-
Book Appointments & Health Checkup Packages
- Access Lab Reports
-
-
Book Appointments & Health Checkup Packages
-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
- Bariatric Surgery - MIBS
- Bariatric Surgery
- Cancer Care
- Cardiology
- Cardiothoracic Vascular Surgery
- General Surgery
- Hemato Oncology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatric And Child Care
- Renal Sciences
- Robotic Assisted Surgery
- Urology
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Other Specialities
- Accident and Emergency Care
- Anesthesiology
- Bone Marrow Transplantation
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- IVF and Infertility
- Laboratory Medicine
- Liver Transplantation Surgery
- Medical Gastroenterology
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Paediatric Cancer Care
- Paediatric Cardiology
- Paediatric Neurology
- Paediatric Surgery
- Pain Medicine
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic, Reconstructive And Cosmetic Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Rheumatology
- Spine Care
- Surgical Gastroenterology
- Doctors
- Yeshwanthpur
-

Bengaluru

-
-

Bhubaneswar

-

Bhubaneswar
-
-

Delhi - NCR

-

Goa

-

Goa
-
-

Jaipur
-

Kolkata

-

Mangaluru
-

Mysuru
-

Patiala
-

Pune

-

Ranchi
-

Salem
-

Siliguri City

-

Vijayawada
- International Patients



Clinics







- Self Registration
- In-Patient Deposit
- Mars - Ambulance
- Home Care
- Organ Donation
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Manipal Insider
- Extended Clinical Arm
- Careers
- Contact Us
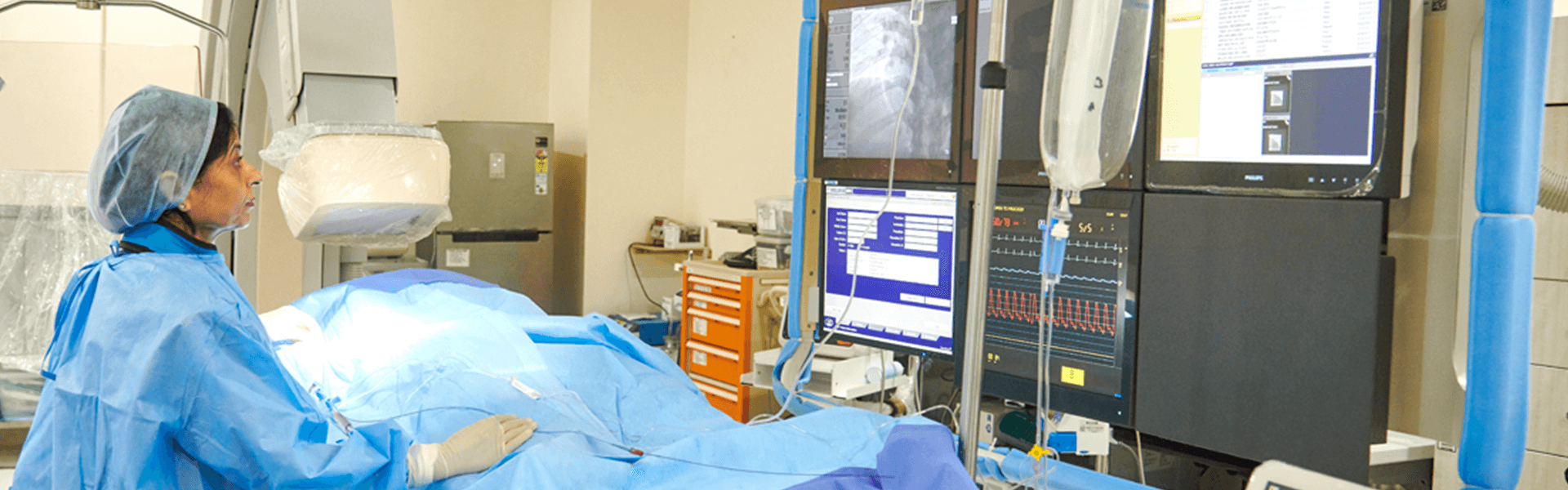
Evaluation and Treatment of Endocrine Tumours
Diabetes centre in Yeshwanthpur, Bangalore
Neuroendocrine Tumours (NETs) are those tumours that are formed in the endocrine system of the body. The affected endocrine cells begin to divide and multiply profusely leading to tumours. The different types of NETs are basically primary tumours that have not metastasized and secondary tumours that have spread around. The most organs affected in the case of secondary NETs are the liver, lungs and lymphatic system. Some of the common primary NETs are listed below.
-
Gastrointestinal Tract: Here the NETs mostly develop in the GI tract locations like the large intestines, appendix or small intestines.
-
Lungs are where the NETs are located after the GI tract. The bronchial system is affected by the circulation of air within the respiratory tract. These may be also known as carcinoid tumours.
-
The pancreas are also another location for NETs to develop and grow. These are also called PNETS (Pancreatic NETs) or islet cell tumours. Visit our diabetes and endocrinology centre in Yeshwanthpur, Bangalore.
The common symptoms of NETs are diarrhoea with cramps in the abdomen, swelling of the hands and feet, shortness of breath, smelly fatty poop, jaundice, etc.
The diagnosis of NETs is done in the following manner.
-
Analysis of urine for abnormalities.
-
Biopsy for extracting cells or fluid from the NETs for microscopic examination.
-
CT scan.
-
Core needle biopsy.
-
MRI scan.
-
Positron Emission Testing (PET) scan.
-
Biochemical testing for detecting abnormal quantities of enzymes or other proteins.
Treatment of NETs includes the following methods.
-
Surgery to extract the tumours from the endocrine glands. This involves the removal of the tumour by a surgical oncologist. Debulking surgery involves removing most of the tumour cells when the tumour is not well differentiated.
-
Targeted therapy involves the use of drugs that are specific for certain genes that will inhibit the growth of cancer cells.
-
Chemotherapy with a range of drugs will destroy the cancerous cells.
-
Somatostatin analogues are used when the body is excessively producing endocrine hormones. These stop the cancerous growth of the tumour despite the fact that it has metastasized and spread around.
-
Immunotherapy helps the body to improve its immune response. Interferons are the molecules involved in boosting the immune system of the body.
-
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PPRT) involves the use of a radioactive drug that binds to the Somatostatin receptor on cancerous cells. The radioactive drug enters the cancerous cells and destroys them. Book an appointment at Manipal Hospitals today for the best treatment.
NETs are often graded in different grades based on the extent of growth. Grade 1 tumours grow slowly, grade 2 tumours grow at a medium rate and grade 3 tumours grow at a quick pace.
Well-differentiated NETs contain cells that look like normal healthy cells as they are well differentiated. Poorly developed NETs contain cells that are not well differentiated and look like cancerous cells.
Home Yeshwanthpur Specialities Diabetes-and-endocrinology Evaluation-and-treatment-of-endocrine-tumours

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services





