
Autoimmune disorders affect millions of people worldwide and are increasingly recognised as a major cause of chronic illness across age groups. These conditions occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissues, leading to inflammation, pain, and organ damage. Our internal medicine doctors in Delhi-NCR highlight that early recognition of autoimmune disorders is critical because timely diagnosis can slow disease progression, reduce complications, and significantly improve quality of life.
This comprehensive guide explains autoimmune disorders in detail, explores autoimmune disease symptoms, discusses common autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, and highlights the importance of early testing, like the ANA test. Understanding immune system disorders empowers individuals to seek care early and manage long-term health effectively.
Synopsis
- What Are Autoimmune Disorders?
- Why Early Detection of Autoimmune Disorders Matters
- Common Autoimmune Disease Symptoms to Watch For
- How the Immune System Turns Against the Body
- Common Types of Autoimmune Disorders
- Autoimmune Diseases vs Other Chronic Conditions
- Diagnostic Tests for Autoimmune Disorders
- Role of the ANA Test in Early Detection
- Risk Factors for Autoimmune Disorders
- Managing Autoimmune Disorders After Diagnosis
- Lifestyle’s Role in Autoimmune Disease Management
- Importance of Specialist Care
- When Should You See a Doctor?
- Key Takeaway
What Are Autoimmune Disorders?
Autoimmune disorders are a group of immune system disorders in which the immune system fails to distinguish between foreign invaders and healthy cells. Instead of protecting the body, immune responses target organs, joints, skin, nerves, or glands.
There are over 80 recognised autoimmune diseases, and many share overlapping symptoms. This overlap often delays diagnosis, making awareness of autoimmune disorders especially important.
Why Early Detection of Autoimmune Disorders Matters
Early detection of autoimmune disorders can make a significant difference in outcomes. When autoimmune diseases are diagnosed early:
-
Inflammation can be controlled sooner
-
Organ damage may be prevented
-
Long-term disability risk is reduced
-
Treatment responses are more effective
Because autoimmune disease symptoms often appear gradually, they are frequently mistaken for stress, ageing, or lifestyle-related issues.
Common Autoimmune Disease Symptoms to Watch For
Autoimmune disease symptoms vary widely depending on the organs involved, but certain warning signs are common across many autoimmune disorders.
Early Autoimmune Disease Symptoms
-
Persistent fatigue not relieved by rest
-
Joint pain, swelling, or stiffness
-
Muscle weakness or numbness
-
Skin rashes or unexplained changes
-
Recurrent low-grade fever
Recognising these autoimmune disease symptoms early allows for timely evaluation and testing.
How the Immune System Turns Against the Body
In immune system disorders, genetic predisposition and environmental triggers combine to disrupt immune regulation. Infections, stress, hormonal changes, or toxins may activate autoimmune disorders in susceptible individuals.
Once triggered, immune cells continue attacking healthy tissues, leading to chronic inflammation and progressive damage.
Common Types of Autoimmune Disorders
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most prevalent autoimmune disorders. It primarily affects joints, causing pain, swelling, stiffness, and eventual joint deformity if untreated. Early treatment can preserve mobility and function.
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is a neurological autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the protective covering of nerves. Symptoms include vision problems, muscle weakness, coordination issues, and fatigue.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder where immune cells destroy insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It typically develops in childhood or young adulthood and requires lifelong insulin therapy.
Psoriasis Autoimmune Disease
Psoriasis autoimmune disease, affects the skin, causing red, scaly patches. It may also involve joints, known as psoriatic arthritis, further classifying it among immune system disorders.
Autoimmune Diseases vs Other Chronic Conditions
Autoimmune diseases differ from infections or degenerative conditions because they are driven by immune dysfunction rather than external pathogens or wear-and-tear. This distinction makes diagnosis more complex and underscores the need for specialised evaluation.
Diagnostic Tests for Autoimmune Disorders
Accurate diagnosis of autoimmune disorders relies on clinical assessment and targeted investigations.
Key Tests Used in Diagnosis
-
ANA test (Antinuclear Antibody test)
-
Blood markers of inflammation
-
Organ-specific antibody tests
-
Imaging studies, when needed
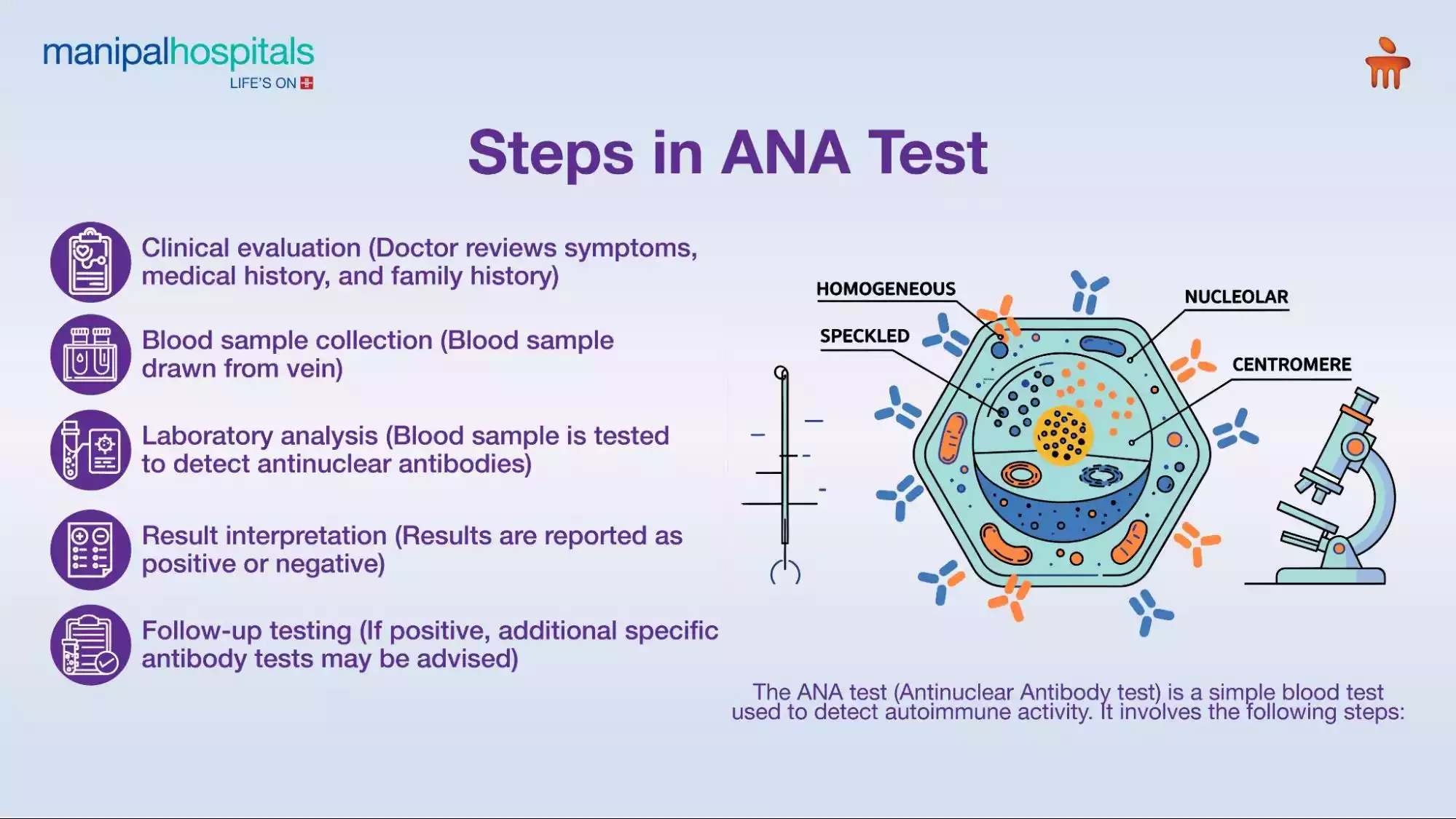
The ANA test is commonly used as a screening tool for autoimmune diseases, helping identify abnormal immune activity.
Role of the ANA Test in Early Detection
The ANA test detects antibodies that attack the body’s own cells. A positive ANA test does not confirm a specific condition but signals the need for further evaluation. Many autoimmune disorders, including lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, are associated with positive ANA test results.
Risk Factors for Autoimmune Disorders
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing autoimmune disorders:
-
Family history of autoimmune diseases
-
Female gender (higher prevalence)
-
Hormonal changes
-
Chronic stress
-
Environmental exposures
Understanding these risks supports early screening and monitoring.
Managing Autoimmune Disorders After Diagnosis
While most autoimmune disorders cannot be cured, they can be effectively managed with early intervention.
Treatment Goals Include
-
Reducing immune system overactivity
-
Controlling inflammation
-
Preventing organ damage
-
Improving quality of life
Treatment plans may involve medications, lifestyle changes, and long-term monitoring.
Lifestyle’s Role in Autoimmune Disease Management
Lifestyle modifications support medical treatment for autoimmune disorders:
-
Balanced anti-inflammatory diet
-
Regular low-impact exercise
-
Stress management
-
Adequate sleep
These measures help stabilise immune system disorders and reduce flare-ups.
Importance of Specialist Care
Because autoimmune disorders often involve multiple organ systems, coordinated care is essential. Our internal medicine doctors in Delhi-NCR play a key role in early diagnosis, treatment planning, and long-term management of autoimmune diseases.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Seek medical evaluation if autoimmune disease symptoms persist beyond a few weeks or worsen over time. Early consultation improves diagnostic accuracy and treatment success, especially for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
Key Takeaway
Autoimmune disorders are complex immune system disorders that require early recognition and ongoing care. Understanding autoimmune disease symptoms, undergoing timely tests such as the ANA test, and recognising conditions like type 1 diabetes or psoriasis autoimmune disease can significantly improve outcomes. With early detection and expert guidance, individuals can live full, active lives despite autoimmune diseases.
FAQ's
Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system attacks the body’s own healthy tissues, causing inflammation and damage.
Fatigue, joint pain, skin changes, muscle weakness, and recurrent infections are common autoimmune disease symptoms.
The ANA test helps detect abnormal immune activity and supports the diagnosis of autoimmune diseases.
Most autoimmune diseases are chronic but manageable with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Internal medicine specialists experienced in immune system disorders, such as our internal medicine doctors in Delhi-NCR, are well-equipped to guide diagnosis and long-term care.






















 7 Min Read
7 Min Read














