Worrying about your health is a natural phenomenon, especially after encountering allergens or pathogens. But in some cases, this concern becomes excessive and persistent. This incessant worry may affirm your belief that you're seriously ill despite medical reassurance. If you are experiencing this, you might be experiencing illness anxiety disorder (formerly known as hypochondria).
Synopsis
Understanding Illness Anxiety Disorder
As per the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), illness anxiety disorder is a psychiatric disorder where there is constant anxiety about being or becoming sick. Also known as health anxiety, illness anxiety disorder can significantly disrupt your daily life. You may overly focus on normal bodily sensations, such as sweating or digestion, misinterpreting them as serious signs and symptoms of illness. This is often a chronic condition, and its intensity can vary over time.
Common Illness Anxiety Disorder Symptoms
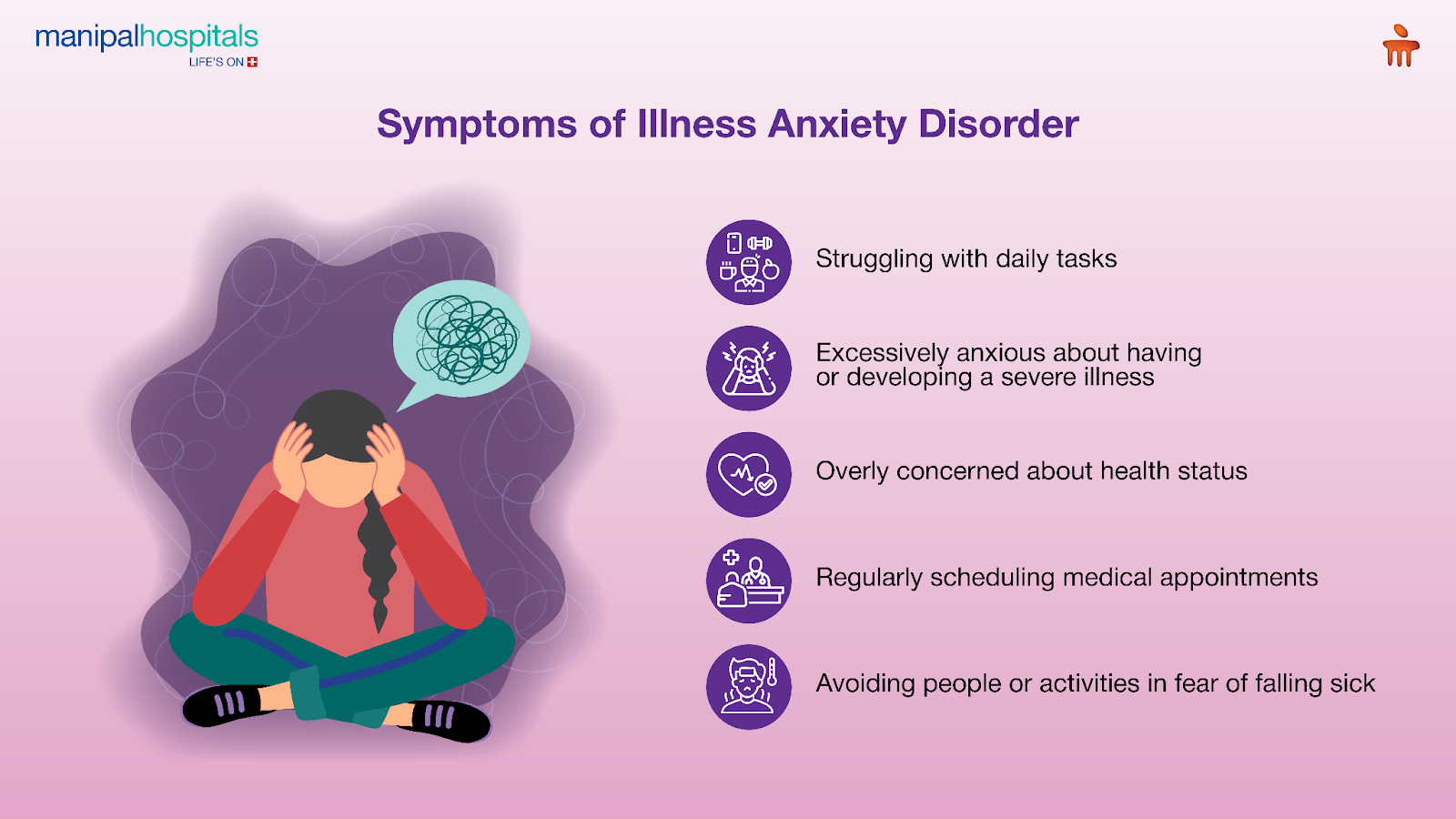
If you're dealing with illness anxiety disorder, you might notice some of these symptoms:
-
Constantly worrying about having or developing a serious health condition.
-
Excessively anxious that minor symptoms or sensations can be a sign of illness.
-
Feeling easily alarmed by your health status.
-
Finding little to no comfort from doctor visits or negative test results.
-
Worrying intensely about a specific health condition or your family's history of it.
-
Struggling with daily tasks because your health worries consume you.
-
Regularly scheduling medical appointments for reassurance, or, conversely, avoiding them owing to a fear of a diagnosis.
-
Avoiding people or activities for fear of falling sick.
-
Frequently discussing your health and perceived illnesses.
-
Constantly searching for symptoms online and self-diagnosing serious conditions.
Potential Causes
The exact cause of illness anxiety disorder is unclear, but several factors might play a role:
-
Beliefs: Inability to tolerate uncomfortable body sensations, leading you to misinterpret them as a serious health condition.
-
Family Influence: If your parents excessively worry about their health or yours, you may also develop health anxiety.
-
Past Experiences: A history of serious illness in childhood can make normal physical sensations frightening.
-
Other Anxiety Disorders: Having underlying mental health conditions like anxiety disorders, including generalised anxiety disorder or panic disorder, increases your risk.
-
Excessive Online Health Research: Spending too much time researching health information online can further exacerbate health anxiety.
Potential Complications
The constant worry associated with illness anxiety disorder can lead to various problems and side effects, including:
-
Issues with family members, partners, and friends, as your constant worrying can frustrate others.
-
Work-related difficulties, such as performance problems or frequent absences.
-
Trouble functioning in daily life, potentially even leading to panic attacks, physical symptoms of anxiety or disability.
-
Financial strain from numerous healthcare visits and medical bills.
-
Developing other mental health disorders, like somatic symptom disorder, other types of anxiety disorders, depression, personality disorder or obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD).
Treatment and Management
Treatment for illness anxiety disorder primarily focuses on helping you cope with your health anxieties.
Building a Strong Patient-Provider Relationship: Your primary care provider should acknowledge your concerns and not dismiss them.
-
Avoiding Over-medicalisation: Once serious medical conditions are ruled out and illness anxiety disorder is diagnosed, avoid unnecessary tests, imaging, and specialist referrals.
-
Referral to Specialists: Consider consulting a mental health professional or psychiatrist who will understand your concerns without judgment.
-
Regular Follow-ups: Having follow-up appointments with both your primary care physician and psychiatrist can reduce unnecessary doctor visits. These appointments also allow the physicians to assess new complaints and their triggers.
Psychotherapy is the first-line treatment:
-
Cognitive-Behavioural Therapy (CBT): This therapy helps you change unhelpful beliefs and behaviours. It might address habits like excessive body checking and educate you about normal body sensations.
- Other beneficial therapies include mindfulness-based cognitive therapy, group therapies, and acceptance and commitment therapy.
Medication is a second-line treatment option:
-
Antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), have proven effective.
-
The concerned specialist may advise you to continue treatment if you respond well to medication.
Most people benefit from a combination of psychotherapy and medication.
Conclusion
Illness Anxiety Disorder can significantly impact your quality of life, leading to persistent worry and distress about your health. If you find yourself constantly preoccupied with illness despite reassurance, remember that effective treatments are available to help you manage these anxieties and regain peace of mind. Our experts at the Department of Neurology at Manipal Hospital, EM Bypass, are well-equipped to understand your concerns and explore personalised treatment options.
FAQ's
Illness Anxiety Disorder is the constant preoccupation with having or acquiring a serious illness, despite having no physical symptoms. According to the illness anxiety disorder DSM 5, this preoccupation is persistent and causes significant distress and impairs daily functioning.
There isn't a single definitive "test" for Illness Anxiety Disorder, like a blood test. A mental health professional typically diagnoses illness anxiety disorder via a thorough clinical interview and evaluation of symptoms against diagnostic criteria.
No, Illness Anxiety Disorder and OCD are distinct conditions, although they share some similarities. While both involve anxiety and repetitive thoughts, illness anxiety disorder vs OCD highlights that the primary focus in the former is on health fears. In contrast, the latter presents a wider range of obsessions and compulsions.
Illness Anxiety Disorder is treatable, primarily through psychotherapy, such as Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT). Medication may also be used in some cases to help manage associated anxiety and depressive symptoms.






















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read