
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin concern that causes dark patches to appear on the skin. These patches can look brown, grey or black in colour. The term ‘hyperpigmentation’ means ‘excess pigmentation’ and is made of two words – ‘hyper’ and ‘pigment’. Hyperpigmentation happens when certain factors trigger skin to produce more melanin than normal. This blog outlines key hyperpigmentation causes and provides effective treatment options and useful tips to prevent it.
Synopsis
What is Hyperpigmentation?
Melanocytes are cells which carry melanin, a pigment that provides colour to your skin, eyes and hair. It also provides protection against the effects of UV radiation. Hyperpigmentation is a common condition which happens due to excess melanin production. This creates dark patches on your skin, which can appear grey, brown or black in colour.
Hyperpigmentation can appear on the face and other parts of the body. It is harmless but is more common in people with darker complexions due to higher melanin concentration.
Different Types of Hyperpigmentation
There are mainly three main types of hyperpigmentation:
-
Melasma: This condition causes dark brown or grey patches to appear on the face, arms and neck. Sun exposure and hormonal changes are some of the main causes of melasma. Patches lighten in winter, but become more prominent in summer.
-
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: It develops as the skin heals from some kind of trauma or inflammation. Cuts, scratches, infection, insect bites, and inflammatory skin conditions like acne, eczema and psoriasis trigger skin to produce excess melanin while it heals.
-
Sunspots: They happen when skin produces excess melanin to protect skin from the effects of sun exposure. Dark spots appear on the skin, especially the face and arms. Sunspots are also called age spots, solar lentigines or liver spots.
-
Age spots: Long-term sun exposure can cause small, darkened spots on the skin, especially in older people. These are called age spots, liver spots or lentigines. Lentigines mainly appear on areas most prone to sun exposure, like the face, shoulders, arms and hands.
-
Freckles: Freckles are small, flat brown spots which appear on the skin, likely due to genetic predisposition. Sun exposure can make freckles appear darker and more prominent, whereas lack of it can make them appear much lighter.
-
Drug-related hyperpigmentation: At times, long-term use of certain medications, like non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chemotherapy drugs or tetracyclines can lead to excess melanin production, which can cause dark patches on the skin.
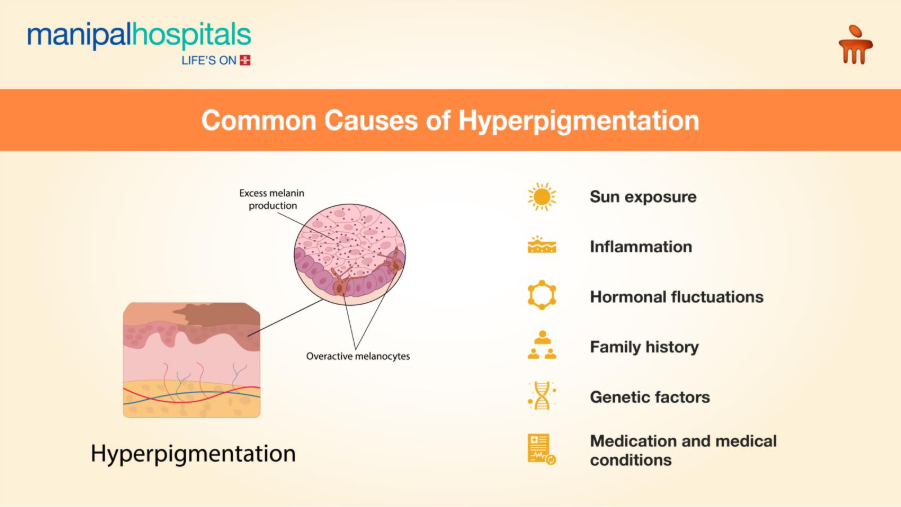
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation happens when certain factors trigger excess melanin production. Some common causes of hyperpigmentation are:
-
Inflammation: Inflammatory skin conditions, including acne, injury and eczema, are some common hyperpigmentation causes. They stimulate melanin production while healing, causing dark spots or patches to form on the skin.
-
Sun exposure: UV radiation from sunlight is one of the most common causes of hyperpigmentation. Skin produces excess melanin to protect against the effects of UV rays, leading to conditions like melasma and sunspots. Sun exposure also causes sunburn and tanning, leading to uneven skin tone.
-
Hormonal fluctuations: Hormonal changes can often cause conditions like melasma. Higher production of oestrogen and progesterone during menstruation and pregnancy can stimulate melanin synthesis, causing dark patches to form on the skin.
-
Family history: People with a family history of hyperpigmentation are more likely to develop it than others.
-
Medication and medical conditions: Certain medications and medical conditions can cause hyperpigmentation. Conditions like Addison’s Disease and acanthosis nigricans, and medications like chemotherapy drugs and non-steroidal medicines, can create dark patches in certain parts of the body.
Hyperpigmentation Treatment
Hyperpigmentation treatment focuses on reducing dark spots, preventing reappearance and improving skin texture. As hyperpigmentation happens due to excess melanin production, the objective is to slow it down and promote faster skin renewal.
-
Topical ingredients: Retinoid, azelaic acid, kojic acid, lactic acid, vitamin c and alpha arbutin are often used as ingredients in products aimed at lightening dark patches from skin.
-
Home remedies: Aloe Vera gel, tea tree oil and liquorice extract are some mild forms of hyperpigmentation treatment at home.
-
Corticosteroid ointment: Corticosteroid ointments are sometimes used to treat hyperpigmentation but prolong use can have adverse effects. Thus, corticosteroids are often recommended in combination with other medications to reduce side-effects.
-
Hydroquinone: Hydroquinone is one of the most effective treatments for hyperpigmentation. It targets tyrosinase, the key enzyme that stimulates melanin production, and inhibits its activity. Hydroquinone is often used alongside corticosteroids to reduce steroidal side-effects.
-
Tretinoin creams: Tretinoin creams reduce the appearance of dark spots on skin by improving cell turnover and promoting healthy cell growth. It improves collagen production and removes dead skin cells. Tretinoin cream is also effective for acne hyperpigmentation.
-
Laser treatment: Laser treatment targets melanocytes and breaks down melanin. It is one of the fastest, most effective ways to treat hyperpigmentation, but should only be performed by a dermatologist.
-
Chemical peels: Chemical peels made with alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) and beta-hydroxy acid (BHA) peel away the top layer of your skin for faster dark spot removal. It is effective for melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and sunspots.
-
Oral medication: Topical medication and laser treatment may not always be sufficient for treating stubborn hyperpigmentation. In that case, oral medications may be prescribed by dermatologists to treat hyperpigmentation.
How to Prevent Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation can be prevented with some simple, consistent steps:
-
Sun protection: Sun protection is essential to prevent hyperpigmentation. Wear sunscreen generously before going out, and avoid peak sunlight hours as much as possible.
-
Skincare: Use gentle cleansers, and keep your skin moisturised to promote cell turnover, prevent dark spots and maintain skin health.
-
Healthy diet: Foods rich in Vitamin C and minerals, such as kiwi, pomegranate, spinach, etc., help in preventing hyperpigmentation.
-
Hydration: Hydration is essential for skin and overall health.
-
Adequate sleep: Sleep is essential to maintain skin health. Proper sleep aids cell turnover, thereby maintaining skin health.
Conclusion
Hyperpigmentation is a common condition, but it can take a toll on your confidence. Mild forms of hyperpigmentation can be treated with home remedies, but stubborn hyperpigmentation, like melasma and sunspots, requires expert intervention. At Manipal Hospitals, our dermatologists will help you with all your skin concerns. From minor problems to major concerns, our experts use advanced diagnostic tools to create personalised treatment plans for you. Visit your nearest Manipal Hospitals unit today for comprehensive care for all your skin concerns.
FAQ's
While hyperpigmentation usually needs some form of treatment to resolve, light spots or mild hyperpigmentation can fade by themselves in a few weeks or months.
Waxing or shaving causes friction, which can cause cuts and irritation. As the skin heals, dark spots can appear due to excess melanin production.
These areas experience constant friction, pressure, and build-up of dry skin. Knees and elbows also have thicker skin compared to other parts of the body. All these factors lead to hyperpigmentation in these areas.
Hormonal changes during pregnancy can give rise to dark patches around the mouth and eyes. This is called perioral hyperpigmentation, also known as “pregnancy mask”.
Fragrance can irritate the skin, leading to hyperpigmentation.






















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read






.png)








