
Not every heart attack is associated with excruciating chest pain or collapse. A silent heart attack can develop quietly and often cause mild or subtle symptoms. While most people ignore or mistake these symptoms for stress, indigestion, or fatigue, many individuals remain unaware that heart damage is occurring.
The inability to recognise the signs of a silent heart attack can result in the delay of diagnosis and treatment. This can increase the risk of serious complications, repeated cardiac events, and long-term damage to heart function. This blog aims to explore more about ‘silent heart attacks’.
Synopsis
Why are silent heart attacks are often missed?
The question many may ask here is, ‘What is a silent heart attack?’ A silent heart attack occurs due to the blood flow being blocked to a part of the heart muscle, with symptoms that are mild, unusual, or completely unnoticed. It may not cause any chest pain like a typical heart attack, but it can lead to subtle sensations like mild discomfort, fatigue, shortness of breath, or heartburn. As a result, these warning signs get easily mistaken for everyday health issues, resulting in delayed medical attention. Low awareness and a busy lifestyle also contribute to people overlooking or dismissing these vague discomforts as acidity, fatigue, stress, or ageing, resulting in delayed medical attention, making them dangerous and potentially life-threatening.
What causes a silent heart attack?
There are several reasons for a ‘silent heart attack’ that often mask the classic symptoms of a heart attack, with reduced pain perception and signs that mimic the common, non-cardiac complaints. This makes diagnosis difficult and increases the risk of complications by delaying recognition and treatment.
Diabetes-related nerve damage (neuropathy) can blunt the pain signals from the heart. This is the reason why individuals often experience vague symptoms like fatigue, breathlessness, or nausea, which are mostly ignored, instead of the classic chest pain.
High blood pressure and high cholesterol cause gradual damage and narrowing of the coronary arteries. The body usually adapts to this slow process, causing symptoms to be subtle rather than sudden and intense.
Smoking and obesity stimulate plaque buildup and reduce oxygen supply to the heart, thereby inducing subtle and insignificant signs, including mild discomfort, indigestion, or shortness of breath, rather than any sharp pain.
Chronic stress and a sedentary lifestyle can strain the heart over time. Symptoms related to these may present in the form of exhaustion or acidity, which are frequently mistaken for routine lifestyle issues.
Older age and hormonal differences (in women) also play a role. Ageing can reduce sensitivity towards pain. Besides, women are prone to experiencing atypical symptoms such as jaw pain, dizziness, or extreme fatigue instead of chest pain. These can make silent heart attacks more likely to be missed.
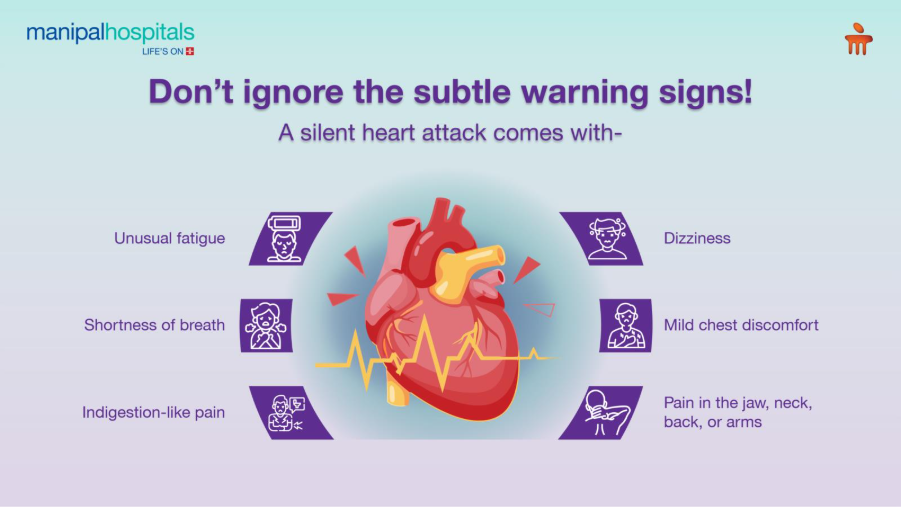
What are the 4 signs of a silent heart attack?
By now, we know that rather than a dramatic chest pain, silent heart attacks mostly present with warning signs that are often subtle and develop gradually. These symptoms lack severity and lead to a delay in medical attention. Identifying them early is crucial for timely intervention that can prevent serious heart damage or life-threatening complications. The 4 silent signs of a heart attack to look out for include-
Unusual fatigue or weakness
Unexplained tiredness persisting after adequate rest can indicate that the heart is struggling to pump enough blood. This mostly gets attributed to stress, lack of sleep, or ageing.
Shortness of breath
Breathlessness during regular activities or at rest may signal a reduced blood flow to the heart. Since this symptom appears without chest pain, it is easily mistaken for anxiety, asthma, or poor fitness.
Mild chest pressure or discomfort
Instead of a sharp chest pain, most individuals feel a dull ache, heaviness, tightness, or a feeling of indigestion. The discomfort being mild, it is often ignored or considered as acidity.
Jaw, neck, back, or arm pain
The subtle pain or discomfort may radiate to areas like the jaw, neck, upper back, or left arm, mostly in women and older adults.
Other than these 4 signs, some may feel dizziness or develop cold sweats.
Who is at a higher risk of a silent heart attack?
Elderly individuals, women, people who have diabetes, and those with a family history of heart disease are in the high-risk group and may experience mild or unnoticed symptoms. Regular health check-ups and cardiac screenings are crucial for early detection, timely treatment, and prevention of serious heart complications.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Silent heart attacks, in most cases, are diagnosed incidentally through some tests. These tests include ECGs that reveal any past heart damage, blood tests that can detect cardiac enzymes, echocardiograms that can assess heart muscle function, or stress tests that show a reduced blood flow.
Treatment is targeted at preventing future cardiac events. Medicines include antiplatelets, statins, and blood pressure drugs. Besides, emphasis is given on lifestyle changes, a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation. In addition to this, cardiac rehabilitation programs can also aid in recovery, enhance fitness, and reduce the risk of recurrent heart problems.
On-going heart damage may need urgent coronary intervention to establish blood supply to cardiac muscles as earlier as possible thus reducing the morbidity.
Conclusion
Silent heart attacks highlight the importance of listening to your body and not dismissing persistent, unexplained symptoms. Awareness of subtle warning signs, understanding personal risk factors, and seeking timely medical evaluation can make a life-saving difference. Regular health check-ups, healthy lifestyle choices, and early intervention are key to protecting heart health and preventing long-term damage from this often overlooked but serious cardiac event. Visit or consult with our Expert cardiologist in Kolkata.
FAQ's
Yes, silent heart attacks can be dangerous. Even without obvious symptoms, they may cause permanent damage to the heart muscle and significantly increase the risk of future, more severe heart attacks, heart failure, or life-threatening complications.
Silent heart attacks are commonly identified during routine ECGs, blood tests, echocardiograms, or stress tests. These investigations can reveal signs of previous or ongoing heart damage, even when no typical heart attack symptoms were noticed earlier.
While silent heart attacks cannot always be prevented, their risk can be significantly reduced through regular health check-ups, a heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, effective stress management, and avoiding smoking or tobacco use.
Consult a doctor promptly if you experience persistent fatigue, unexplained breathlessness, or unusual discomfort. Seeking timely medical advice is especially important for individuals at high risk, as early evaluation can help prevent serious heart-related complications.
Yes, silent heart attacks can lead to serious long-term complications. They may weaken the heart muscle, increase the risk of heart failure and abnormal heart rhythms, and raise the likelihood of future, more severe heart attacks.






















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read









.png)









