Teething is the natural process by which an infant’s first teeth emerge through the gums. The first primary tooth (also known as a deciduous or milk tooth) to erupt is the mandibular central incisor, which typically emerges any time after 6.5 months of age, with the Indian average being 10.24 months. During teething an infant experiences significant discomfort. Parental knowledge on how to identify the signs of teething and a few practical tips to manage the symptoms can significantly ease the baby’s distress. An expert paediatrician in Doddaballapur, Bangalore, shares some essential insights into teething, including common signs and symptoms during this developmental stage.
Synopsis
What is Teething?
Teething is a natural process in which your baby's first teeth emerge through the gums, often causing discomfort and sensitivity.
When Does Teething Start?
Most babies begin teething around six months of age. However, the first signs of teething can appear as early as four months, and the first tooth typically emerges between six and ten months, though delays up to twelve to eighteen months can occur.

Common Signs and Symptoms of Teething
When babies undergo teething, their discomfort produces various behavioural modifications. The most typical signs and symptoms which indicate teething in babies include:
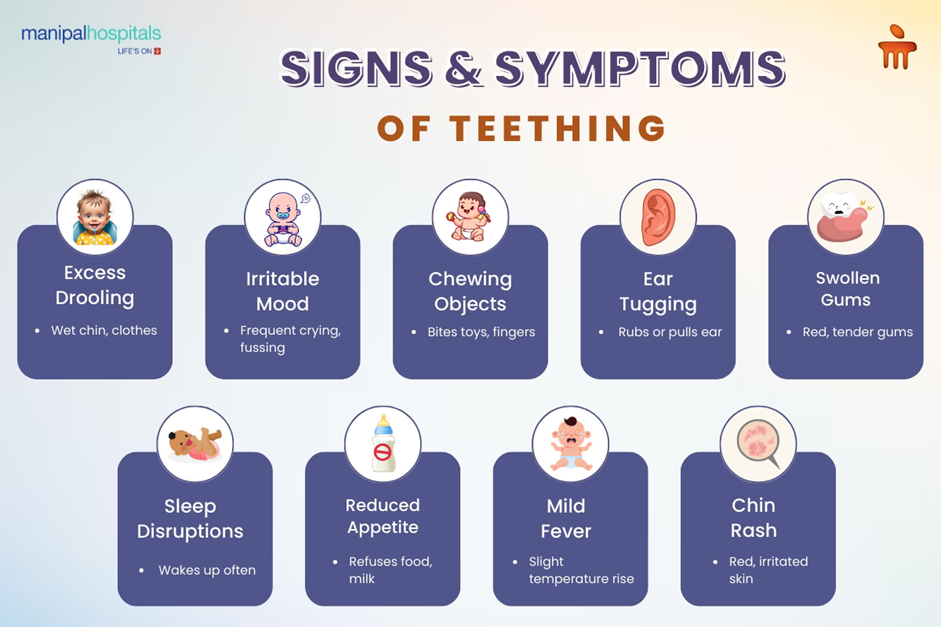
- Drooling: Saliva production increases as a typical symptom when teeth start to emerge.
-
Irritability and Fussiness: The discomfort in their gums usually causes babies to become irritable.
-
Chewing: Babies exercise their tendency to gnaw by using their fingers and toys together with other items.
-
Ear Rubbing: Some babies rub their ears because teething pain can radiate. Infants tend to touch their ears since ear pain from teething often ascends.
-
Swollen or Tender Gums: Teeth that rise through the gums create redness or puffiness around their visible areas.
-
Difficulty Sleeping: Discomfort and pain tend to disrupt the standard sleeping patterns of children.
-
Mild Temperature: The body temperature may rise slightly during teething but does not cause a fever.
-
Rash Around the Mouth: Excess saliva can cause skin irritation on the chin and cheeks.
What to Do to Soothe Teething Pain?
Teething pain can make your baby uncomfortable and fussy. Simple remedies can help soothe the discomfort and make the process easier.
Below are ways to relieve teething pain:
-
Offer Safe Objects to Chew On: Provide cool teething rings or rubber toys to ease gum pressure. These can be a simple yet effective solution to manage teething troubles.
-
Rub the Gums: Gently massage your baby’s gums with a clean, damp washcloth or finger.
-
Use Cold Items: Chilled (not frozen) spoons or teethers can help numb gum pain.
-
Maintain Oral Hygiene: Wipe away excess drool to prevent skin irritation and rashes.
-
Distract with Play: Engaging activities can help take your baby’s mind off discomfort, especially during persistent teething troubles.
-
Avoid Teething Gels or Creams: These may contain harmful chemicals and are not recommended.
-
Consult a Doctor: If symptoms are not usual or unusual, seek medical advice.
When to See a Doctor for Teething?
Teething is a natural process, but sometimes symptoms may indicate other health issues. Knowing when to seek medical advice is essential.
Below are signs you should consult an experienced paediatrician in Bangalore:
-
High Fever: If your baby’s temperature exceeds 100.4°F (38°C), it may not be due to teething.
-
Severe Irritability: If your baby cries excessively and cannot be comforted.
-
Refusal to Eat or Drink: If teething pain prevents your baby from feeding properly.
-
Diarrhoea or Vomiting: These are not typical teething symptoms and may indicate an infection.
-
Bleeding or Pus in Gums: Signs of infection or other dental issues need medical attention.
-
Rashes or Allergic Reactions: If drool causes severe skin irritation or swelling.
-
Symptoms Last Too Long: Consult an expert paediatrician if teething discomfort persists beyond a few days.
Conclusion
Teething is a normal process, but some symptoms may need medical attention. High fever, severe irritability, refusal to eat, diarrhoea, or gum infections are not typical teething signs. Consult a paediatrician to rule out diseases or other health concerns if symptoms persist. Early medical advice from an expert paediatrician ensures your baby’s comfort and well-being. Continuously monitor changes in behaviour and seek help when needed. For expert care, consult Manipal Hospital's paediatric care in Doddbalaapur, Banagalore.
FAQ's
No, teething does not directly cause diarrhoea. However, excessive drooling may lead to loose stools. Consult a doctor if diarrhoea persists.
No, some babies experience little to no discomfort during teething, while others may experience irritability and swollen gums.
Yes, teething can cause discomfort, making it harder for babies to fall or stay asleep. Providing teething relief can help.
Mild congestion may occur due to increased saliva, but a persistent runny nose or cough may indicate an illness.
Teething discomfort can last a few days per tooth. Once the tooth breaks through, the pain usually decreases.





















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read