
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a common viral infection that plays a key role in the development of cervical cancer. Understanding HPV and cervical cancer, including prevention, vaccination, symptoms, and treatment, is essential for protecting women's health. Our gynaecological oncology experts in Delhi-NCR emphasise awareness and proactive care to reduce the burden of this disease.
Synopsis
- Understanding HPV and Cervical Cancer: The Essentials
- HPV and Cervical Cancer Symptoms: What to Watch For
- HPV Infection Symptoms: Low-risk vs High-risk HPV
- HPV Infection Treatment: Managing Risks and Preventing Progression
- HPV Vaccine and Cervical Cancer: A Powerful Preventive Tool
- The Role of Screening in HPV and Cervical Cancer Control
- Lifestyle and HPV and Cervical Cancer: Tips for Supportive Care
- Common Myths About HPV and Cervical Cancer Debunked
- Advanced Insights into HPV and Cervical Cancer
- HPV and Cervical Cancer Symptoms: Advanced Warning Signs
- HPV Infection Symptoms and Early Detection Strategies
- HPV Vaccine and Cervical Cancer: Global Impact Data
- Conclusion
Understanding HPV and Cervical Cancer: The Essentials
-
HPV and cervical cancer are closely linked; certain HPV strains cause changes in cervical cells that can develop into cancer.
-
HPV is transmitted primarily through sexual contact.
-
Most HPV infections clear spontaneously, but persistent infection with high-risk HPV types can lead to cervical cancer over time.
-
Early detection and vaccination are critical to prevention.
HPV and Cervical Cancer Symptoms: What to Watch For
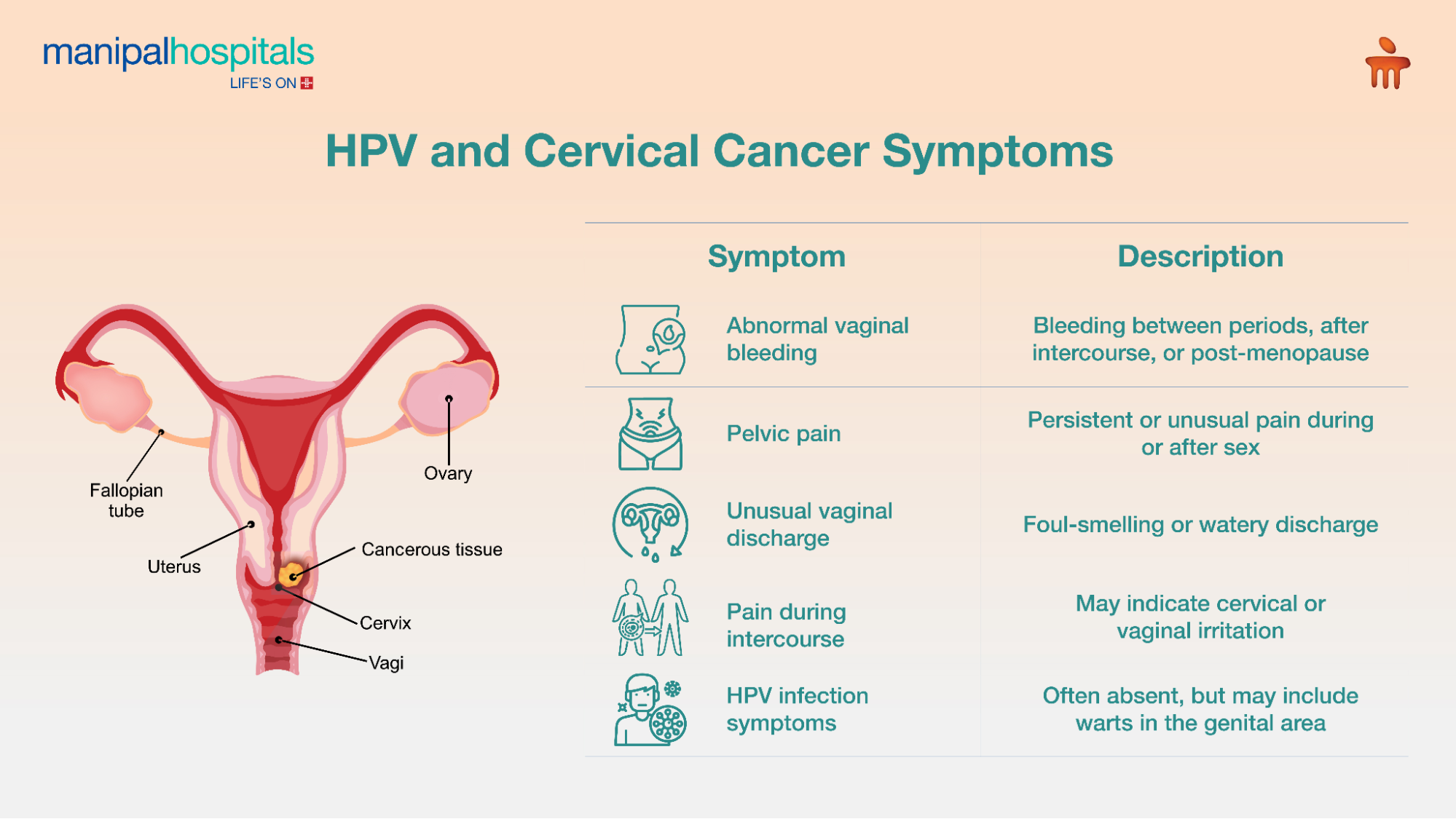
|
Symptom |
Description |
|
Abnormal vaginal bleeding |
Bleeding between periods, after intercourse, or post-menopause |
|
Persistent or unusual pain |
|
|
Unusual vaginal discharge |
Foul-smelling or watery discharge |
|
HPV infection symptoms |
Often absent but may include warts in the genital area (low-risk HPV) |
Regular screenings with Pap smears help detect cervical changes before symptoms appear. Our gynaecological oncology experts in Delhi-NCR recommend routine check-ups for early detection of potential problems.
HPV Infection Symptoms: Low-risk vs High-risk HPV
-
Low-risk HPV types may cause genital warts but rarely lead to cancer.
-
High-risk HPV types may not cause visible symptoms but can cause precancerous changes.
-
Persistent high-risk HPV infection is the main cause of cervical cancer.
HPV Infection Treatment: Managing Risks and Preventing Progression
-
No antiviral cure exists for HPV infection itself; management focuses on monitoring and treating abnormal cervical cells.
-
Treatments include removal or destruction of precancerous lesions via cryotherapy, LEEP, or conization.
-
Follow-up care is crucial to prevent progression to cancer.
-
Lifestyle measures to boost immunity can help the body clear HPV.
HPV Vaccine and Cervical Cancer: A Powerful Preventive Tool
-
The HPV vaccine protects against the most common cancer-causing HPV types.
-
Best administered before the onset of sexual activity—recommended for girls and boys both beginning from age 9 to 26.
-
Vaccination dramatically reduces cervical cancer rates.
-
Our gynaecological oncology experts in Delhi-NCR strongly advocate for HPV vaccination as a cornerstone of cervical cancer prevention.
How the HPV Vaccine and Cervical Cancer Prevention Work Together
|
Aspect |
Details |
|
Vaccine Protection |
Guards against HPV types causing ~70% of cervical cancers |
|
Ideal Timing |
Before potential exposure to HPV |
|
Vaccination Schedule |
Two or three doses, depending on age |
|
Monitoring |
Regular cervical screening is still necessary post-vaccination |
The Role of Screening in HPV and Cervical Cancer Control
-
Pap smear and HPV DNA tests detect precancerous changes.
-
Early intervention on abnormal cells prevents progression.
-
Our gynaecological oncology experts in Delhi-NCR provide comprehensive screening programs with counselling.
Lifestyle and HPV and Cervical Cancer: Tips for Supportive Care
-
Avoid smoking and limit alcohol to reduce risk.
-
Practice safe sex to reduce HPV transmission.
-
Maintain a healthy diet and exercise to support immune function.
-
Discuss vaccination and screening options with our obstetrics and gynaecological oncology experts in Delhi NCR.
Common Myths About HPV and Cervical Cancer Debunked
|
Myth |
Fact |
|
HPV only affects promiscuous women |
HPV is common; anyone sexually active can get it |
|
The vaccine causes HPV infection |
The vaccine is safe and does not contain a live virus |
|
Negative Pap smear means no cervical cancer risk |
Regular screening is still needed; changes can develop later |
Advanced Insights into HPV and Cervical Cancer
-
The HPV and cervical cancer connection involves specific oncogenic strains like HPV 16 and 18.
-
Understanding HPV infection and its progression to pre-cancerous lesions helps in timely intervention.
-
Regular screening helps detect HPV infection or pre-cancerous changes, which can be treated before they progress to cervical cancer.
HPV and Cervical Cancer Symptoms: Advanced Warning Signs
|
Advanced Symptom |
Associated HPV and Cervical Cancer Risk |
|
Post-coital bleeding |
High risk indicator |
|
Intermenstrual bleeding |
Often linked to cervical abnormalities |
|
Persistent lower back pain |
May signal advanced cervical cancer |
|
Leg swelling or pain |
Indicates possible spread |
|
Weight loss and fatigue |
Late-stage cervical cancer symptoms |
Our gynaecological oncology experts in Delhi-NCR guide patients through symptom evaluation for HPV and cervical cancer.
HPV Infection Symptoms and Early Detection Strategies
-
Subtle HPV infection symptoms require vigilant screening.
-
Colposcopy follows abnormal Pap tests to visualise cervical changes.
-
Biopsy confirms precancerous lesions linked to HPV and cervical cancer.
HPV Infection Treatment: Modern Approaches
-
Laser therapy ablates abnormal tissue effectively.
-
Cold knife conization removes deeper lesions.
-
Vigilant follow-up prevents recurrence of HPV infection symptoms.
|
Treatment Method |
Best for HPV Infection Treatment |
|
Cryotherapy |
Superficial lesions |
|
LEEP |
Moderate dysplasia |
|
Laser ablation |
Precise removal |
|
Surgical conization |
Deep or glandular involvement |
HPV Vaccine and Cervical Cancer: Global Impact Data
-
Countries with high vaccination rates show an 80-90% reduction in precancerous lesions.
-
The HPV vaccine and cervical cancer prevention save lives through herd immunity.
-
Booster doses under study for long-term HPV and cervical cancer protection.
Long-term Monitoring After HPV and Cervical Cancer Treatment
-
Annual HPV DNA testing post-treatment.
-
Colposcopy surveillance for high-risk patients.
-
Lifestyle counselling complements medical follow-up for sustained HPV and cervical cancer prevention.
Conclusion
Our gynaecological oncology experts in Delhi-NCR provide expert guidance and advanced care to help women navigate HPV and cervical cancer prevention confidently. Reach out to us for comprehensive vaccination, screening, and counselling services tailored to your individual health needs.
FAQ's
Early HPV infection symptoms are usually absent, but cervical cancer symptoms include abnormal bleeding and pelvic pain.
The HPV vaccine protects against the majority of cancer-causing HPV types and significantly reduces cervical cancer risk.
Vaccination is recommended from age 9 to 26 before exposure to HPV; consult our gynaecological oncology experts in Delhi-NCR for personalised advice.
While there is no cure for HPV itself, abnormal cervical cells caused by HPV can be treated to prevent cancer.
Regular Pap smears and HPV DNA tests are advised every 3-5 years, depending on age and risk factors, as recommended by our gynaecological oncology experts in Delhi.






















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read














