When you're trying to conceive or are already pregnant, your body goes through several changes. It’s a time of hope, excitement, and sometimes anxiety. Most pregnancies begin in the uterus, but in some rare cases, the fertilised egg implants itself outside the uterus. This is known as an ectopic pregnancy. Though uncommon, ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition. The condition can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated on time.
Synopsis
- What is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
- Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
- How is an Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
- Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment Options
- Recovery After an Ectopic Pregnancy
- Future Fertility After an Ectopic Pregnancy
- Can Ectopic Pregnancy Be Prevented?
- When to See a Doctor?
- Conclusion
What is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy happens when a fertilised egg attaches itself somewhere outside the womb. This occurs most often in one of the fallopian tubes. This is commonly referred to as a "tubal pregnancy." In rare cases, it can also occur in the ovary, abdomen, or cervix.
The womb is the only place designed to safely support a growing pregnancy. Other locations in the body cannot provide the right conditions for the embryo to develop properly. An ectopic pregnancy cannot continue normally and must be treated as early as possible. If not treated, an ectopic pregnancy causes harm to both the mother and the fetus.
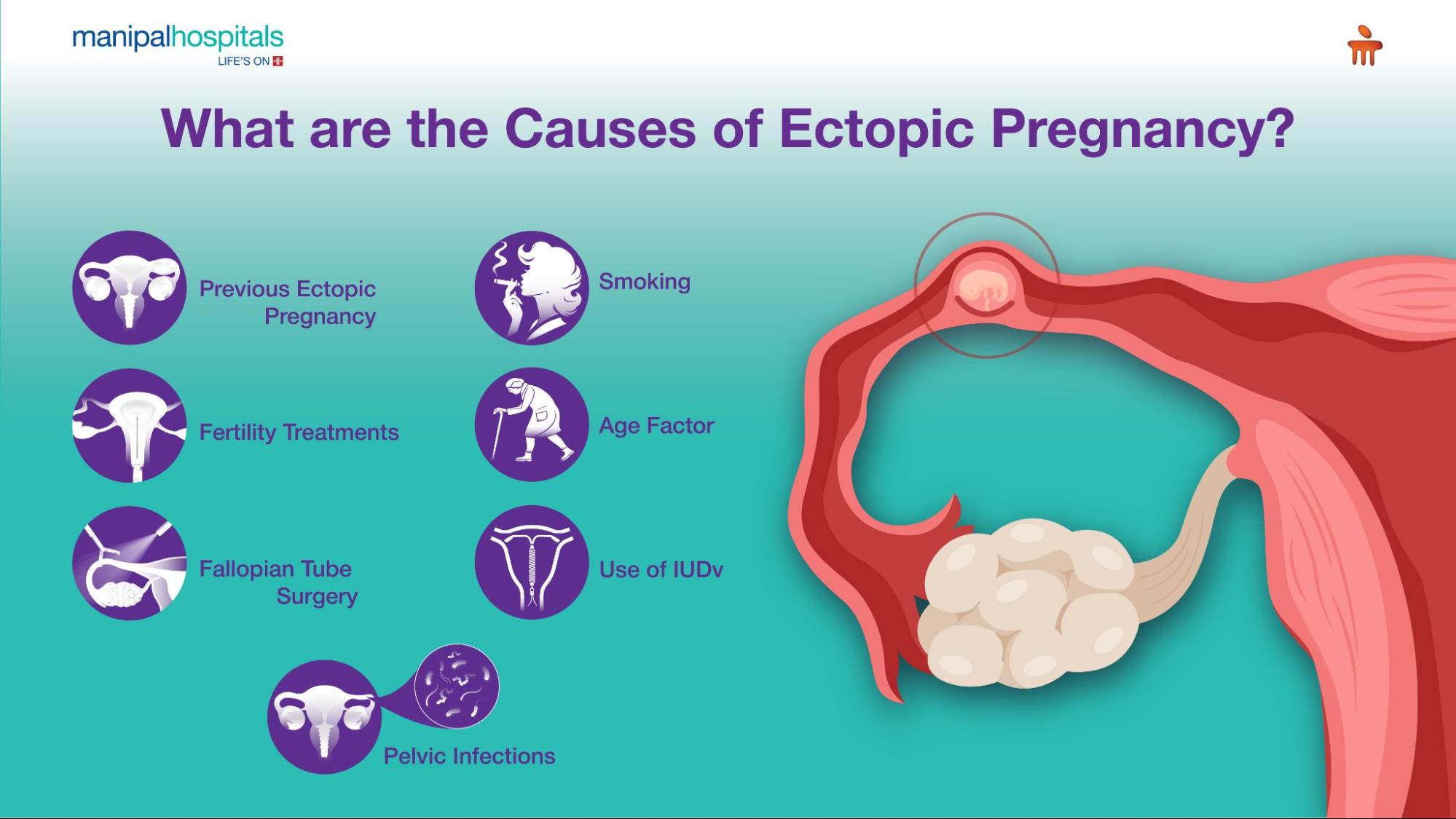
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
There’s no single cause of ectopic pregnancy, but certain factors can increase your risk. Below are the ectopic pregnancy:
-
Previous Ectopic Pregnancy: If you've experienced an ectopic pregnancy before, your chances of having another one are slightly higher.
-
Pelvic Infections: Infections like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can damage the fallopian tubes, making it difficult for the egg to travel to the uterus.
-
Fallopian Tube Surgery: Surgery to correct a blocked or damaged fallopian tube may increase your risk.
-
Fertility Treatments: Women undergoing IVF or other fertility treatments may have a slightly higher risk of ectopic pregnancy.
-
Smoking: Smoking during or before pregnancy can affect the normal function of the fallopian tubes.
-
Age: Women over 35 have a higher risk.
-
Use of IUD: Getting pregnant while using an intrauterine device (IUD) for birth control, although rare, increases the risk.
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy symptoms usually appear between the 4th to 12th weeks of pregnancy. At first, they may feel like normal pregnancy signs, which makes early detection a challenge.
-
Missed Period & Positive Test: These are the usual pregnancy signs. But in an ectopic pregnancy, light vaginal bleeding may also occur, which is a warning sign. Light or heavy bleeding that's different from your usual period.
-
Pain in the Lower Abdomen or Pelvis: This can feel sharp, stabbing, or cramp-like, often on one side. The pain might be steady or come and go.
-
Shoulder Tip Pain: This may sound odd, but internal bleeding from a ruptured tube can irritate the nerves connected to the shoulder.
-
Dizziness or Fainting: This could be a sign of internal bleeding and should never be ignored.
If you notice any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
How is an Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
Doctors use a combination of tests to confirm if a pregnancy is ectopic:
-
Blood Tests: These measure hormone levels, especially human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which rises differently in an ectopic pregnancy compared to a healthy one.
-
Pelvic Exam: A physical exam to check for pain, tenderness, or a mass in the fallopian tube.
-
Ultrasound Scan: A transvaginal ultrasound helps locate where the fertilised egg has implanted. If no pregnancy is seen in the uterus, it may indicate an ectopic pregnancy.
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment Options
Ectopic pregnancy treatment depends on how early the condition is detected, the size and location of the pregnancy, and your overall health.
1. Medication: If diagnosed early, a medicine called methotrexate can be used. It stops the pregnancy cells from growing and allows the body to absorb them naturally.
-
No surgery is needed.
-
You will need follow-up blood tests to ensure the hCG levels are dropping.
2. Surgery: If the ectopic pregnancy is large or has ruptured, immediate surgery may be needed. There are two main types:
-
Laparoscopy (Keyhole Surgery): A small incision is made to remove the ectopic tissue.
-
Laparotomy: A larger cut may be needed in emergency cases.
Depending on the damage, doctors may remove the affected fallopian tube. This may affect future fertility, but it is often necessary to protect your health.
Recovery After an Ectopic Pregnancy
Recovery can be physical and emotional. After surgery or treatment:
-
Most women return to normal physical activity within a few weeks.
-
You may feel tired or sore for some time.
-
Emotional recovery may take longer. It’s okay to grieve and seek support.
-
Counselling or support groups can help you cope with loss and fear about future pregnancies.
Future Fertility After an Ectopic Pregnancy
Many women go on to have healthy pregnancies after an ectopic pregnancy. However, your chances may depend on:
-
The condition of your remaining fallopian tube(s)
-
The cause of your ectopic pregnancy
-
Your general reproductive health
Doctors may advise waiting 2–3 months before trying to conceive again. If one fallopian tube is removed, you can still conceive naturally with the other. However, if both tubes are damaged or blocked, assisted reproductive methods such as IVF may be necessary.
Can Ectopic Pregnancy Be Prevented?
While you can't always prevent an ectopic pregnancy, understanding your risk factors and getting early check-ups can help reduce the chances:
-
Treat any pelvic infections early.
-
Quit smoking.
-
Avoid sexually transmitted infections (STIs) by practising safe sex.
-
Discuss your risk with your doctor if you’ve had surgery or a previous ectopic pregnancy.
When to See a Doctor?
Don’t wait if you experience:
-
Severe abdominal pain
-
Heavy bleeding
-
Shoulder tip pain
-
Dizziness or fainting
These may be signs of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy and need urgent care.
Conclusion
Ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency, but with early diagnosis and timely treatment, you can recover well and even go on to have healthy pregnancies in the future. Awareness is your first step. If you are pregnant or planning to be, speak openly with your doctor. Listen to your body and don’t ignore any signs that feel unusual. Your health and safety always come first. Consult with our best Obstetrician in Salt Lake, Kolkata.
FAQ's
In most cases, an ectopic pregnancy will show typical pregnancy signs like a missed period, nausea, or sore breasts. But if you also experience sharp pain in the belly, shoulder pain, light bleeding, or dizziness, it could be a warning sign. Always see a doctor if something feels wrong.
A home pregnancy test can detect pregnancy because it checks for the hormone hCG, which is still present in ectopic pregnancy. But it cannot tell you if the pregnancy is located in the wrong place. If you feel pain or notice spotting after a positive result, visit your doctor for further tests and an ultrasound.
Yes, many women have normal, full-term pregnancies after an ectopic pregnancy. It depends on how much damage occurred and whether one fallopian tube had to be removed. Your doctor may suggest early scans in your next pregnancy to confirm the baby is growing in the right place.
Having one ectopic pregnancy does raise your risk slightly. Around 10–15% of women may experience another one. Early prenatal care and monitoring are essential to catch any issues quickly.
Yes, it’s possible. Even without known risks, some women develop ectopic pregnancies due to minor inflammation, hormonal changes, or unknown fallopian tube issues. That’s why it’s important to report any unusual symptoms early, no matter your medical history.
When symptoms are mild or unclear, doctors usually do blood tests to measure hCG levels and perform a transvaginal ultrasound to find the location of the pregnancy. Multiple blood tests over time can help track how hormone levels are changing, which is useful in making an early diagnosis.
Doctors usually advise waiting 2 to 3 months after treatment before trying to get pregnant again. This allows your body time to recover. It’s always best to talk to your gynaecologist before planning your next pregnancy, to make sure it’s safe and timely.





















 7 Min Read
7 Min Read