
Finding mucus in stool can make you pause for a moment and wonder if something might be wrong. It’s one of those things people don’t discuss much, but everyone notices if something looks different in their stool. A thin layer of clear mucus is considered normal on occasion. It’s how your intestines keep things moving and protect the lining inside. If the mucus is thick or comes with pain, blood, or loose stool with mucus, it might mean there’s an infection. Knowing how to reduce mucus in stool starts with understanding what is causing it in the first place.
Synopsis
What Does Mucus in Stool Mean?
The intestines have special cells that produce mucus to protect the inner lining of the intestines. It also helps the stool move through the gut without friction. This thin, jelly-like layer acts like a natural lubricant and a barrier against stomach acids and bacteria.
|
Normal Mucus |
Mucus Signals a Problem |
|
A trace of clear or slightly cloudy mucus that appears once in a while. |
The mucus becomes thick, white, or yellow. |
|
Stools are otherwise well-formed, with no pain, bloating, or blood. |
It shows up often or comes with cramping, loose stools, or urgency. |
|
It usually happens when you’re mildly dehydrated or have minor diet changes. |
You notice blood mixed with stool or mucus that continues for days. |
Common Causes of Mucus in Stool
Finding mucus in stool more often than usual can leave you wondering what’s really happening inside your gut. This can be a result of one or several conditions, minor or more serious. They can make your intestines produce extra mucus or shed the lining often. How it looks and what comes with it often gives doctors a good idea of where the issue lies. Here are some of the major causes:
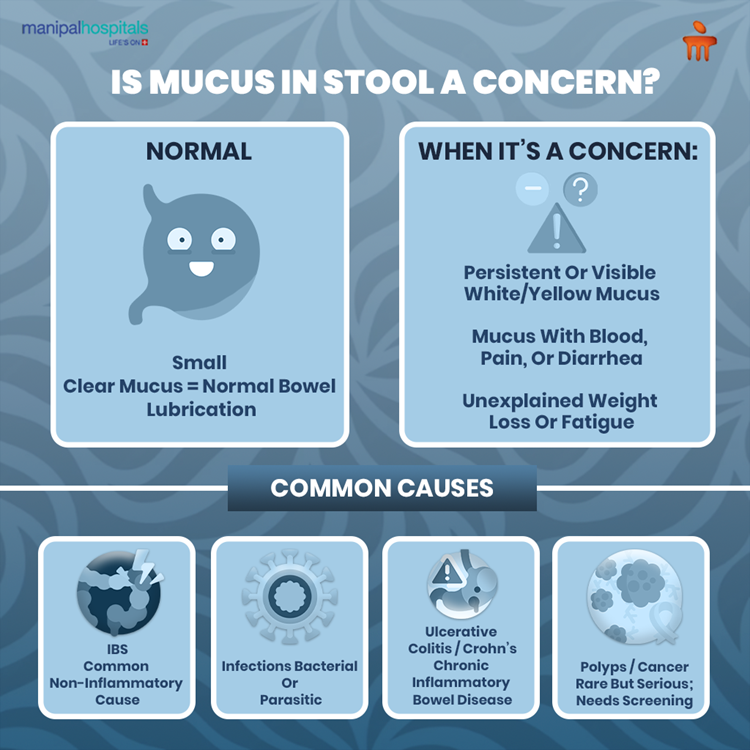
1. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
This is one of the most common reasons. The bowel gets sensitive and reacts to stress or certain foods by producing extra clear or white mucus. It’s uncomfortable but not dangerous.
2. Infections (bacterial or parasitic)
If you’ve ever had a stomach infection that led to sticky, jelly-like mucus in stool, that’s your body fighting inflammation. It often shows up suddenly with cramps or diarrhoea.
3. Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease
These are long-lasting inflammatory conditions. The gut lining gets irritated and swollen, releasing thicker mucus that can mix with blood or pus during flare-ups.
4. Polyps or Colorectal Cancer
This is rarer but still important to mention. Growths in the colon can cause mucus, bleeding, or a sudden change in how your bowel moves. It’s one reason doctors suggest screening when symptoms don’t settle.
Diagnosing the Cause of Mucus in Stool
Diagnosing involves performing a range of tests to figure out the underlying cause and ruling out other possibilities. It involves:
1. Medical History and Exam
Your doctor checks your diet, bowel habits, medications, and stress levels, then gently examines your abdomen for tenderness or bloating.
2. Stool Tests
A stool test looks for bacteria, parasites, or hidden blood, often explaining loose stool with mucus or mucus diarrhoea.
3. Colonoscopy or Sigmoidoscopy
If symptoms persist, doctors examine the colon directly and may take a small biopsy to check for ulcerative colitis or what causes jelly-like mucus in stool.
Treatment Options Based on the Diagnosis
Once doctors figure out what’s really behind the mucus in stool, the next step is helping your gut settle down and heal.
1. IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
If it’s a case of IBS, the treatment would involve small but steady adjustments. Doctors often suggest adding fibre slowly, cutting down foods that trigger gas, and managing stress because the gut reacts strongly to it. Some people need mild medicines to calm spasms or ease discomfort when there is a flare-up.
2. Infections
If it’s an infection, the treatment would involve targeting the organism causing it. Tests may be performed to identify the exact bacteria or parasite causing the infestation. Your doctor will then prescribe antibiotics or antiparasitic medication. Rest, fluids, and simple food help your intestines recover faster.
3. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Ulcerative Colitis or Crohn’s)
These conditions require more care and patience. Anti-inflammatory medicines, immune-controlling drugs, or advanced biologic treatments are used to keep the inflammation reduced and stop excess mucus production. It’s about managing flare-ups and keeping them from coming back.
4. Polyps or Cancer
When polyps or growths are found, they’re usually removed during a colonoscopy. If it turns out to be cancer, doctors bring in specialists to plan further treatment like surgery, medication, or close follow-up, depending on what’s needed.
Practical Tips on How to Reduce Mucus in Stool
While the underlying causes are up to your doctor to diagnose and treat, you can also make some changes to reduce mucus in your stool. Here are some tips:
-
Stay hydrated to keep the intestines functioning well.
-
Eat a balanced diet with moderate fibre, not too high, not too low.
-
Include probiotic foods like curd or kefir to restore gut bacteria.
-
Avoid ignoring changes that last beyond a week.
Conclusion: When to Reach Out for Help
Shedding a little clear mucus on occasion can be considered normal, especially if you have had heavy or spicy food. But if it becomes frequent, or the mucus appears thick, or comes with blood or pain, you have to visit a doctor. Changes like these can signal infection, inflammation, or other digestive issues that need proper care.
At Manipal Hospitals Bangalore, our specialists can help find the exact cause and offer effective treatment. If you’ve been noticing persistent mucus in stool or other unusual bowel changes, don’t wait it out. Book a consultation today.
FAQ's
Frequent mucus in stool can mean your intestines are irritated. It could indicate an infection, mucus shedding because of IBS, or inflammation that needs to be looked at.
White mucus in stool usually appears when the colon produces extra mucus, often seen in conditions like IBS or mild gut infections.
Yes, if it’s caused by a mild infection or a diet change. But if loose stool with mucus lasts beyond a few days, see a doctor.
Jelly-like mucus in stool often points to inflammation from infection or bowel irritation. Occasionally it’s linked to ulcerative colitis.
Stay hydrated, eat balanced meals, and include probiotics. Understanding how to reduce mucus in stool starts with treating the cause, not just the symptom.






















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read










