
Many people experiencing involuntary muscle contractions often wonder what dystonia is and why it disrupts normal movement and posture. “What is dystonia?” is a question that arises when muscles tighten uncontrollably, leading to abnormal twisting movements or sustained postures. Medically, what is dystonia refers to a neurological movement disorder affecting the brain’s control over muscle activity. Understanding what dystonia is, its causes, symptoms, and management options is essential for early diagnosis and improved quality of life.
This comprehensive guide explains what dystonia is, explores dystonia disease, outlines dystonia causes, highlights dystonia symptoms, and discusses the most effective dystonia treatment strategies.
Synopsis
- What Is Dystonia? A Medical Overview
- Understanding Dystonia Disease
- Dystonia Causes: Why Does It Occur?
- Common Dystonia Symptoms
- Types of Dystonia
- Focal Dystonia and Cervical Dystonia
- Diagnosis of Dystonia Disease
- Best Dystonia Treatment Options
- Dystonia Medication: Role and Benefits
- Living With Dystonia: Lifestyle and Support
- Conclusion
What Is Dystonia? A Medical Overview
To clearly answer what dystonia is, it is a chronic neurological condition characterised by involuntary muscle contractions. These contractions may cause repetitive movements, tremors, or abnormal postures. Dystonia is not a single disease but a group of disorders with varying severity and distribution.
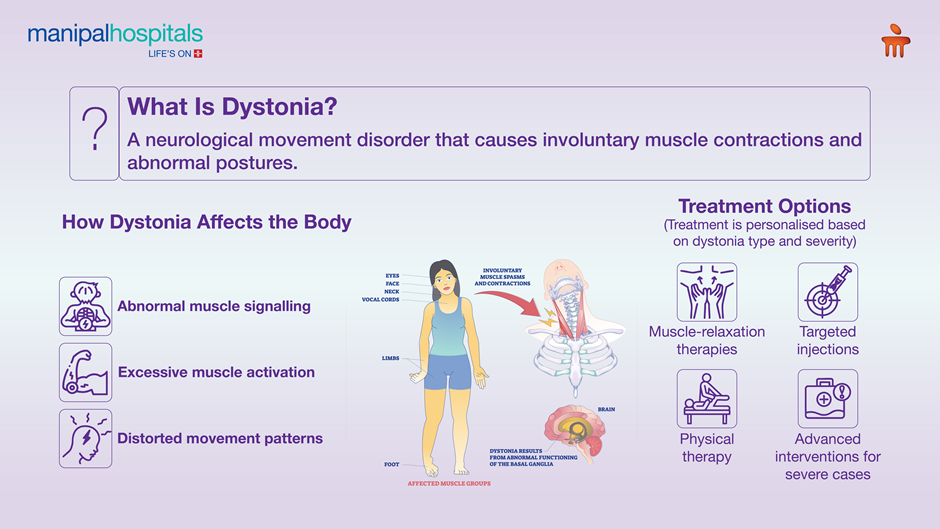
Key characteristics of dystonia disease include:
-
Sustained or intermittent muscle contractions
-
Worsening symptoms with activity
-
Improvement during rest or sleep
According to our neurologists in Delhi-NCR, dystonia can affect people of all ages, from childhood to late adulthood.
Understanding Dystonia Disease
Dystonia disease originates from dysfunction in brain regions responsible for movement coordination, particularly the basal ganglia. Unlike muscle disorders, dystonia is neurological in origin.
How Dystonia Disease Affects the Body
-
Disrupts normal muscle signalling
-
Causes excessive muscle activation
-
Leads to abnormal movement patterns
Early identification of dystonia disease allows timely intervention and better symptom control.
Dystonia Causes: Why Does It Occur?
Understanding dystonia causes is essential for targeted treatment. Dystonia causes may be primary or secondary.
Primary Dystonia Causes
-
Genetic mutations
-
Idiopathic neurological changes
Secondary Dystonia Causes
-
Brain injury or stroke
-
Infections
-
Medication side effects
In many cases, the cause of dystonia remains unknown, which makes clinical evaluation crucial. Our neurologists in Delhi-NCR emphasise detailed neurological assessment to identify underlying triggers.
Common Dystonia Symptoms
Dystonia symptoms vary depending on the muscles involved and the type of dystonia.
Key Dystonia Symptoms
-
Involuntary muscle contractions
-
Twisting or repetitive movements
-
Abnormal postures
-
Muscle pain or fatigue
Some dystonia symptoms are task-specific, appearing only during activities like writing or speaking. Recognising early dystonia symptoms can prevent progression.
Types of Dystonia
There are multiple types of dystonia, classified based on distribution and cause.
Major Types of Dystonia
1. Focal Dystonia - Affects a Single Body Part
Focal dystonia is the most common form among the major types of dystonia and is characterised by involuntary muscle contractions affecting one specific body part. This condition often begins subtly and may initially appear only during certain activities. Common examples include writer’s cramp affecting the hand, blepharospasm involving excessive blinking of the eyes, and cervical dystonia impacting the neck muscles.
2. Segmental Dystonia - Affects Adjacent Areas
Segmental dystonia involves involuntary muscle contractions affecting two or more adjacent body regions. Unlike focal dystonia, which is limited to a single area, segmental dystonia spreads across neighbouring muscle groups, such as the neck and shoulders or the face and jaw. Patients may experience sustained muscle spasms, abnormal postures, and discomfort that interferes with daily activities. Segmental dystonia can develop gradually and may evolve from focal dystonia over time.
3. Generalised Dystonia - Involves Multiple Body Regions
Generalised dystonia is a more severe form of dystonia disease in which involuntary muscle contractions affect multiple body regions, often including the trunk, limbs, and neck. This type frequently begins in childhood or adolescence and may have a genetic basis. As symptoms progress, abnormal postures, twisting movements, and difficulty walking may develop, significantly impacting mobility and independence.
4. Task-Specific Dystonia - Triggered by Specific Actions
Task-specific dystonia is a unique form of focal dystonia that occurs only during specific, repetitive activities. Common examples include writer’s cramp in individuals who write extensively, musician’s dystonia affecting fine motor control during instrument playing, and typing-related dystonia. Outside of the triggering task, muscle function may appear completely normal. This form of dystonia is thought to result from maladaptive brain plasticity due to repetitive motor patterns.
Understanding the types of dystonia helps guide personalised treatment plans.
Focal Dystonia and Cervical Dystonia
Focal dystonia is the most common form of dystonia, affecting one specific muscle group.
Examples of Focal Dystonia
-
Writer’s cramp
-
Blepharospasm
-
Cervical dystonia
Cervical dystonia affects the neck muscles, causing abnormal head tilting or rotation. Patients with cervical dystonia often experience pain and restricted movement. Among types of dystonia, cervical dystonia is frequently encountered in clinical practice.
Diagnosis of Dystonia Disease
Diagnosing dystonia disease involves:
-
Detailed medical history
-
Neurological examination
-
Imaging tests to rule out secondary causes
Accurate diagnosis of dystonia ensures appropriate dystonia treatment selection. Our neurologists in Delhi-NCR stress early evaluation for better outcomes.
Best Dystonia Treatment Options
Effective dystonia treatment focuses on symptom relief and functional improvement.
Primary Dystonia Treatment Approaches
-
Dystonia medication to relax muscles
-
Botulinum toxin injections
-
Physical therapy
-
Deep-brain stimulation (DBS) in severe cases
The choice of dystonia treatment depends on the type of dystonia and severity.
Dystonia Medication: Role and Benefits
Dystonia medication plays a vital role in managing symptoms.
Common Dystonia Medication Types
-
Muscle relaxants
-
Anticholinergic drugs
-
Dopaminergic agents
While dystonia medication does not cure the condition, it significantly improves daily functioning. Our neurologists in Delhi-NCR individualise dystonia medication plans based on patient response.
Living With Dystonia: Lifestyle and Support
Managing dystonia disease requires a holistic approach.
Supportive Measures
-
Regular physiotherapy
-
Stress management
-
Ergonomic adjustments
With consistent dystonia treatment, many patients lead productive lives. Long-term care planning is often coordinated by our neurologists in Delhi-NCR.
Conclusion
Understanding what dystonia is is the first step toward effective management. From identifying dystonia causes and recognising dystonia symptoms to choosing the right dystonia treatment, informed care makes a significant difference. With advances in dystonia medication and therapy options, patients with various types of dystonia, including focal dystonia and cervical dystonia, can achieve meaningful symptom control and improved quality of life.
FAQ's
Dystonia refers to involuntary muscle contractions causing abnormal movements or postures.
Dystonia disease is not curable, but symptoms are manageable with appropriate dystonia treatment.
Typical dystonia symptoms include muscle stiffness, twisting movements, and abnormal posture.
Cervical dystonia is commonly treated with botulinum toxin injections and supportive therapy.
The best dystonia medication varies by patient and type of dystonia, requiring medical evaluation.






















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read


















