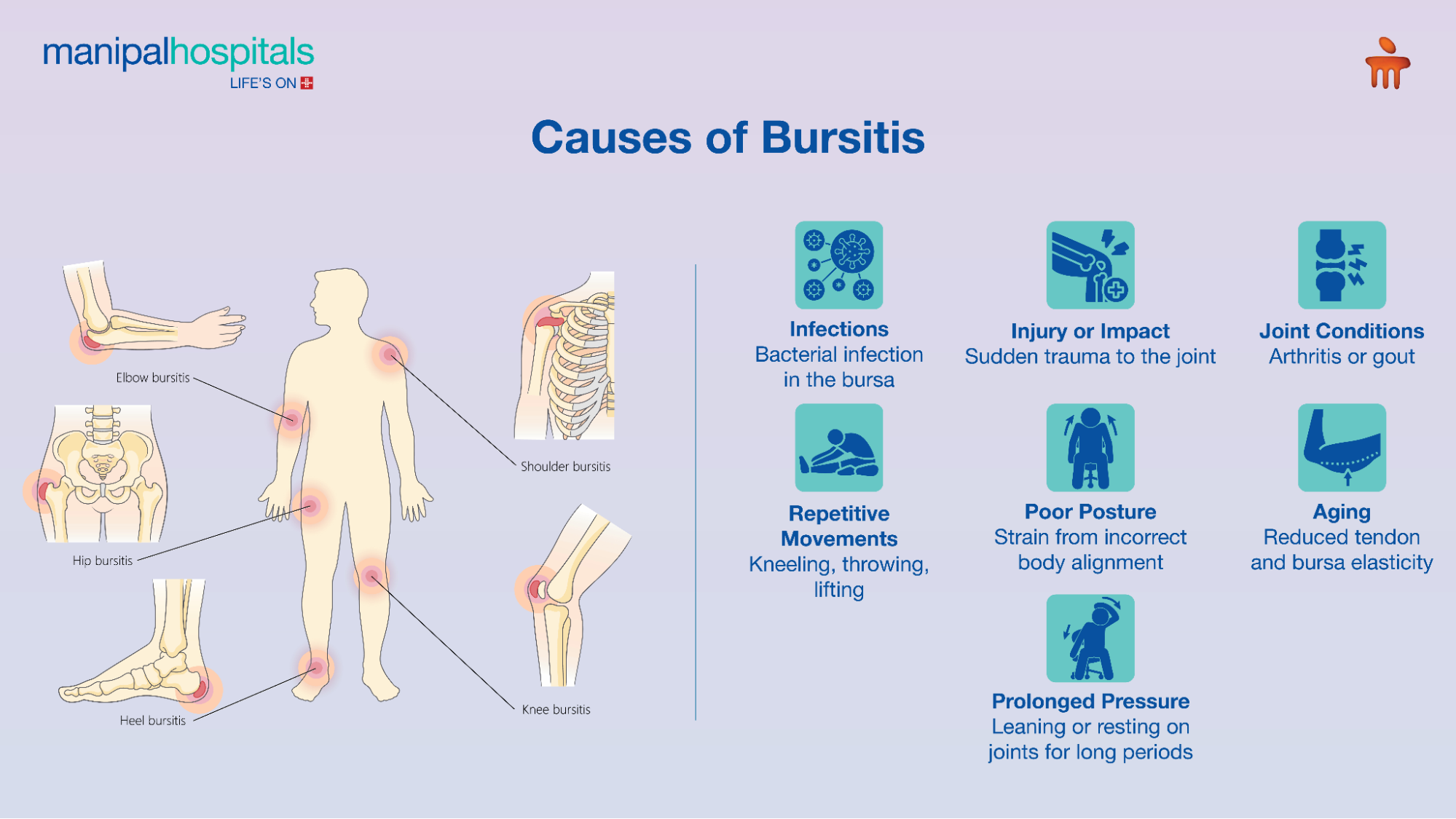
When inflamed, they cause pain, swelling, and limited movement in the affected joint. The most commonly affected areas include -
-
Shoulder (subacromial bursitis)
-
Elbow (olecranon bursitis)
-
Hip (trochanteric bursitis)
-
Knee (prepatellar bursitis)
-
Heel (retrocalcaneal bursitis)
At Manipal Hospital Pune, our orthopaedic specialists frequently treat these cases using advanced techniques to ensure faster recovery and minimal discomfort.
Common Causes of Bursitis
Bursitis often develops due to repetitive motions or prolonged pressure on a joint. Some of the main bursitis causes include:
-
Repetitive activities: Frequent kneeling, throwing, or lifting can irritate the bursa.
-
Sudden injury: A fall or impact can trigger inflammation.
-
Prolonged pressure: Leaning on elbows or kneeling on hard surfaces for long periods.
-
Infections: Sometimes bacteria can infect the bursa, especially near the elbow or knee.
-
Aging: As we age, the elasticity of tendons and bursae reduces, making them more prone to injury.
-
Arthritis and gout: These joint conditions can increase the risk of bursitis flare-ups.
-
Poor posture: Incorrect posture while sitting or exercising puts unnecessary strain on joints.
Recognising the Symptoms of Bursitis
The signs of bursitis can develop suddenly or build up over time. Watch out for the following bursitis symptoms:
-
Pain: A dull ache that worsens with movement or pressure.
-
Swelling: Visible puffiness around the affected joint.
-
Tenderness: The area may be sore to the touch.
-
Restricted motion: Difficulty moving the joint freely.
-
Warmth or redness: Especially in cases where infection is present.
The pain usually intensifies with activity but may ease during rest. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to chronic bursitis or repeated flare-ups.
At Manipal Hospital Baner, doctors emphasise early diagnosis to prevent long-term joint issues and ensure effective treatment.
Who Is at Risk?
While bursitis can affect anyone, certain factors increase the risk:
-
People aged over 40
-
Occupations involving repetitive motions (e.g., plumbers, gardeners, athletes)
-
Overweight individuals (extra pressure on knees or hips)
-
Poor physical conditioning or tight muscles
-
Existing joint or bone problems
Diagnosing Bursitis
A doctor typically diagnoses bursitis through:
-
Physical examination: Assessing pain, swelling, and range of motion.
-
Imaging tests: X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI may help rule out fractures or arthritis.
-
Lab tests: If infection is suspected, fluid from the bursa may be analysed
Manipal Hospital Pune uses advanced imaging and diagnostic tools to accurately identify bursitis and design a personalised treatment plan.
Treatment & Recovery Tips for Bursitis
Most cases of bursitis improve with simple home care and a few weeks of rest. However, persistent cases might need medical intervention. Here’s how you can aid recovery:
1. Rest the Affected Joint
Avoid activities that worsen the pain. Rest helps the inflamed bursa settle down.
2. Apply Ice Packs
Use an ice pack for 15–20 minutes several times a day to reduce swelling and pain.
3. Use Compression or Support
Elastic wraps or braces can provide gentle support and reduce fluid build-up.
4. Elevate the Joint
If possible, elevate the affected area to reduce inflammation.
5. Take Anti-inflammatory Medicines
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen can ease discomfort.
6. Gentle Stretching & Physiotherapy
Once the pain subsides, physiotherapy helps restore flexibility and prevent recurrence.
Doctors at Manipal Hospital Baner often recommend guided exercises for safe recovery.
7. Maintain Good Posture
Whether at your desk or during exercise, proper posture prevents unnecessary joint stress.
8. Avoid Pressure
Use cushioned pads when kneeling or leaning on elbows to protect the bursa.
9. Address Underlying Conditions
Managing arthritis, gout, or other joint conditions reduces future flare-ups.
10. Medical Treatments (If Severe)
-
Aspiration: Removing fluid from the bursa to relieve pressure.
-
Corticosteroid injections: Reduce inflammation rapidly.
-
Antibiotics: Used if infection is the cause.
-
Surgery: Rarely needed, only for chronic or infected bursitis.
How I Cured My Bursitis: A Real Experience
Many patients recover through simple yet consistent self-care. For example, a middle-aged office worker with shoulder bursitis found relief through:
-
Daily application of cold compresses
-
Adjusting his work posture
-
Doing physiotherapist-recommended stretches
Within a month, his pain significantly reduced, and he could move freely again. The key was rest, correct posture, and gradual movement rather than overexertion.
At Manipal Hospital Baner, doctors encourage combining self-care with guided physiotherapy for long-lasting results.
Prevention Tips
Preventing bursitis is easier than curing it. Here’s how to protect your joints:
-
Warm up before physical activity
-
Strengthen muscles around joints
-
Take breaks during repetitive tasks
-
Use proper techniques in sports and lifting
-
Wear supportive footwear
-
Maintain a healthy body weight
Seek medical advice if:
-
Pain or swelling persists for more than two weeks
-
You notice redness, warmth, or fever (possible infection)
-
The pain restricts movement severely
Early diagnosis ensures quicker recovery and prevents long-term joint damage. Manipal Hospital Pune and Manipal Hospital Baner provide expert care to guide patients through recovery safely.
With proper treatment and care, most people recover from bursitis within a few weeks. Chronic bursitis can develop if the joint is overused or left untreated. Following preventive habits and gentle exercise can help maintain healthy, pain-free joints for years.
Conclusion
Bursitis might seem minor, but it can seriously impact your comfort and daily life. Recognising early symptoms and taking corrective steps like rest, physiotherapy, and lifestyle changes can make all the difference.
If you experience persistent pain or swelling in your joints, don’t ignore it. Consult an orthopaedic specialist at Manipal Hospital Pune or Manipal Hospital Baner, where experienced doctors provide personalised care using advanced diagnostic tools to ensure faster recovery and pain-free mobility.
FAQ's
Mild joint pain, swelling, and tenderness are usually the first signs of bursitis.
Most cases heal within two to six weeks, depending on severity and care.
Yes, overexertion can worsen it. Gentle stretching after recovery helps prevent recurrence.
No, with proper rest and treatment, bursitis usually resolves completely.
If pain, redness, or swelling persists despite home care, or if you develop a fever, consult a doctor immediately.






















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read