
Joint pain or ‘arthralgia’ is the discomfort or pain in joints which is accompanied by swelling and stiffness. The pain can be felt in any single joint or throughout the body. There may be several reasons behind joint pain, and at times, this may indicate an underlying condition, like arthritis, bursitis, or muscle pain. The discomfort caused by the aching joints may range from a mild ache to severe, debilitating pain. If left untreated, these sore joints can cause reduced mobility, muscle weakness, or joint deformity and in severe cases, may lead to increased risk for heart attack and stroke.
Synopsis
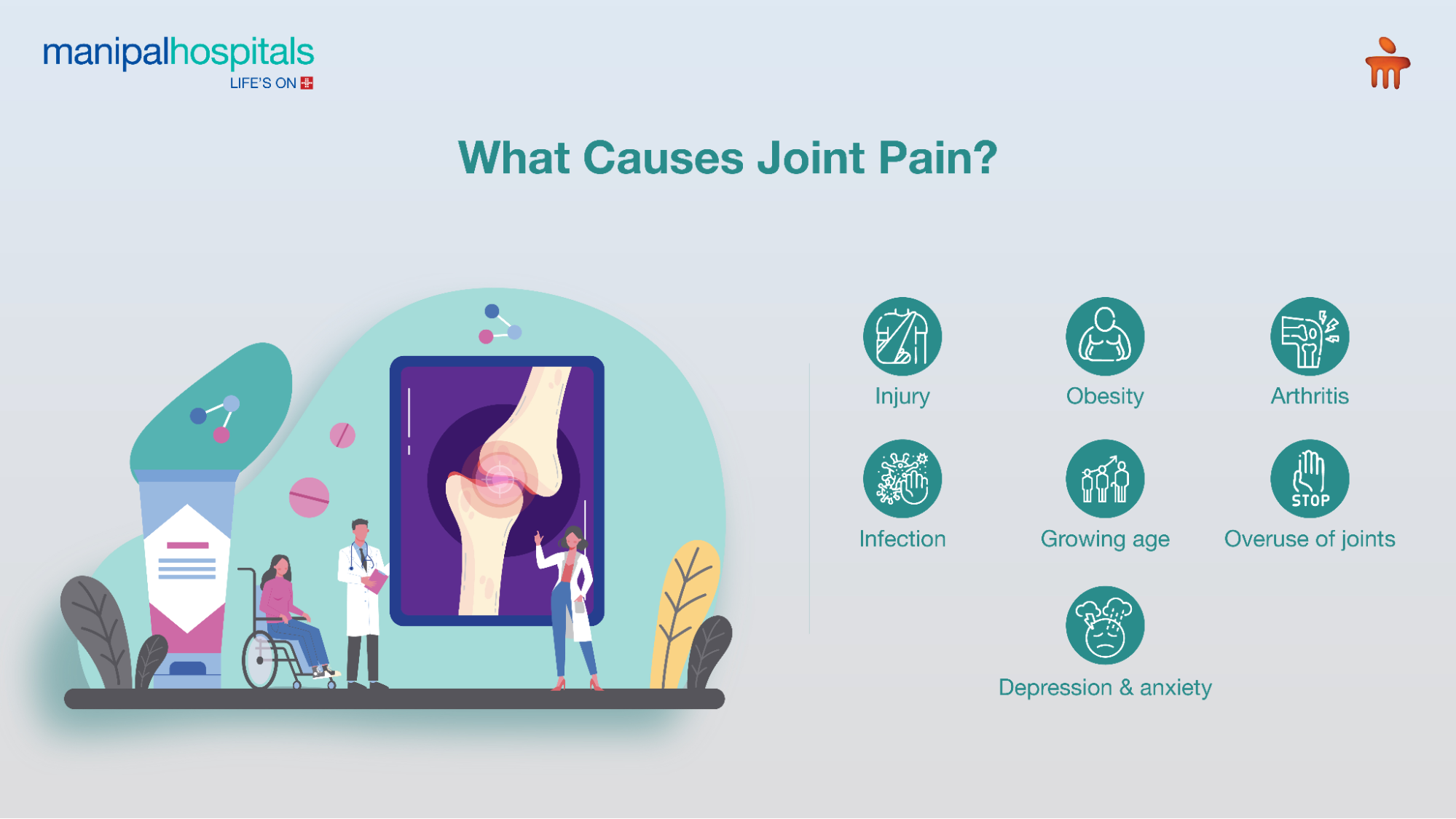
What causes joint pain all over the body?
The major joint pain causes can be listed under:
-
Age- The natural wear and tear of joints increases with age.
-
Mental state- Depression, anxiety or stress can cause certain chemical reactions in the body and brain, leading to muscle tightness and joint pain.
-
Arthritis- This includes conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout, causing inflammation, degeneration, and chronic joint pain.
-
Injury- Existing injuries to joints resulting from accidents, falls, or sports can lead to trauma and pain.
-
Obesity- Excess body weight (with a BMI over 25 or 30) can put stress on the weight-bearing joints like knees, hips, and spine.
-
Overuse- Repetitive motions and vigorous activities, without rest in between, may strain the joints and the surrounding tissues.
-
Infections- This can be caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi. ‘Infectious Arthritis’ or ‘Septic Arthritis’ is an emergency where infection has spread to any joint or the fluid surrounding it, from some other part of the body or through a wound.
-
Autoimmune diseases- Conditions like lupus and psoriatic arthritis can cause pain in the joints.
-
Other chronic conditions- Some chronic conditions, like Bursitis (inflammation in the fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joints) and Tendonitis (inflammation in the thick cords connecting muscles to bones), may also trigger joint pain.
What are the symptoms of joint pain?
Besides pain or discomfort, the typical signs of joint pain include-
-
Redness or warmth around the joint
-
Swelling in the affected area
-
Stiffness which is more pronounced in the morning, after waking up
-
Joint locking or immobility
-
Grating or clicking sound while moving the joint
-
Weakness and tenderness around the joint
-
Fatigue or tiredness due to consistent pain
Timely medical intervention can help detect the cause early and facilitate better outcomes for joint issues. Seek immediate consultation from an expert orthopaedist if you have-
-
Sudden onset of pain and swelling
-
Severe pain that lasts more than seven days
-
Pain that is accompanied by fever
-
Completely locked and immobile joint
-
Deformity in the joint
-
Unexplained weight loss
How is joint pain diagnosed?
Early diagnosis enhances the effectiveness of joint pain treatment. An orthopaedist would advise a few tests to determine the true cause. These may include:
-
Physical examination- the doctor checks for signs of swelling, tenderness, warmth, or deformity by palpating and checking the range of motion.
-
Imaging- to check for joint structure and extent of damage. These include tests like X-rays, MRI, ultrasound, and CT scans.
-
Blood tests- include screening for inflammation and biomarkers for autoimmune diseases, like ESR, CRP, and antinuclear antibody.
-
Joint fluid analysis- this is done to rule out the presence of any infection or crystals.
How is joint pain treated?
Joint pain treatment may not provide a complete cure, but it can help manage the symptoms. This involves:
-
Medication- these include over-the-counter pain relievers, NSAIDs, DMARDs, corticosteroids, and biologics.
-
Physiotherapy & exercise- physical therapies like manual mobilisation therapies, massage, heat and cold therapies, electrotherapy, ultrasound therapy, bracing, taping and functional training can help, along with strength training, flexibility exercises, and aerobics.
-
Hot/cold compression- cold compression can help reduce pain and swelling from new injuries, whereas hot compression can reduce stiffness and chronic pain by improving blood flow and relaxing muscles.
-
Weight management- managing weight is a significant approach in managing joint pain. This can be effectively achieved through healthy and balanced eating along with muscle-building exercise.
-
Injections- in severe cases, injections like corticosteroids and hyaluronic acid can provide temporary joint pain relief. Other than these, platelets and cells (bone marrow or fat) from the patient’s own body can be injected into the site to stimulate healing.
-
Surgeries- Surgical treatment of joint pain includes arthroscopy (minimally invasive procedure), arthroplasty (joint replacement), and arthrodesis (joint fusion).
-
Alternative solutions- These involve yoga, tai chi, topical creams, acupuncture, assistive devices, and meditation.
-
Home remedies- Low-impact activities like swimming, Epsom salt bath, application of essential oils like ginger or lavender oil can improve flexibility and reduce pain.
How to relieve pain in joints with lifestyle changes?
Consistent or routine practices and healthy lifestyle choices can prevent pain flare-ups as well as reduce aching joints. It is essential to:
-
Stay active and exercise through low-impact workouts
-
Eat healthy to maintain the right BMI
-
Be cautious and careful about the posture
-
Get adequate sleep (7-9 hrs.)
-
Stay hydrated
-
Avoid overuse of joints or injuring them
Conclusion
Joint pain can affect daily life and mobility, but with timely diagnosis and proper management, it is possible to relieve discomfort and prevent complications. Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, maintaining an ideal weight, staying active, and seeking medical guidance early can go a long way in ensuring long-term joint health and improved quality of life. Do not overlook any kind of joint pain that bothers you or a close one. Consult our specialists at the Orthopaedic department at Manipal Hospitals Siliguri. The amalgamation of advanced technology and superior expertise ensures the right diagnosis with prompt treatment to guarantee the best possible outcomes.
FAQ's
Joint pain can result from several reasons, including arthritis, bursitis, injuries, overuse, infections, or autoimmune diseases. Sometimes, age-related wear and tear (osteoarthritis) is the main cause.
You should seek medical advice if the pain lasts more than a few days, causes swelling, redness, warmth, or limits movement, or if you have a fever or unexplained weight loss.
Yes. Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, using proper posture, and avoiding repetitive strain on joints can help prevent joint pain and associated disorders.
Acute joint pain appears suddenly, often due to injury or infection, and lasts a short time. Chronic joint pain persists for weeks or months and is often linked to conditions like arthritis or autoimmune disorders.
With age, cartilage wears down, and joint lubrication also decreases. This leads to stiffness and pain in the area. Regular exercise and proper nutrition can slow this process.






















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read










