Every year, March 24th is observed as World TB Day to spread awareness about tuberculosis, a major health challenge in India. In 2023, India registered 2.8 million new TB cases, which represented more than one-quarter of global TB cases. The ongoing myths about tuberculosis in India create barriers that block successful strategies to stop and treat the disease. This blog challenges widespread misconceptions while making you aware of TB facts to boost public knowledge about TB control.
Synopsis
Understanding Tuberculosis (TB)
TB is a contagious bacterial disease that is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The infection primarily targets the lungs, although it possesses the ability to spread to various other body parts. TB spreads through the air when sick individuals release tiny droplet particles while coughing or sneezing.
Common Signs of TB
It is very important to know the common signs of tuberculosis (TB) so that timely medical assistance can be sought at the earliest.
The most common symptoms of TB disease include:
-
A persistent cough that lasts for 3 or more weeks
-
Coughing up sputum (phlegm), which may contain blood
-
Fever
-
Night sweats
-
Unexplained weight loss
Common TB Myths vs. Facts
TB creates widespread misunderstandings, which people transform into stigma and fear because of public misconceptions about the disease. Misconceptions about tuberculosis, especially in countries like India, prevent people from getting prompt medical help, which results in delays in diagnosis and poor control of TB. Thus, we must debunk these public misconceptions to be able to eliminate TB entirely.
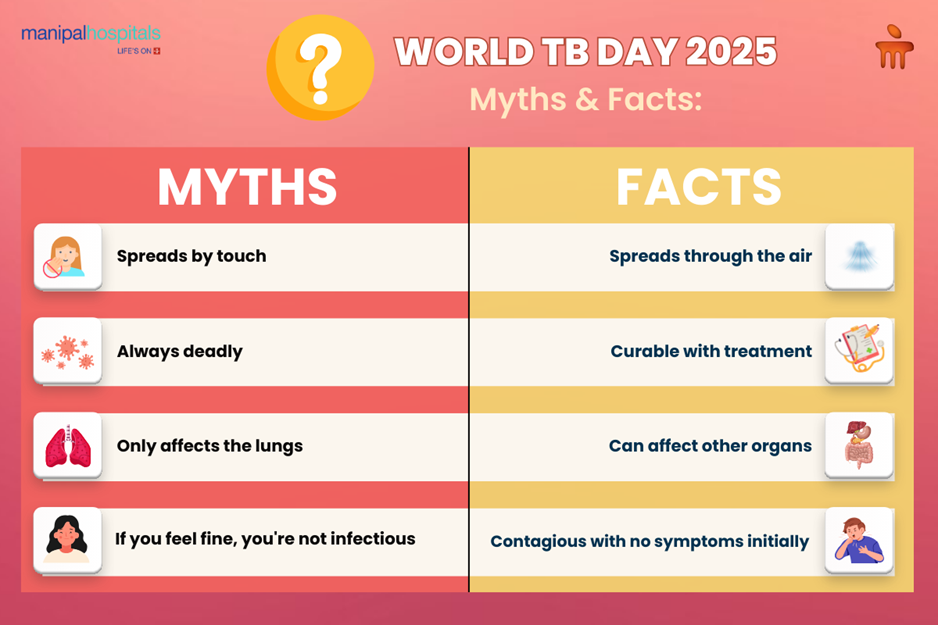
Below are some common myths and facts about TB:
-
Myth 1: TB Only Affects the Poor
Fact: TB can infect anyone, although there can be socioeconomic factors that increase the risk of TB. Transmission depends on exposure to the bacteria through close contact with an infected person and not solely on economic status.
-
Myth 2: TB Is Incurable
Fact: TB is highly curable with proper treatment. Standard medical therapy has the ability to eliminate the bacteria if taken correctly.
-
Myth 3: Only Coughing Spreads TB
Fact: TB spreads through airborne droplets expelled from coughing, sneezing, talking, or even singing, especially in close, poorly ventilated environments.
-
Myth 4: TB Treatment Is Always Long and Difficult
Fact: Modern TB treatment regimens have shorter durations and better success rates for most patients. However, some drug-resistant forms of TB may require extended treatment.
-
Myth 5: Once Cured, TB Never Returns
Fact: Although successful TB treatment eliminates active infection, reinfection or reactivation of dormant bacteria can cause TB in individuals with weakened immune systems.
-
Myth 6: TB is hereditary.
Fact: TB is not inherited; it is an infectious disease that spreads from person to person. However, people living in the same household have a higher risk of infection due to close proximity.
Read this blog: Tuberculosis – Role Of Diet In The Prevention Of TB
How India Is Fighting TB: Progress & Challenges
India has intensified efforts to eliminate TB by 2025 through better diagnosis, treatment, and awareness. Despite progress, challenges like drug resistance and delayed detection came as hindrances in the complete eradication of TB.
Progress
-
Free Diagnosis & Treatment: The government provides free TB testing and medication under the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP) in an effort to achieve a TB-free India.
-
Newer & Shorter Treatments: Shorter drug regimens improve recovery rates, reducing treatment duration for drug-resistant TB cases.
-
Improved Awareness Campaigns: Initiatives like "TB Harega, Desh Jeetega" raise awareness about tuberculosis (TB), early detection, and stigma reduction.
Challenges
-
Rising Drug-Resistant TB Cases: Multidrug-resistant TB strains require more potent, costlier treatments with lower success rates.
-
Delayed Diagnosis: Many TB cases in India remain undetected due to a lack of awareness and limited access to healthcare.
-
Social Stigma & Fear: Misconceptions about TB discourage people from seeking timely medical help, leading to the further spread of the disease.
How You Can Help in the Fight Against TB
Even you can contribute to eliminating TB by spreading awareness, supporting patients, and promoting early diagnosis. Small actions can make a big difference in controlling TB spread.
Here are ways you can help:
-
Spread Awareness: To reduce stigma and misinformation, educate friends and family about TB symptoms, treatment, and prevention.
-
Encourage Early Testing: Guide those with persistent cough or fatigue to get tested for TB at health centres.
-
Support TB Patients: Offer emotional and social support to those undergoing TB treatment to ensure they adhere to their medication as prescribed by the doctor.
-
Follow Preventive Measures: Practice good hygiene, wear masks in crowded areas, and ensure proper ventilation to limit the spread of TB.
Conclusion
Get in touch with an experienced pulmonologist if you have had a cough for over 2 weeks, unexplained weight loss, fever, or night sweats. Early diagnosis prevents complications and reduces TB transmission. Timely treatment ensures a full recovery and protects others from infection. Do not ignore symptoms—TB is curable with proper care.
If you have been exposed to a TB patient or are experiencing fatigue and chest pain, visit the Pulmonology Department in Manipal Hospital Salem and meet our expert pulmonologists in Salem.
FAQ's
TB can affect the spine, brain, kidneys, and other organs. This is called extrapulmonary TB and requires specialised treatment.
TB does not spread through food, water, or surface contact. It spreads through airborne droplets from infected individuals.
The BCG vaccine protects children from severe forms of TB in children; however, it is not fully effective in providing lifelong immunity against all TB infections, especially pulmonary TB in adults.
Yes, latent TB infections exist where bacteria remain dormant without any TB symptoms in the patient. These individuals are not contagious but may develop active TB later.
Yes, smoking and alcohol weaken the immune system, making it easier for TB bacteria to cause infection or worsen the disease.





















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read

--Symptoms,-Causes,-and-Treatment.png)