Obesity affects around 13% of the global adult population and is caused by a combination of genetic, behavioural and environmental factors. These include a poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, limited options for healthy food, and medical conditions and medications that directly or indirectly contribute to weight gain.
Synopsis
- What is Bariatric (Metabolic) Surgery?
- Understanding the Link Between Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
- Mutual Impact
- Types of Bariatric Surgery and Their Impact on Diabetes
- Can Bariatric Surgery Help Reverse Type 2 Diabetes?
- Can Bariatric Surgery Lead to Diabetes Remission?
- Is Bariatric Surgery a Permanent Cure for Type 2 Diabetes?
- Who is Eligible for Bariatric Surgery?
- Post-Surgery: What to Expect
- Advantages of Bariatric Surgery
- Conclusion
What is Bariatric (Metabolic) Surgery?
Bariatric surgery, also referred to as weight loss surgery or metabolic surgery, is a medical procedure for weight loss in severely obese individuals when conventional methods like diet and exercise have not yielded results, or obesity-related health issues are severe. It is not just cosmetic but also aims to improve overall health and manage obesity-related complications such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnoea, and joint problems. Bariatric surgeries are of various types, including gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, duodenal switch, biliopancreatic diversion, and adjustable gastric banding.
Understanding the Link Between Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
Obesity and diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, are linked in a bi-directional manner. The correlation illustrates the importance of integrated care and a holistic approach to managing both conditions. Addressing lifestyle factors, such as diet and physical activity, is often crucial in preventing and managing both obesity and diabetes. Here’s how both are correlated:
Body mass index (BMI) is an important tool used in obesity classification and an indicator of an individual’s likeliness of developing insulin resistance. The overweight category ranges from a BMI of 25 to 29.9. Moderate obesity, or Obesity Class I, ranges from 30 to 34.9. Severe obesity (Class II) ranges from 35 to 39.9, and a BMI of 40 or above is classified as morbid or extreme obesity (Class III).
Mutual Impact
Obesity and diabetes have shared complications of cardiovascular disease, making them even riskier for health in tandem and sometimes complicating control of one when you are addressing the other, such as when some diabetes medications can contribute to weight gain and thus complicate obesity management.
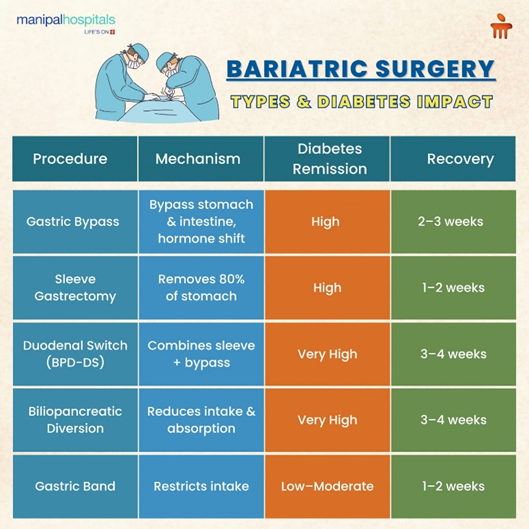
Types of Bariatric Surgery and Their Impact on Diabetes
As stated above, there are five main types of bariatric surgeries that have a proven and significant impact on glycemic control. These include:
-
Gastric Bypass: The Roux-en-Y gastric bypass procedure is performed by creating a stomach pouch and connecting it to a part of the small intestine. Since food now bypasses a large portion of the stomach and the initial part of the small intestine, it reduces food intake and calorie absorption, contributing to significant weight loss. Besides this, the procedure also improves insulin sensitivity and secretion by altering the production of various gut hormones like GLP-1.
-
Sleeve Gastrectomy: The gastric sleeve procedure is where much of the stomach is removed, leaving only a small tube-like sleeve, decreasing its capacity to hold food and reducing the production of the hunger hormone ghrelin, which decreases total food intake considerably.
-
Biliopancreatic Diversion (BPD): This involves removing portions of the stomach, as well as bypassing a significant portion of the small intestine, making the meals take up less volume and reducing nutrient absorption. It also increases GLP-1 production and insulin sensitivity. However, due to the nutritional risks involved, BPD is rarely performed on its own.
-
Duodenal Switch: The Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD-DS) is a two-step surgery involving gastric restriction and intestinal bypass that combines sleeve gastrectomy and modified BPD. The procedure also significantly improves glycaemic control, often leading to rapid remission of type 2 diabetes.
Can Bariatric Surgery Help Reverse Type 2 Diabetes?
Bariatric surgery is a powerful method to reverse type 2 diabetes. It happens through various mechanisms:
-
Rapid Weight Loss: Significant and sustainable weight loss can enhance insulin sensitivity and lower insulin resistance, with normal blood sugar levels resulting.
-
Hormonal Effects: The alteration of gut hormones also increases production and secretion of insulin - this occurs , for example, in gastric bypass surgery and results in better blood sugar control.
-
Reduced Inflammation: Weight loss surgery reduces chronic inflammation, which enhances insulin sensitivity.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Surgery and weight loss encourage healthy eating habits and increased physical activity, which aids in improved blood sugar control.
Can Bariatric Surgery Lead to Diabetes Remission?
Diabetes remission—most commonly seen in type 2 diabetes—refers to achieving normal blood sugar levels, defined as an HbA1c below 6.5%, without the use of any glucose-lowering medications for at least three months. Evidence presented by a number of studies and clinical trials has shown that successful remission through bariatric surgery is higher among younger individuals and those with early-stage type 2 diabetes. To achieve long-term type 2 diabetes reversal, individuals need to maintain glycaemic control and insulin sensitivity through a balanced diet, regular exercise and consistent lifestyle improvements.

Is Bariatric Surgery a Permanent Cure for Type 2 Diabetes?
Although many people can experience significant improvement and even remission of type 2 diabetes after having bariatric surgery, it is essential to know that weight loss surgery is not a permanent cure. Some may also experience a return of elevated blood sugar levels or diabetes symptoms at some point in the future.
Who is Eligible for Bariatric Surgery?
Many people ask, “How do you qualify for bariatric surgery?” The answer lies in meeting the following criteria:
-
BMI of 40 or BMI of 35 with obesity-related health issues (based on standard obesity classification)
-
Failed prior attempts at non-surgical weight loss methods
-
Commitment to lifelong lifestyle changes.
Post-Surgery: What to Expect
Post-operative care and monitoring after bariatric surgery are essential for healing and to minimise complications, including nausea, vomiting, infections, and blood clots, just to name a few. For the first 24 hours following the surgery, patients will not be permitted to orally consume anything, while for the next 2-3 weeks, only liquids will be permitted, with soft or pureed solids expected during the fourth or fifth week of recovery. Patients can begin to resume a regular diet 4-6 weeks after surgery. It is also critical to manage blood glucose levels during this time to prevent diabetes-related complications.
Advantages of Bariatric Surgery
The following are the key advantages that weight loss surgery offers, besides significant loss of weight:
-
Resolution of Health Issues: Often leads to the remission or improvement of obesity-related health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
-
Enhanced Quality of Life: Common benefits include improved mobility, self-esteem, and reduced emotional stress.
-
Long-Term Results: Lasting weight loss is achieved compared to many other weight loss methods.
-
Reduced Medication Dependence: Decreases the need for medications, lowering healthcare costs.
-
Positive Impact on Mental Health: Improved body image, self-confidence, and reduced psychological stress.
-
Reduction in Cardiovascular Risk: Lowers heart disease and stroke risk due to weight loss.
-
Management of Sleep Apnoea: Can alleviate sleep apnoea symptoms.
-
Enhanced Fertility: Can improve fertility in individuals with obesity-related fertility issues.
Conclusion
Bariatric surgery offers a promising avenue for reversing type 2 diabetes while addressing obesity. At Manipal Hospital Millers Road, we are equipped with 4K ultra HD monitors, 4k optic systems, high-quality Trocars, and tri-stapler technology to improve surgical outcomes. With smooth coordination with a multidisciplinary team, the surgery and the post-op care aid in fast-tracking the recovery.
Visit Manipal Hospitals Millers Road for any advanced surgical needs or concerns, and consult with the best bariatric surgeon in Bangalore to determine your eligibility for bariatric surgery.
FAQ's
Bariatric surgery is generally a safe choice because they are performed often and minimally under invasive techniques. Pre-operative screening processes, and specific criteria for weight loss surgery limits risks. For more information on bariatric surgery in Bangalore, consider visiting Manipal Hospital Millers Road to seek consultation with an expert Bariatric Surgeon.
Bariatric surgery effectively reverses type 2 diabetes because of the substantial weight loss that leads to insulin sensitivity improvement, inflammatory processes reduction, and benefits of balanced healthy eating and habits.
Yes, your health insurance covers bariatric surgery, you just need to provide documentation which includes a doctor’s prescription along with medical reports (proofs) to validate your comorbidities.
Recovery after bariatric surgery can vary based on a number of factors, including the type of surgery, and individual factors. Patients are able to get 'up and walk' within two hours of the surgery and discharged no later than 48 hours after admission.
Yes - post-surgery dietary guidelines are very important in achieving successful outcomes. Early on in recovery, a liquid or soft diet is often suggested, then progressing to regular foods in steps as well as decremented supplements.





















 9 Min Read
9 Min Read








10.png)