Women’s health is deeply connected with hormones, and even a small imbalance can show up in unexpected ways, from irregular periods to weight changes and skin problems. Two of the most commonly heard terms in this space are PCOD (Polycystic Ovarian Disease) and PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome). While many people use them interchangeably, the truth is they are not exactly the same. If you’ve ever wondered why you’re experiencing irregular cycles, difficulty losing weight, or hormonal acne, you may have asked yourself: Is it PCOD or PCOS?
In this blog, let’s break it down simply: what PCOD and PCOS actually are, how they differ, PCOD and PCOS symptoms to look out for, possible causes, diagnosis, PCOS treatment options, and how you can manage life with either condition.
Synopsis
What is PCOD?
PCOD stands for Polycystic Ovarian Disease. It happens when the ovaries release a lot of immature eggs. These eggs can turn into small cysts in the ovaries, which may lead to the ovaries enlarging and producing excess androgens (male hormones).
PCOD is fairly common among young women, especially adolescents. While it can cause symptoms like irregular periods, weight gain, and hormonal changes, it is generally considered a lifestyle-related condition. With timely lifestyle adjustments, like a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, PCOD symptoms can be managed well and usually do not cause severe long-term complications.
What is PCOS?
PCOS, or Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, is more than an ovarian disease. It's a metabolic and hormonal disorder that impacts how your body processes insulin and makes hormones. With PCOS, the ovaries release excess levels of androgens, which can interfere with ovulation, result in multiple cysts, and cause symptoms that reach beyond reproductive health, including insulin resistance, trouble losing weight, and a higher risk of diabetes and heart disease.
Unlike PCOD, PCOS symptoms have a more severe effect on long-term health and fertility. It's not as frequent as PCOD, but it requires careful medical treatment and frequently a programmatic PCOS treatment regimen.
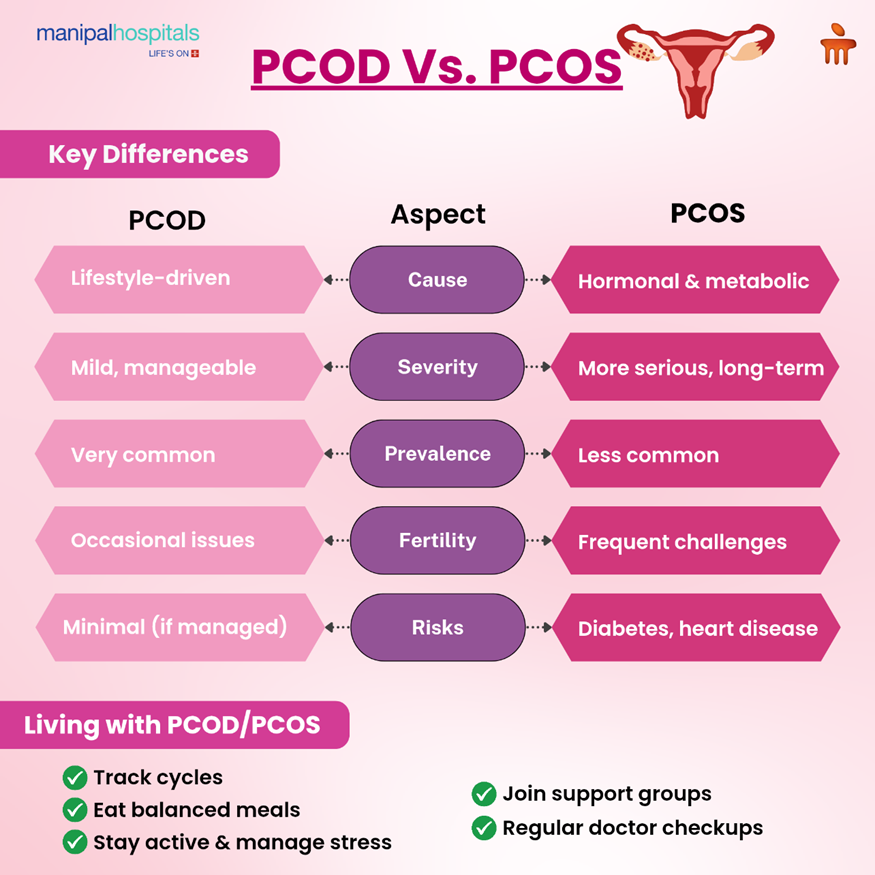
Key Differences Between PCOD and PCOS
It's very easy to confuse the two. Here's an easy table to have a clear vision of the difference between PCOD and PCOS:
|
Aspect |
PCOD |
PCOS |
|
Cause |
Mostly lifestyle-related (diet, stress, inactivity) |
Primarily a hormonal and metabolic imbalance |
|
Severity |
Mild; often managed with lifestyle changes |
More serious; may need medical treatment |
|
Occurrence |
Very common among women |
Less common compared to PCOD |
|
Impact on Fertility |
Occasional fertility issues, but usually manageable |
Frequent fertility challenges due to a lack of ovulation |
|
Long-term Risks |
Minimal if managed well |
Higher risk of diabetes, infertility, and heart disease |
So, if you’ve been wondering, “Is PCOS more serious than PCOD?”, yes, PCOS generally has more severe health implications.
Common PCOD and PCOS Symptoms
Both PCOD and PCOS have various overlapping symptoms, hence the confusion. Here are the common PCOD and PCOS symptoms you need to watch out for:
-
Irregular periods – too long, too short, or completely missed cycles
-
Weight gain – especially in the waist area, is more difficult to lose despite dieting
-
Acne and oily skin – caused by excess androgens
-
Excess hair growth (hirsutism) – particularly on the face, chest, or tummy
-
Hair loss or hair thinning – just like male-pattern baldness
-
Inability to conceive – abnormal ovulation makes it more difficult to get pregnant
-
Fatigue and mood swings – hormonal swings can disrupt energy and emotions
While both diseases can present with these signs, in PCOS, they are more intense and chronic, particularly regarding fertility and metabolism.
Causes and Risk Factors
The specific causes of PCOD and PCOS are not yet clear, but there is a general consensus that they are multi-factorial. Among the most frequent triggers and risk factors are:
-
Genetics – if your sister or mother has PCOS/PCOD, your likelihood grows
-
Habits in lifestyle – unhealthy eating, inactivity, and excessive stress can exacerbate symptoms
-
Insulin resistance and PCOS – more prevalent, where your body cannot effectively use insulin
-
Hormonal imbalance in women – higher androgens, insulin, and LH levels disrupt ovulation
-
Obesity – excess weight can throw off your hormonal balance further
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
If you’ve been struggling with irregular cycles, persistent acne, or unexplained weight gain, it’s worth getting evaluated. Here’s how doctors typically diagnose PCOD or PCOS:
-
Physical examination – checking symptoms like excess hair growth or acne
-
Blood tests – to assess hormone levels, insulin, and thyroid function
-
Ultrasound – to rule out ovarian cysts
-
Rome IV criteria & symptom assessment – eliminating other conditions such as thyroid disease or diabetes
-
Early PCOS diagnosis is particularly crucial, as it can prevent long-term complications.
Treatment Options
The good news? Both conditions are treatable. Treatment typically depends on your PCOD and PCOS symptoms and health objectives (such as controlling weight, regulating acne, or enhancing fertility).
A. Lifestyle Changes
-
Switch to a balanced diet—low-GI and anti-inflammatory foods.
-
Keep physically active to boost the insulin sensitivity of the body.
-
Make time for stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, or even basic breathing exercises.
B. Medical Treatments
-
Birth control pills - to regulate periods and support hormonal imbalance treatment
-
Metformin - for insulin resistance and PCOS
-
Fertility medications - if you are trying to conceive
-
Anti-androgen drugs - to control acne and excessive hair growth
C. Alternative Therapies
Some women find relief with:
-
Ayurvedic and herbal treatments
-
Acupuncture to promote hormonal balance
-
Yoga and meditation to ease stress-induced triggers
Complications If Left Untreated
Neglecting PCOD or PCOS could precipitate the onset of many life-threatening health conditions, including:
-
Problems in conception or infertility
-
Type 2 diabetes through the mechanism of insulin resistance
-
Higher chances of endometrial cancer due to prolonged missed periods
-
Heart attacks and elevated cholesterol levels
-
Depressed and anxious due to a hormonal imbalance in women
-
Sleep apnea (most prevalent in obese women)
Living with PCOD or PCOS: Tips and Support
Living with PCOD or PCOS might become overwhelming at times, but taking small, regular steps can work wonders. Some suggestions are:
-
Develop a sustainable lifestyle with proper nutrition, exercise, and sleep
-
Monitor your menstrual cycles to catch abnormalities early
-
Drink plenty of water and prioritise sleep
-
Join support groups or online forums for solidarity
-
Stay in touch with your gynaecologist or endocrinologist frequently
Conclusion
PCOD and PCOS might seem almost alike, but they're not the same. Though PCOD is more prevalent and usually milder, PCOS has more extensive hormonal and metabolic implications that need to be handled with caution. What is crucial is listening to your symptoms, receiving an early diagnosis, and adhering to a workable PCOS treatment regimen. With Manipal Hospitals, our women's health experts are available to counsel you with personalised treatment and integrated care. Contact us today and own your reproductive well-being.
FAQ's
Yes, most women with PCOD or PCOS become pregnant with the appropriate management. At times, it can take lifestyle adjustments, medications, or fertility treatment. The most important thing is to seek early medical advice and not give up hope; pregnancy is achievable.
PCOS is generally more serious since it impacts not only the ovaries but also metabolism and overall health. PCOD, in contrast, is typically less severe and often treated effectively with lifestyle modifications.
There isn't a one-size-fits-all, but a low-GI diet with increased whole grains, fresh produce, vegetables, and lean proteins is beneficial. Reducing sugar and processed food also does much to stabilise hormones and regulate symptoms.
Yes, PCOD is actually quite common in teenagers, especially if cycles are irregular from the start. Symptoms like acne, weight gain, or excess hair growth should not be ignored and need medical attention early on.
If your periods are consistently irregular, or you’ve been struggling with sudden weight gain, persistent acne, or difficulty conceiving, it’s time to see a gynaecologist. Early evaluation helps in better management of both PCOD and PCOS.






















 9 Min Read
9 Min Read