Have you ever thought about what a brain tumor is, or if every tumor in the brain is a brain cancer? A brain tumor is simply an abnormal increase in cells within or near the brain, and it may occur in anyone at any age. The tumor can significantly impact your daily functioning, emotional well-being, and the lives of those around you. In this blog, a top neurosurgeon in Yeshwanthpur discusses the types, myths, symptoms, and diagnosis of brain tumors.
Synopsis
What Are Brain Tumors?
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth of the brain or its covering structures. But not every tumor is a brain cancer. These tumors might be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and their effects mainly depend on their size, type, and location in the brain. Some develop slowly and might not produce the usual symptoms in the beginning, whereas others develop fast and cause interference with essential brain functions. Some common early signs of a brain tumor include persistent headaches, vision changes, balance difficulties, memory issues, or personality changes.
Identification of early signs of brain tumor and proper medical evaluation are essential for determining the right course of brain tumor treatment with enhanced outcomes.
Types of Brain tumors
Brain tumors exhibit various behaviors, natures, and modes of treatment. The various types are important to be known, as they have minimal impact on the brain and need different medical interventions. Brain tumors are basically grouped according to origin, behavior, and cell type.
-
Primary Brain Tumors: They are in the brain or the surrounding tissues. They are either benign (not cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Primary brain tumors do not spread to other parts of the body.
-
Secondary (Metastatic) Brain Tumors: These are formed when cancer cells in a tumor from a different location within the human body migrate to the brain. These are more common in adults than primary brain tumors and have a high stage of cancer, often requiring intense treatment with combination therapy.
-
Mixed Tumors: Mixed or hybrid tumors in the brain are the tumors that contain both cancerous and benign cells. These hybrid tumors would need a specialized pathological and molecular study and likely a personalized and multidisciplinary approach to treatment.
-
Benign Tumors: They are not cancerous, and the majority of them develop at a very slow rate, but certain problems can be caused because of their size, depending on where in the brain the tumors arise.
-
Malignant tumors: These are aggressive and grow rapidly, and can invade local brain tissue. Malignant brain tumors usually need to be treated urgently with multi-modal therapy, such as surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
-
Age-related: Brain tumors in children and adults both have different types and behaviors. As an example, medulloblastoma and pilocytic astrocytoma tend to occur more frequently in children, while glioblastoma and meningioma tend to happen in adults.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
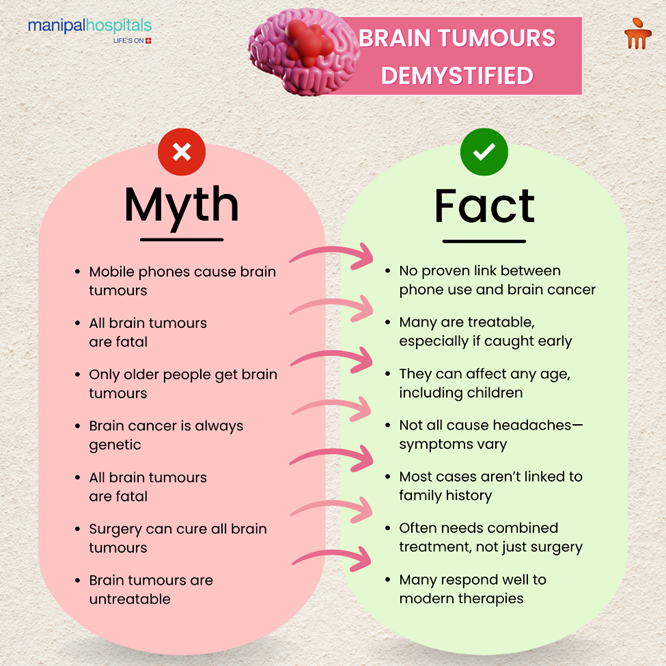
A common misconception about brain tumors may cause unnecessary fear and confusion. There are numerous myths surrounding their causes, symptoms, and treatment. It is essential to draw a clear distinction between facts and fiction so that patients, families, and the general public can be better informed and make more informed decisions.
-
Myth: Mobile phones cause brain tumors.
-
Fact - Current research does not support a link between cell phone use and brain cancer, so there is no need to panic over your phone.
-
-
Myth: All brain tumors are brain cancers.
-
Fact – No. Not all brain tumors are cancerous. Some brain tumors are benign, and if diagnosed early, treatment can be very successful.
-
-
Myth: Brain tumors only occur in older adults.
-
Fact - Brain tumors can affect anyone, including children, so it’s essential to watch for symptoms at any age.
-
-
Myth: Brain tumors always cause headaches
-
Fact - While headaches can be a symptom, not everyone with a tumor will experience them, so don’t rely only on this sign.
-
-
Myth: Brain cancer is always genetic.
-
Fact - Genetics can be a factor, but most brain cancers are not preceded by any family history or identifiable cause.
-
-
Myth: Surgery Can Cure All Brain tumors?
-
Fact - Brain tumor treatment is multimodal. Surgery is only one component of an overall treatment plan that may involve radiation or medication.
-
-
Myth: Brain tumors Are Untreatable.
-
Fact - With newer and advanced treatments now available, with early diagnosis of brain tumor, treatments are very promising. Many individuals go on to lead active, satisfying lives after a diagnosis of a brain tumor.
-
Diagnosis of Brain Tumor
Diagnosis of brain tumor involves a combination of clinical evaluation and advanced imaging techniques. Doctors begin by taking a detailed medical history and conducting a neurological examination to assess for symptoms such as headaches, changes in vision, or seizures.
-
Neurological Exam: A physician tests your reflexes, coordination, and memory to identify brain function abnormalities that could indicate a tumor.
-
MRI Scans: MRI scans are the most sophisticated imaging technique, which produces a 3D image of the brain displaying tumor size and position.
-
CT Scans: Usually employed if an MRI is not possible, CT scans take a rapid glance at the structure of the brain to detect unusual growths.
-
Biopsy: Occasionally, a small piece of the tumor is removed to know precisely the type of tumor and treatment planning.
-
Symptom Awareness: Early signs of brain tumor like increasing headaches, vision changes, or an abrupt personality change should never be neglected.
-
Liquid Biopsy: A more recent method that identifies tumor DNA in spinal fluid or blood and assists in monitoring treatment response with less pain.
-
Follow-up Tests: Ongoing imaging and check-ups enable tumor change or treatment effect to be monitored over time.
Conclusion
Brain tumors might feel like a frightening subject, but learning about them makes you feel in control. From learning about the various types to refuting myths and identifying symptoms, knowledge is your greatest weapon. Early diagnosis of brain tumor can make the difference in treatment results. Keep in mind that brain tumors are not an all-for-one situation. Treatment of brain tumors and the outcomes can greatly differ based on tumor type, location, and stage. Stay informed and if you suspect any symptoms book a consultation with expert neurosurgeons at Manipal Hospital Yeshwanthpur.
FAQ's
Initial symptoms can be headache that deteriorates over time, vision changes, sudden personality changes, or seizures. The symptoms vary based on the location of the tumor, hence any unusual signs need a check-up with the doctor.
Though the cause is not known, not smoking and not using tobacco, keeping a healthy weight, and avoiding radiation can lower risk. Healthy practices promote general brain and body health but don't assure prevention.
Treatment discomfort depends on the type used. Surgery has some pain of recovery, whereas chemotherapy or radiotherapy may cause fatigue or nausea. Physicians do their best to control pain and side effects to make you comfortable.
Brain tumors represent approximately 1.6% of all Indian cancers, with approximately 40,000 new cases diagnosed annually and over 24,000 deaths every year. These statistics best explain the need for awareness and early detection.
Treatment may involve surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and more recent alternatives such as immunotherapy and proton therapy. The most effective option is determined by the type, size, location, and general health, usually a combination of several treatments.





















 7 Min Read
7 Min Read