-
Book Appointments & Health Checkup Packages
- Access Lab Reports
-
-
Book Appointments & Health Checkup Packages
-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
- Bariatric Surgery - MIBS
- Bariatric Surgery
- Cancer Care
- Cardiology
- Cardiothoracic Vascular Surgery
- General Surgery
- Hemato Oncology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatric And Child Care
- Renal Sciences
- Robotic Assisted Surgery
- Urology
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Other Specialities
- Accident and Emergency Care
- Anesthesiology
- Bone Marrow Transplantation
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- IVF and Infertility
- Laboratory Medicine
- Liver Transplantation Surgery
- Medical Gastroenterology
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Paediatric Cancer Care
- Paediatric Cardiology
- Paediatric Neurology
- Paediatric Surgery
- Pain Medicine
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic, Reconstructive And Cosmetic Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Rheumatology
- Spine Care
- Surgical Gastroenterology
- Doctors
- Yeshwanthpur
-

Bengaluru

-
-

Bhubaneswar

-

Bhubaneswar
-
-

Delhi - NCR

-

Goa

-

Goa
-
-

Jaipur
-

Kolkata

-

Mangaluru
-

Mysuru
-

Patiala
-

Pune

-

Ranchi
-

Salem
-

Siliguri City

-

Vijayawada
- International Patients



Clinics







- Self Registration
- In-Patient Deposit
- Mars - Ambulance
- Home Care
- Organ Donation
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Manipal Insider
- Extended Clinical Arm
- Careers
- Contact Us
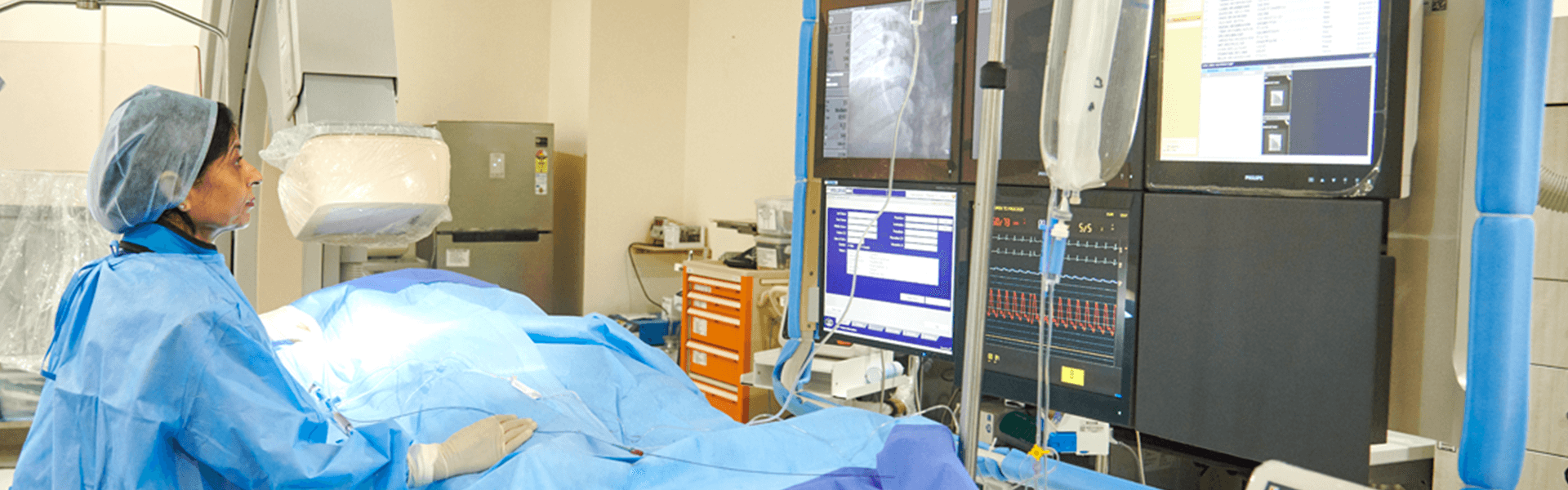
Thyroid Disorders Associated with Diabetes
Diabetes centre in Yeshwanthpur, Bangalore
The endocrine system includes a cluster of glands that release hormones to help in the regulation of reproduction, growth, and the use of nutrients by the cells of the body. The thyroid gland is one of the glands that control these processes and glucose metabolism is influenced by the way the thyroid gland works. When the thyroid gland malfunctions, it affects the way the absorption of glucose is carried out in the body or diabetes in other words. So if the thyroid malfunctioning is left untreated, it can lead to serious diabetes complications. But any abnormal activity by the thyroid gland is easily detected by simple blood tests. Therefore, a diabetic individual is always advised to test the blood for thyroid abnormalities regularly.
The thyroid gland is a small-sized butterfly-shaped gland that is located within a person's neck region above the collarbone and below Adam's apple. Thyroxine or T4 and Triiodothyronine or T3 are the two major hormones produced by this gland. These hormones influence the working of the other glands in the body like the pancreas, liver, heart, etc. The brain region that works with the thyroid is the Hypothalamus along with the Pituitary gland as an integrated system that controls the thyroid gland. Thyrotropin-releasing Hormone or TRH is released by the Hypothalamus which signals the Pituitary gland to then secrete Thyroid Stimulating Hormone or TSH. The TSH then stimulates the thyroid gland to produce T3 and T4. The quantities of these two thyroid hormones are controlled by the Pituitary gland. Visit our Diabetes care hospital in Bangalore for the best treatment.
Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland underperforms and does not produce sufficient thyroid hormones in the body. Thyroxine replacement therapy is therefore the practical approach used by endocrinologists to tackle the lack of the hormone. The condition is mainly seen in older women but with exceptions in some children too. The common symptoms include depression, mood swings, goiter formation, weakness in muscles, retention of fluid, constipation, etc. Although the cause of hypothyroidism is a lack of iodine in the diet in some cases, an autoimmune condition called Hashimoto Thyroiditis is the other major cause. The autoimmune disease is seen when the body produces antibodies against the thyroid gland and harms it by degrading the thyroid tissues. This causes slack in the production of thyroid hormones and may even lead to failure of the thyroid gland.
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland overperforms and produces excess thyroid hormones. The symptoms differ in different sexes and age groups. Whilst young women get irregular menstruation and frequent miscarriages, children are prone to overgrowth, hyperactivity, lack of concentration, memory loss, etc. The common cause of hyperthyroidism is the autoimmune condition called Grave’s disease in which the body harms the thyroid gland by producing antibodies against it. This is prominently seen as a goiter formation in which the thyroid gland is stimulated to overgrow and overproduce the thyroid hormones.
The incidence of thyroid malfunction is more prominent in the case of a diabetic individual. The incidence of Type 1 diabetes individuals developing an autoimmune is seen to be increasing especially in women who give birth. This is called ‘Postpartum thyroiditis’. People who have Type 2 diabetes also develop thyroid disorders frequently although there is no cause explained yet. Hypothyroidism is mostly seen in Type 2 diabetic individuals. Book an appointment at Manipal Hospitals for the best treatment facilities.
Since the normal functioning of the thyroid gland is required to maintain the energy levels of the body, an abnormally working thyroid gland can jeopardize glucose metabolism. In hyperthyroidism, the diabetic individual needs repeated insulin boosts. The liver is prone to overproduce glucose which leads to over-absorption of glucose through the intestines. This causes insulin resistance where the body does not recognize the importance of insulin. This causes spikes in blood sugar levels. A diabetic person with hyperthyroidism may also suffer from heart malfunction and heart failure. The heart sometimes has a rapidly overworking condition leading to chest pains, interfering with the heart medications, and eventually leading to heart failure. Osteoporosis is another symptom of hyperthyroidism seen in diabetic persons where there is increased bone thinning. This causes more frequent fractures in the bones from frequent falls due to imbalances in the body, especially in the elderly.
In Hypothyroidism, there are changes in blood lipid levels seen. The cholesterol levels, triglycerides, and LDL levels are all seen to peak up. This in turn leads to cardiovascular disease complications like heart failure or paralysis.
Home Yeshwanthpur Specialities Diabetes-and-endocrinology Thyroid-disorders-associated-with-diabetes

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services





