
In India, outbreaks of Nipah virus have shown a worrying pattern, the disease often appears small at first, but can turn fatal very fast. In past Indian outbreaks, the fatality rate has ranged from 40% to over 70%, making Nipah one of the deadliest viral infections known.
What makes it more dangerous is that early Nipah virus symptoms look like common flu or viral fever. By the time severe signs appear, the virus may already have affected the brain or lungs. Understanding what is Nipah virus, how it spreads, and how it is treated can help people seek care early and save lives.
Synopsis
- What is Nipah Virus?
- Why Nipah Virus Is Considered So Dangerous
- Nipah Virus Transmission: How Does It Spread?
- Early Nipah Virus Symptoms
- Serious Nipah Virus Symptoms That Should Not Be Ignored
- How Nipah Virus Affects the Body
- Who Is More Likely to Get Infected?
- How Nipah Virus Is Diagnosed
- Nipah Virus Treatment
- Can Nipah Virus Be Prevented?
- When to Seek Medical Help
- Conclusion
What is Nipah Virus?
Nipah virus is a zoonotic virus that spreads from animals to humans. It belongs to the Henipavirus family and is mainly carried by fruit bats. This is also known as flying foxes.
Humans do not normally get infected unless:
-
They come into contact with infected animals
-
They eat contaminated by bats
-
Or they come into close contact with an infected person
Once the virus enters the human body, it can attack the brain, lungs, and nervous system, leading to severe illness.
Why Nipah Virus Is Considered So Dangerous
Nipah virus is not just another viral fever. It is classified as a high-risk pathogen because of how quickly it can damage vital organs, especially the brain and lungs. In several outbreaks, even healthy people have developed severe illness within days of their first symptoms.
Unlike many viral infections, Nipah virus can:
-
Progress very rapidly
-
Cause inflammation of the brain (encephalitis)
-
Lead to breathing failure
-
Trigger coma and death in severe cases
There is no specific antiviral cure for Nipah yet.
This makes early detection and hospital care extremely important.
Nipah Virus Transmission: How Does It Spread?
Understanding nipah virus transmission helps prevent infection.
1. From bats to humans: Fruit bats carry the virus naturally. They pass it through:
-
Saliva
-
Urine
-
Droppings
Fruits or raw palm sap contaminated by bats can infect humans.
2. From animals to humans: Animals like pigs can get infected by bats and then pass the virus to people.
3. From person to person: Close contact with an infected person can spread Nipah through:
-
Cough droplets
-
Saliva
-
Nasal secretions
-
Blood or other body fluids
This is why hospitals isolate suspected cases.
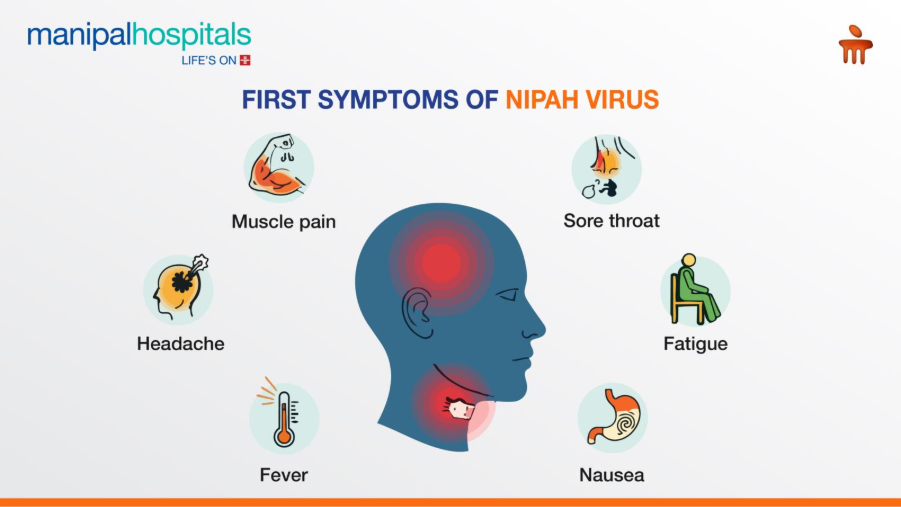
Early Nipah Virus Symptoms
The biggest danger with Nipah virus is that early symptoms look mild.
Initial symptoms (first few days)
These often appear 4–14 days after exposure:
At this stage, many people think it is a normal viral fever.
Serious Nipah Virus Symptoms That Should Not Be Ignored
Nipah virus is considered dangerous because it attacks multiple systems in the body at the same time. It can inflame the brain, disrupt breathing, and affect vital organs. Unlike routine viral infections, Nipah does not follow a slow or steady course. In some patients, the condition can turn critical within 48 to 72 hours of symptom onset.
These danger signs include:
-
Drowsiness
-
Mental confusion
-
Difficulty speaking
-
Loss of balance
-
Seizures
-
Severe headache
-
Shortness of breath
These symptoms suggest brain swelling or respiratory failure, which can be life-threatening.
How Nipah Virus Affects the Body
Nipah virus causes damage in two major systems:
1.Brain:
The virus leads to encephalitis, which means inflammation of the brain. This can cause:
-
Memory loss
-
Behaviour changes
-
Coma
-
Long-term neurological problems
2.Lungs
Some patients develop:
-
Cough
-
Breathlessness
-
Fluid in the lungs
-
Severe pneumonia
This is why oxygen and ventilator support may be required.
Who Is More Likely to Get Infected?
Nipah virus does not affect everyone in the same way. Certain people face a higher risk because of where they live, their daily exposure, or their health status. Identifying these groups helps in early monitoring and timely care. People at higher risk include:
-
Those living in outbreak areas
-
Healthcare workers
-
Family members of infected patients
-
People who eat unwashed fruits
-
People who drink raw palm sap
-
Those with weak immunity
Children and elderly people may develop more severe disease.
How Nipah Virus Is Diagnosed
Nipah virus cannot be confirmed through symptoms alone. Accurate diagnosis requires specialised laboratory testing and careful evaluation of exposure history. This helps doctors isolate cases quickly and prevent further spread. Doctors diagnose Nipah using:
-
Blood tests
-
Throat or nasal swabs
-
Urine tests
-
Brain fluid tests (in some cases)
Doctors also ask about:
-
Travel history
-
Contact with infected people
-
Exposure to animals or bats
Early testing helps control the spread.
Nipah Virus Treatment
Since Nipah virus has no targeted cure, medical care focuses on supporting the body while it fights the infection. Treatment aims to manage complications, protect vital organs, and prevent the condition from becoming life-threatening. This includes:
-
Hospital isolation
-
Oxygen therapy
-
IV fluids
-
Medicines to reduce fever
-
Medicines to control seizures
-
Breathing support if needed
Patients with severe disease are treated in the ICU.
The earlier treatment starts, the better the chances of survival.
Can Nipah Virus Be Prevented?
Although Nipah virus is serious, the risk of infection can be greatly reduced. Simple hygiene practices and safe food habits play a key role in stopping the virus from entering the body.
Key prevention methods
-
Wash fruits well before eating
-
Do not eat fallen or bitten fruits
-
Avoid raw palm sap
-
Avoid contact with bats
-
Wear masks around sick people
-
Follow hospital infection guidelines
Prevention is more effective than treatment.
When to Seek Medical Help
Medical care is needed urgently if:
-
Fever is followed by confusion or headache
-
There is sudden weakness or seizures
-
Breathing becomes difficult
-
There was recent contact with an infected person
-
Travel to an affected area happened recently
Conclusion
Nipah virus may be rare, but its impact can be severe and sudden. Early recognition of nipah virus symptoms and timely medical care can prevent serious complications. If unusual fever, confusion, or breathing trouble appears, expert neurological and infectious disease care is essential. Prompt evaluation can protect both individual health and the wider community.
FAQ's
Yes, Nipah virus can spread through close contact with infected people, especially via respiratory droplets, saliva, or other body fluids during the later stages of illness.
Nipah virus transmission occurs through contaminated fruits, contact with infected bats or animals, or direct exposure to the body fluids of an infected person.
Nipah virus treatment mainly includes hospital care, oxygen, fluids, and medicines to manage complications, as there is currently no antiviral drug that directly cures the infection.
Nipah virus symptoms usually develop within five to fourteen days after exposure, but in some cases, the illness may appear slightly later.
People with fever, confusion, breathing difficulty, or recent contact with infected individuals or outbreak areas should undergo Nipah virus testing without delay.
Nipah virus is far more dangerous than flu because it can cause brain swelling and respiratory failure, leading to severe illness or death if not treated early.






















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read

.png)




.png)








