Angioplasty is a revolutionary treatment in the field of cardiology that offers effective and less invasive solutions for heart ailments. The procedure saves lives and reduces heart muscle damage in an emergency setting. In this blog, we will uncover what angioplasty is, why angioplasty is done, its procedure, and much more.
Synopsis
What is Angioplasty?
Angioplasty surgery is a minimally invasive medical procedure, aims to widen a narrow coronary artery by implanting a stent into the heart. The procedure keeps the artery open and restores blood flow. Around 66% of Angioplasty procedures are performed in critical scenarios, addressing life-threatening events such as heart attack, unstable angina, worsening chest pain, or chest pain while resting. The main reason why Angioplasty is done is to alleviate chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart.
By addressing arterial blockages, Angioplasty is vital to improving the quality of life and reducing mortality in millions of people. Once stented, it restores the blood flow to the heart muscle in individuals suffering from worsening angina within 15 to 20 minutes and eases pain. This prevents further damage to the heart muscles and promotes recovery. Therefore, the patients may be able to exercise longer than before.
For non-emergency cardiac conditions, a stress test is performed to identify blockages in the heart's arteries. An Elective Angioplasty is planned and carried out when deemed beneficial to prevent heart attacks in patients with symptoms. If the patient has no symptoms, Angioplasty is unnecessary, but medical therapy is considered safe and affordable.
Types of Angioplasty
Angioplasty procedures are of two main types:
-
Balloon Angioplasty: The procedure involves using pressure from an inflating balloon to clear plaque that blocks the artery. It is performed if the doctors are unable to place the stent in the required location.
-
Stent placement: A stent is placed in the artery where plaque is present. It helps prevent the artery from narrowing after an Angioplasty procedure. If the stent contains a coating of medication, it is called a drug-eluting stent, which is less likely to allow plaque recurrence.
Angioplasty Procedure
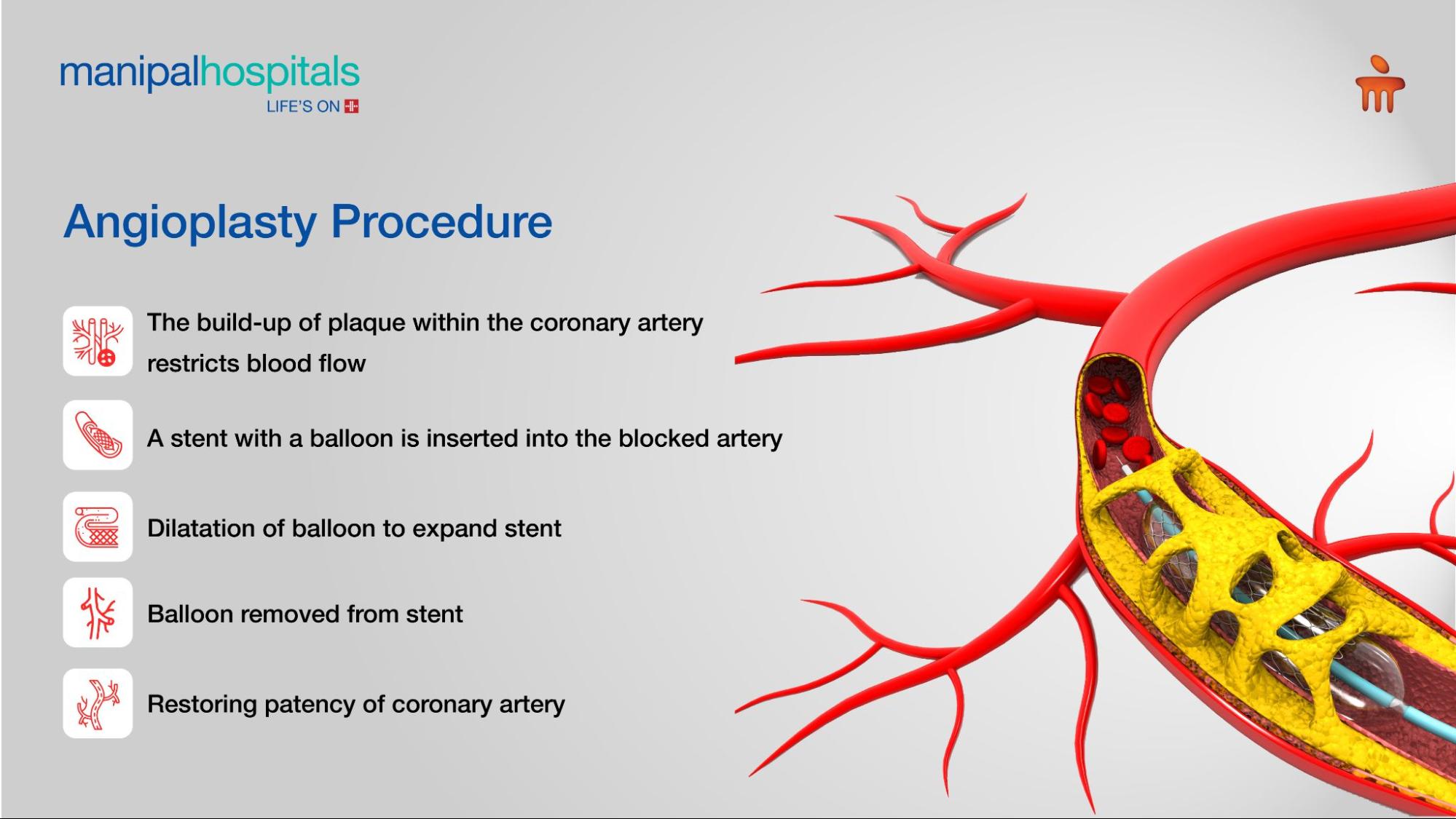
The Angioplasty procedure typically involves a balloon catheter and a stent to address artery blockages. During the procedure, the doctor inserts a catheter into the vessel, typically in the wrist or groin. The cardiologist navigates the vessel with the help of X-rays until the catheter reaches the blocked coronary arteries. A wire and a balloon are introduced. When inflated, the balloon pushes the obstructing plaque to the side, restoring blood flow to the heart muscle.
While complications are rare, some patients develop bleeding at the catheter insertion site. They may require a blood transfusion to control the bleeding. Older patients and those with heart disease, severe heart blocks, or chronic kidney disease have a higher risk of developing complications.
Medical Treatment Options
While Angioplasty is an effective intervention for many people with blocked arteries, alternative treatments may be beneficial based on the patient’s circumstances. For example, for patients diagnosed with narrowed arteries in a stress test but no active symptoms, Angioplasty may not be an effective solution to reduce the risk of a heart attack. Additionally, for patients diagnosed with mild ischaemia during stress tests and exhibiting mild chest pain during exercise, medications may be a better option.
Therefore, doctors prescribe beta-blockers as an alternative treatment to lower a patient's heart rate and nitroglycerin levels and temporarily widen the blood vessels. The medications provide relief and improve mobility, facilitating the patient’s ability to cover longer distances.
Conclusion
Understanding what Angioplasty is and why it is done will help you in making the right choice. Angioplasty is a standard procedure used by doctors to clear atherosclerosis and restore blood flow to the heart. The Angioplasty surgery is safe for treating acute heart problems caused by blocks within the arteries. If you or your loved one is struggling with clogged arteries, Manipal Hospitals, Goa, supports your journey towards better heart health. As a renowned institution with highly skilled cardiologists, we offer comprehensive cardiac care services. Book an appointment with a cardiology expert now.
FAQ's
Angioplasty is performed to open blocked or narrowed coronary arteries and restore blood flow. It helps treat heart attacks and angina.
Patients are monitored in the hospital after the procedure. They will be prescribed medications to help prevent blood clots after the procedure. Patients are advised to refrain from strenuous physical activities for at least a week. You may expect some bruising, bleeding, or discomfort where the catheter was inserted. The complications typically resolve within a few weeks.
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure and is low risk compared to traditional procedures. The recovery time is faster after Angioplasty.
Major complications after Angioplasty are rare. A patient may develop heavy bleeding at the catheter insertion site and may require further medical attention. There is also a minimal risk of blood clots and recurring blockages.
Sometimes, the catheter used in Angioplasty cannot be successfully passed through the artery because of a significant blockage within the artery. Therefore, the inflation of the balloon to push the plaque against the artery wall becomes difficult.
To schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, contact our Cardiology Department or visit our website.





















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read





12.png)
.png)