Did you know that women are 2-3 times more likely to experience migraines, largely due to hormonal fluctuations? According to the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2021 data, India reported the highest number of migraine cases in South Asia, carrying the largest share of the regional burden for this disabling condition.
Synopsis
Understanding Migraine: More Than Just a Headache
Migraines are not typical headaches – they are a neurological condition usually believed to occur due to a combination of environmental, genetic, and neurological factors. It is usually marked by intense, throbbing pain or a pulsating feeling, typically affecting one side of the head. Migraines can worsen with strong smells, noise, bright light, or movement, and frequent episodes can severely impact social life and mental well-being.
Symptoms of Migraine
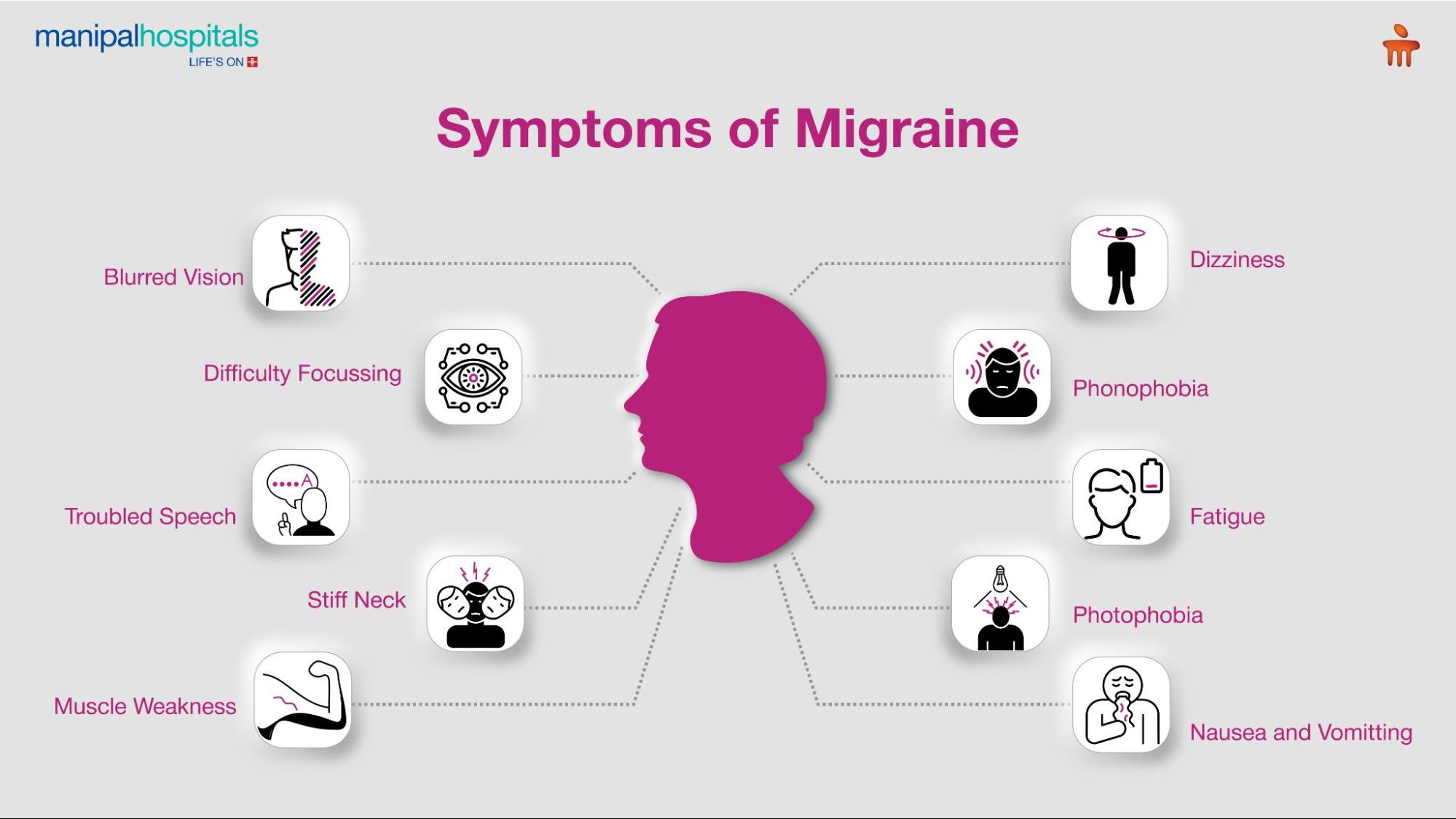
Symptoms are distinct based on the stages of migraines, which include:
-
Prodrome (up to 24 hours before attack): Subtle signs like mood swings, poor concentration, and sleep disturbances.
-
Aura (5 to 60 minutes before or during the migraine): Symptoms such as ringing in the ears, visual disturbances, or temporary muscle weakness.
-
Attack Phase (Lasts 4 to 72 hours): Intense headache, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, facial numbness or weakness, and sensitivity to light, sound, or smell.
-
Postdrome (After the headache subsides): Lingering effects like fatigue, stiff neck, and difficulty focusing.
What Are the Types of Migraine Headaches?
There are several types of migraine headaches. These include:
-
Migraine with aura: Involves brief, reversible episodes of symptoms like visual, sensory, or speech disturbance, followed by headache and other symptoms of migraine.
-
Migraine without aura: Recurring headache lasting 4–72 hours with nausea, light, and sound sensitivity.
-
Chronic migraine: Occurs 15+ days/month for over 3 months.
-
Menstrual migraine: Linked to the menstrual cycle.
Other types of migraine headaches include abdominal migraine, hemiplegic migraine, ocular migraine, status migraine, etc.
How Neurologists Diagnose Complex Migraine?
Diagnosis for complex migraines usually starts with medical history, followed by diving deep into symptoms that are exhibited; their duration and intensity; and the location of the headache.
Based on the initial assessment, neurologists may order blood tests and imaging tests like a CTScan or an MRI brain. In some cases, an electroencephalogram (EEG) is performed to see if you are diagnosed with other conditions.
Migraine Treatments – Newer and Current Therapies
Migraine treatment aims to ease symptoms and prevent future attacks. Medications are of two types:
Pain-relieving medications – Also called abortive medicines, it is taken at the onset of symptoms. These include:
-
OTC drugs like aspirin and ibuprofen offer quick relief but must be used cautiously to avoid side effects.
-
Triptans (e.g., sumatriptan) are standard treatments that boost serotonin.
-
CGRP antagonists (e.g., rimegepant) are newer drugs for short- or long-term use.
-
Ergot derivatives (e.g., ergotamine) work best in the early stages.
-
Botulinum toxin A is used in chronic migraine (15+ days/month).
-
Anti-nausea drugs (e.g., metoclopramide) relieve migraine-related nausea.
Preventive medications — The drugs aim to reduce the frequency and severity of the migraines that affect you. These include:
-
Antiseizure drugs (e.g., Topiramate) are for those with less frequent migraine attacksbut have side effects and are not for pregnant women.
-
Beta blockers and calcium channel blockers (e.g., propranolol, verapamil) are used especially for migraine with aura.
-
Antidepressants help balance brain chemicals involved in migraine.
The latest or newest migraine treatments, alternatives to pharmacological ones that are used to treat complex migraines, include:
-
Single Pulse Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (STMS): A portable device placed on the back of the head that delivers magnetic pulses to disrupt migraine-related brain signals.
-
External Trigeminal Nerve Stimulator (e-TNS): Worn on the forehead, it sends electrical pulses to the supraorbital nerve (part of the trigeminal nerve), helping prevent migraines.
-
Non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation (nVNS): Delivers mild electrical pulses to the vagus nerve to ease migraine pain, especially in episodic cases.
Several newer approaches also include devices such as remote electrical neuromodulators, combined occipital and trigeminal neurostimulation, and cognitive behavioural therapy. Although not well-studied, the role of surgery is also under research in treating migraines that cannot be treated with conventional methods.
Home Remedies for Migraines
Some home remedies for migraine you can follow to ease its symptoms include:
-
Placing an ice pack or a cool/warm compress on your forehead or behind your neck
-
Drinking plenty of water
-
Adequate rest in a dark, quiet room
-
Massaging your scalp
-
Keeping yourself calm
Conclusion
Complex migraine may require more than just a painkiller and rest, and many studies are being done abroad with precision to understand migraine on a deeper level and to discover how accurately migraine attacks can be predicted.
At Manipal Hospitals, Broadway, we understand that every migraine journey is unique. If you or your loved ones are suffering from migraine, are looking for treatments, or exploring options for your diagnosis, our neurologist will help you offer a personalised path to relief.
FAQ's
Causes of migraines in females are usually linked to fluctuating oestrogen levels, particularly due to menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause. Other causes or triggers include abnormal sleep cycle and stress. Those with a family history also have the risk of developing migraines.
Migraines are not usually life-threatening. However, depending on the type, severity, and frequency, migraines can significantly impact your daily life and well-being. In some cases, chronic migraines can increase the risk of conditions like a heart attack and stroke.
Consult a neurologist if your migraines are getting worse or lasting longer than usual. If you persist for more than a week, or if you aren’t able to control the condition, immediate care is recommended. For women, it is important to have a doctor visit if they frequently experience migraines before or during periods.
Make good adjustments to your lifestyle, like a proper sleep cycle, exercise, and a good diet. Moreover, identify triggers and avoid them. It is also important to manage your stress. Limit caffeine as much as you can, and quit smoking and drinking. Consider taking vitamin and magnesium supplements. If you are on medications, stick to them and follow up with your doctor.
You can schedule an appointment with our neurologists at Manipal Hospitals, Broadway, by contacting us or visiting our website.
Visit: https://www.manipalhospitals.com/broadway/specialities/neurology/
Contact no: 033 6907 0001






















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read