.png)
Leukaemia is a complex and potentially life-threatening form of blood cancer that affects thousands of individuals globally every year, including many in India. It can strike both children and adults, and it often progresses silently until it reaches an advanced stage. Early diagnosis and prompt medical attention are key to improving outcomes. By understanding the types, symptoms, and treatments available for leukaemia, individuals can make informed decisions about their health.
At Manipal Hospital Gurugram, patients receive state-of-the-art diagnostic facilities and comprehensive treatment plans delivered by a highly skilled team of haematologists, oncologists, and medical experts. This guide is designed to help you recognise early warning signs and gain insight into the various types of leukaemia.
Synopsis
What Is Leukaemia?
Leukaemia is a type of cancer that starts in the bone marrow, the soft, spongy tissue inside the bones where blood cells are formed. Normally, bone marrow produces red blood cells (which carry oxygen), white blood cells (which fight infection), and platelets (which help blood clot). In leukaemia, the body starts producing an excessive number of abnormal white blood cells that don’t function properly.
These abnormal cells crowd out healthy blood cells, resulting in symptoms such as fatigue, frequent infections, and easy bruising. Leukaemia is broadly classified based on how fast it progresses (acute vs. chronic) and which type of blood cell is affected (lymphoid or myeloid).
Types of Leukaemia
Leukaemia is grouped into four primary types, each with distinct characteristics:
1. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALL)
-
Most common in children, but can occur in adults
-
Rapid onset and progression
-
Affects immature lymphoid cells
-
Requires immediate and aggressive treatment, often involving chemotherapy and sometimes bone marrow transplantation
2. Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML)
-
More prevalent in adults, but it can affect children
-
Rapidly progressing cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells
-
Leads to a shortage of red cells, platelets, and functional white cells
-
Requires prompt medical attention and intensive therapy
3. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia (CLL)
-
Typically affects older adults (aged 60 and above)
-
Progresses slowly and may remain undetected for years
-
Some patients do not need treatment right away and are monitored regularly
-
Treatment includes chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapies when necessary
4. Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia (CML)
-
Most common in adults
-
Associated with a genetic mutation known as the Philadelphia chromosome
-
Initially slow-growing, but can become aggressive without treatment
-
Targeted therapy, particularly tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), has significantly improved prognosis
At Manipal Hospital Gurugram, each case of leukaemia is diagnosed and managed through a personalised, evidence-based treatment plan designed to offer the best chances for remission and long-term health.
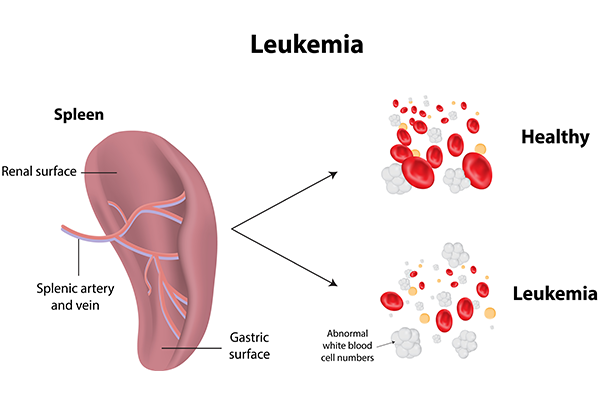
Early Symptoms of Leukaemia
Detecting leukaemia early can significantly influence the treatment outcome. However, early symptoms are often subtle and may mimic common viral illnesses. Being aware of these signs is essential.
Common early signs and symptoms include:
-
Persistent fatigue or unexplained weakness
-
Recurring infections or fevers
-
Easy bruising or unusual bleeding, such as frequent nosebleeds
-
Pale complexion
-
Unintentional weight loss
-
Swollen lymph nodes, especially in the neck, armpits, or groin
-
Pain in bones or joints
-
Shortness of breath during minimal activity
-
Skin changes like petechiae (tiny red spots), rashes, or lumps
In some cases, skin leukaemia symptoms, such as red/purple patches, skin nodules, or small pinpoint spots, can be the first visible signs. These are more common in subtypes like leukaemia cutis, where cancer cells infiltrate the skin.
If you or a loved one are experiencing these symptoms, especially if they are persistent or unexplained, consult a medical expert. The specialists at Manipal Hospital Gurugram offer comprehensive evaluations to determine the cause and suggest appropriate next steps.
How Is Leukaemia Diagnosed?
A precise diagnosis is the foundation for effective treatment. At Manipal Hospital Gurugram, diagnosis typically involves a combination of the following tests:
1. Complete Blood Count (CBC):
Checks the number and types of blood cells. Abnormal levels often point toward leukaemia.
2. Peripheral Blood Smear:
Microscopic examination of blood cells to assess shape, size, and maturity.
3. Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy:
Used to confirm diagnosis and identify the specific type of leukaemia by analysing samples from the bone marrow.
4. Cytogenetic and Molecular Testing:
Identifies genetic abnormalities, such as the Philadelphia chromosome, and helps guide targeted therapy.
5. Flow Cytometry:
Analyses the physical and chemical characteristics of blood and bone marrow cells to classify leukaemia subtypes.
These advanced diagnostic tools help determine the type, stage, and treatment options for each individual case.
Leukaemia Treatment Options
Treatment for leukaemia depends on the type, patient age, overall health, and disease progression. The main treatment options include:
1. Chemotherapy
-
The most common treatment approach
-
Uses anti-cancer drugs to kill leukaemia cells
-
Administered in cycles with rest periods
-
Can be oral or intravenous
2. Targeted Therapy
-
Focuses on attacking specific genes or proteins in cancer cells
-
Particularly effective in CML and some subtypes of ALL
-
Fewer side effects compared to chemotherapy
3. Immunotherapy
-
Strengthens the body’s natural defenses to fight cancer
-
Includes monoclonal antibodies and CAR-T cell therapy
-
Often used in cases where other treatments have failed
4. Radiation Therapy
-
Uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells or shrink enlarged lymph nodes or spleen
-
Rarely used alone; often combined with other therapies
5. Bone Marrow/Stem Cell Transplant
-
Replaces diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells
-
May be from a donor (allogeneic) or the patient’s own cells (autologous)
-
Recommended for aggressive or relapsed cases
At the cancer care department in Manipal Hospital Gurugram, each treatment plan is tailored based on comprehensive diagnostic findings and patient-specific factors. The hospital’s integrated approach ensures patients receive compassionate, holistic care from diagnosis through recovery.
Conclusion
Leukaemia, though serious, is increasingly treatable—especially when caught early and managed with advanced therapies. Awareness of its types, symptoms, and treatment options empowers patients and families to act swiftly.
Manipal Hospital Gurugram is at the forefront of cancer care in India, offering cutting-edge diagnostics, advanced therapies, and personalised treatment plans for leukaemia. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms, do not delay. Timely evaluation by a specialist can make a life-saving difference.
Take the first step toward better health. Schedule your consultation with an experienced medical oncologist at Manipal Hospital Gurugram today.





















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read