Arthritis isn’t just a condition affecting the elderly – it is a common yet often misunderstood condition that affects people of all ages. Globally, over 350 million people have arthritis. With more than 100 known types, osteoarthritis (OA) affects 22% of adults over 40, while 14 million people globally live with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), according to the World Health Organisation (WHO)1,2. In India, the RA burden has risen significantly in prevalence, incidence, and disability (DALYs) from 1990 to 2021, with further increases projected through 2026.
Synopsis
Understanding Arthritis – Causes, Types, and Arthritis Symptoms
Arthritis is a general word for inflammation of the joints. A swollen joint, if not addressed promptly, can cause harm. There are several forms of arthritis, and the causes and treatments vary depending on the type.
For example, OA results from wear and tear over time. On the other hand, conditions like RA, scleroderma, etc., occur when the immune system attacks its body tissues by mistake. Gout happens due to crystal accumulation in the joint. Genetics link several types of arthritis, with the HLA-B27 genetic marker associated with a higher risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis.
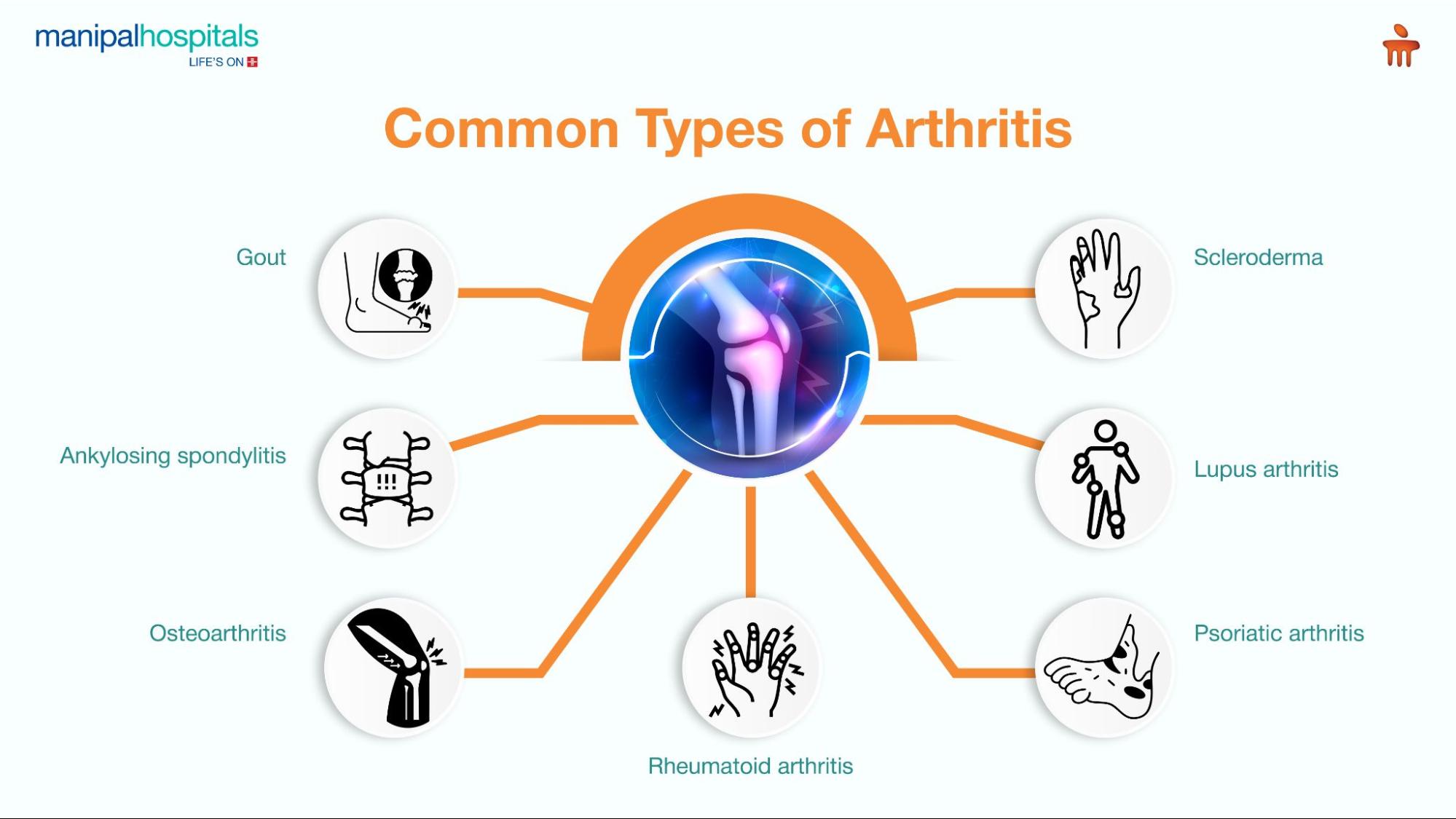
Types of Arthritis
-
Gout – A kind of inflammatory arthritis characterised by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. Gout often affects the big toe, although it can occur in other joints like ankles, knees, wrists, and fingers.
-
Ankylosing spondylitis – Also known as axial spondyloarthritis, this autoimmune disorder primarily affects the spinal joints and sometimes the base of the spine.
-
Osteoarthritis - A common type of arthritis and a degenerative joint disease that causes the breakdown of cartilage, resulting in stiffness, pain, and reduced joint function.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis – Another prevalent kind of arthritis is a chronic autoimmune illness that mostly affects joints and causes swelling, discomfort, and irritation.
-
Scleroderma – A type of autoimmune arthritis characterised by hardening and tightening of skin and other body tissues due to collagen overproduction.
-
Lupus arthritis - An autoimmune illness that affects the joints, kidneys, blood cells, heart, lungs, and other body components. It is also called systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
-
Psoriatic arthritis – A type of chronic, progressive inflammatory condition affecting joints and, in some cases, other body parts. It is commonly connected with psoriasis, a skin ailment that generates red, scaly areas.
There are other types of arthritis, such as juvenile idiopathic arthritis, reactive arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, and more.
Symptoms of Arthritis
Common arthritic symptoms vary by kind but often include.
-
Joint pain or stiffness
-
Swelling of joints
-
Sensitivity to touch or tenderness
-
Heart sensation near the joint
Other symptoms that occur along with include weight loss, fever, difficulty breathing, and rashes.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Arthritis
Diagnosing arthritis typically begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination. Doctors assess arthritis symptoms such as joint pain, stiffness, swelling, etc. If there is any suspicion, the doctor confirms it by recommending additional tests.
-
Blood tests: Parameters like erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), CRP (C-reactive protein), rheumatoid factor assay, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies, uric acid, etc., help assess inflammation levels, RA, or gout.
-
Imaging tests: Diagnostic imaging, like X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRIs), and ultrasounds, helps provide detailed visuals of early joint changes.
-
Screening Procedures: These include Joint aspiration, HLA tissue typing, skin and muscle biopsy.
Treatment of Arthritis
The goal of arthritis treatment is to relieve symptoms and improve the function of joints. Depending on the type and severity of the disease, treatment may vary, either single or a combination.
-
Medications: Medications vary depending on arthritis type. These include Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) [e.g., ibuprofen and naproxen sodium], Counterirritants, Steroids, and Disease-modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs).
-
Therapy: Occupational and Physical Therapy can improve mobility and strength. As part of therapy, patients may also require splints or braces to help their joints rest and protect them from injury.
-
Surgery: If conventional treatments do not achieve results, surgery is recommended. Depending on the condition, interventions may include Arthroscopy, Joint Fusion, or Replacement.
Lifestyle Tips
Most arthritis symptoms can be effectively managed with lifestyle changes.
-
Heat & cold: Applying heating pads or ice packs can help relieve pain from arthritis.
-
Weight loss: Since excess weight can put pressure on weight-bearing joints, shedding the extra calories can improve your mobility and limit future joint injury.
-
Exercise: Regular exercise can keep your joints flexible and healthy. Opting for swimming or water aerobics can significantly reduce stress on your weight-bearing joints.
-
Balanced diets: Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods such as leafy greens, fatty fish, or nuts in your everyday diet to reduce inflammation and promote joint health.
-
Assistive devices: In severe cases of arthritis pain, you can opt for canes, walkers, raised toilet seats, or other assistive devices to overcome joint pain and improve your quality of life.
Conclusion
Arthritis can occur at any age, but with early diagnosis and proper care, you can effectively manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. If you or your loved ones are experiencing joint pain, stiffness, or swelling, Visit Manipal Hospitals, Broadway, for tailored and comprehensive care.
FAQ's
The cause of arthritis can vary depending on the type you have. Osteoarthritis can develop naturally as you age, while gout develops because of high uric acid in the blood. Rheumatoid arthritis occurs as a response to an immune attack on the joint. In some cases, viral infections may also trigger arthritis.
Some of the risk factors that can raise your susceptibility to arthritis are tobacco use, family history, a low physical activity level, and the presence of health conditions such as autoimmune diseases and obesity.
Arthritis can occur at any age; however, OA begins in individuals over the age of 50, whereas RA develops between 30 and 60. Other types of arthritis, such as post-traumatic arthritis, occur after injury. Gout may develop when uric acid levels are high for several months.
Humidity and cold can trigger joint pain. Also, people tend to be inactive during the rainy and winter seasons. The stiffness caused by cold temperatures and inactivity can worsen arthritis.
You must visit a healthcare expert if you notice the following symptoms:
-
Severe pain
-
Worsening stiffness
-
If you persistently experience a flare-up of symptoms
You can schedule an appointment with our orthopaedic at Manipal Hospitals, Broadway, by contacting us or visiting our website.
Visit: https://www.manipalhospitals.com/broadway/specialities/orthopaedics/
Contact no: 033 6907 0001






















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read