
Dementia is a global health crisis affecting at least 44 million people worldwide, including more than 4 million in India. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia, accounting for nearly 75% of all dementia cases. This impairs the person’s ability to perform everyday tasks and affects memory. However, understanding Alzheimer’s disease symptoms, causes, and treatment can help in better managing this condition.
Synopsis
What is Alzheimer's Disease?
Alzheimer’s disease is a brain disorder that causes changes in the brain, affecting a person’s memory, learning, thinking, and organising skills. These changes lead to the accumulation of certain proteins in the brain, causing the brain cells to shrink and die. This disease worsens with time and affects mostly people above the age of 65. Alzheimer’s affects the person’s ability to function properly, leading to changes in their personality, behaviour, memory, thinking, and other cognitive functions.
Difference between Alzheimer’s and Dementia
Dementia is not a specific disease; it's an umbrella term to describe a decline in a person’s mental state, affecting their memory and other cognitive abilities. There can be many causes of dementia disease, with Alzheimer’s being the most common form. All Alzheimer's symptoms are dementia symptoms, but not all dementia symptoms are caused by Alzheimer’s disease. Understanding this distinction helps in getting the appropriate dementia treatment based on the underlying cause.
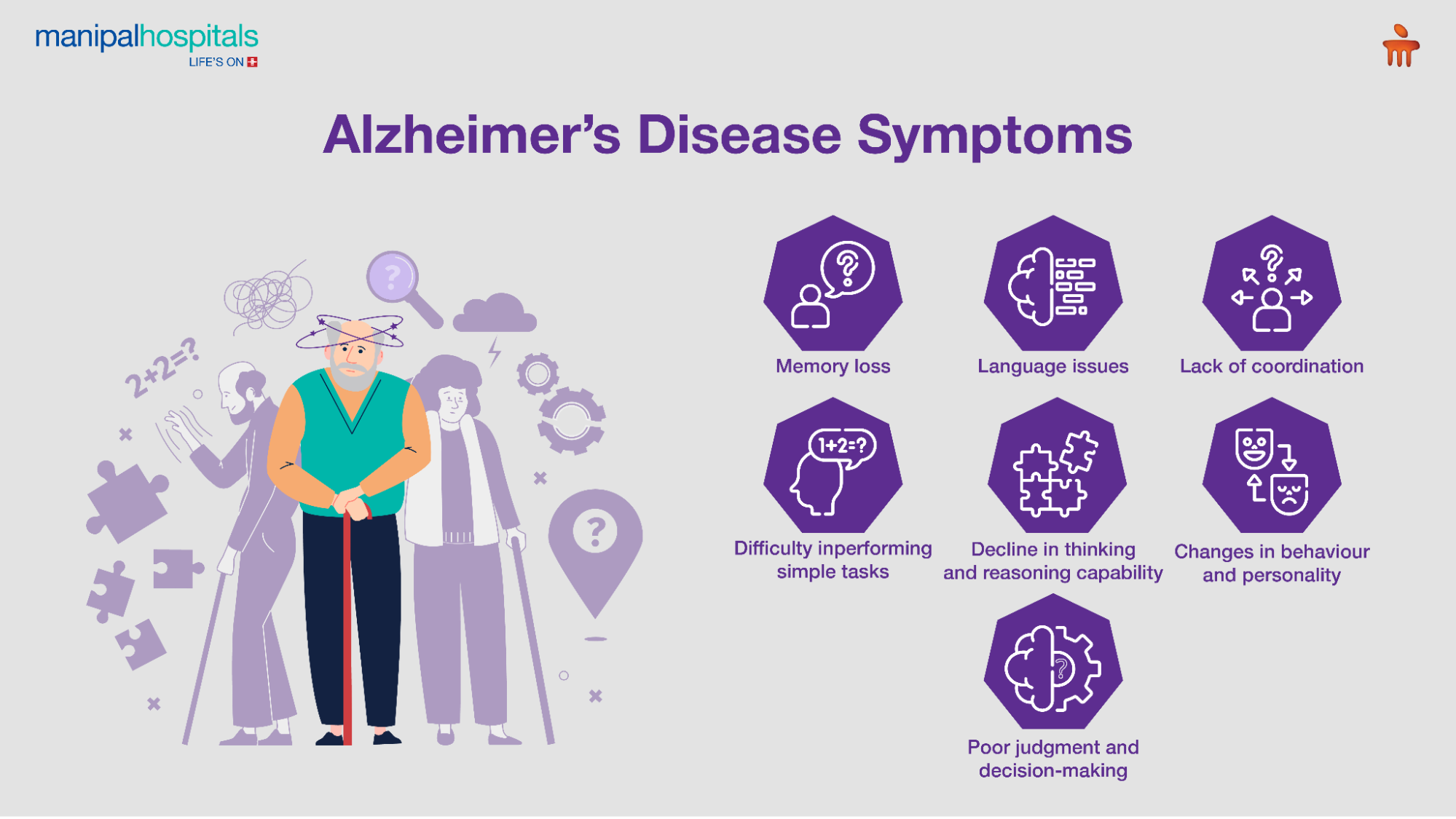
Alzheimer’s Disease Symptoms
Alzheimer’s progresses slowly with time, and its symptoms vary based on the stage of the condition and from person to person.
These include:
-
Memory loss: This is the key symptom, and the person starts forgetting recent events and conversations.
-
Behaviour and personality changes, including mood swings, depression, anxiety, social withdrawal, loss of interest in activities, etc.
-
Difficulty in performing simple and familiar tasks
-
Language issues
-
Lack of coordination
-
Decline in thinking and reasoning capability
-
Poor judgment and decision-making
In the later stages, individuals may experience total memory loss, lose the ability to communicate, become vulnerable to infections, and need help even with basic everyday tasks.
If you experience any of these Alzheimer’s symptoms, seek consultation with a neurologist.
Causes of Alzheimer’s Disease
The exact causes of Alzheimer’s disease are still not known. As per research, the amyloid proteins build up in the brain, causing masses called plaques. This disrupts the functioning of the brain cells, leading to their death.
Also, the cause of Alzheimer’s disease may be a combination of lifestyle, genetic, and environmental factors. These include:
-
Age
-
Family history and genetics
-
Head trauma
-
Brain changes
-
Bad lifestyle choices and heart health
-
Down syndrome
-
Sex
Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease
There is no proper cure for Alzheimer’s disease; only the symptoms can be managed using medications and other therapies, improving their quality of life. Starting this treatment at an early stage can result in better functioning and treatment outcomes. It's crucial to understand that this disease affects every individual differently, so get personalised treatment from an expert.
The treatment options include:
-
Medications: To treat and improve symptoms, medications are prescribed. They may also be given to manage behavioural symptoms. These include:
-
NMDA Antagonists: These include Memantine used for moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease, which keeps the brain cells healthier.
-
Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Donepezil, Galantamine, and Rivastigmine drugs are used to block the action of acetylcholinesterase, responsible for destroying acetylcholine, which is a neurotransmitter involved in memory. Thus, these drugs improve memory and reduce other symptoms.
-
-
Lifestyle Changes: Alzheimer’s can be managed in a better way by making lifestyle changes such as eating a diet rich in fruits, whole grains, and vegetables and exercising regularly, which improves overall brain health. Additionally, engaging individuals in activities such as reading, puzzles, and staying socially active can improve cognitive and emotional well-being.
-
Support and Care: Create a safe and supportive environment for the people suffering from this life-changing disease. Getting emotional and physical support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals improves their quality of life. Strengthen their daily routines and make their lives simpler by cutting down on tasks that require memory. Get professional assistance for daily tasks, if needed.
Many clinical trials and research are ongoing, with new treatments like Monoclonal Antibodies and Anti-amyloid Therapies showing promising potential in slowing the progression of the disease.
Conclusion
Alzheimer’s disease is a challenging yet emotionally taxing condition, both for those diagnosed and for their families. While there is no cure, early detection and proper management are essential for living a normal, quality life. Ongoing research offers hope that future treatments will further improve outcomes and may one day lead to a cure. If you or a loved one is experiencing memory loss or other symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical advice early from a professional at Manipal Hospitals, Kolkata, for proper diagnosis and treatment.
FAQ's
Although the risk of developing Alzheimer’s is higher in people with a family history, it can also affect people who do not have a history of this disease.
There is no proper evidence regarding the prevention of this disease. However, following a healthy lifestyle can lower the risk of developing this disease by boosting brain health. Other strategies that can help decrease its risk include staying socially, mentally, and physically active.
Yes, females have a greater risk of developing dementia and Alzheimer’s. The reason is that women live longer than men, and it's an old-age disorder.
Stress is not directly linked to dementia, but it has a role in the development or progression of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
There is generally no proper cure for dementia, as it is caused by different diseases, so a single cure is not sufficient. Research is ongoing to find a cure for dementia diseases such as Alzheimer's.
You can schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, Kolkata, by contacting us or visiting our website.
Visit: https://www.manipalhospitals.com/kolkata/
Contact no: 1800 102 5555






















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read










.png)








