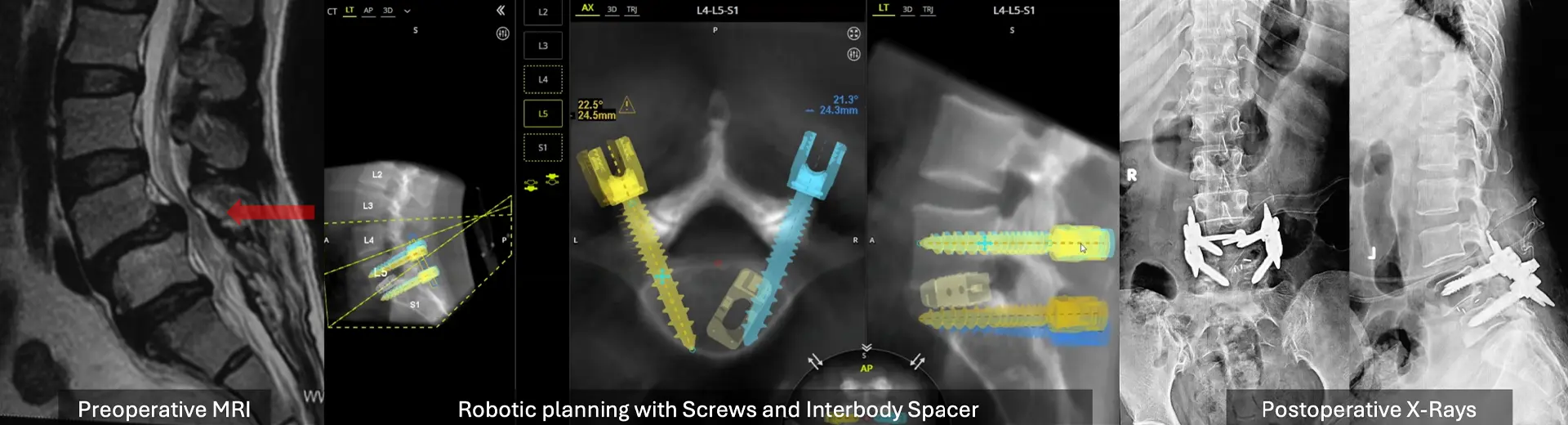
Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) serves as an extensive surgical approach for treating severe cases of lumbar canal stenosis and spinal instability. These conditions cause pain, numbness, and functional limitations that significantly affect quality of life. Two main conditions necessitating treatment are spinal instability from degenerative disc disease or spondylolisthesis, which causes nerve compression due to abnormal vertebral movement. When conservative treatments like physiotherapy, medications, and injections fail to benefit patients, surgery becomes the only viable treatment option.
PLIF surgically removes deteriorating spinal discs and establishes spinal support using bone grafts or interbody cage implants. This procedure offers several benefits by restoring disc height, relieving compressed nerves, and creating spinal stability. PLIF fuses the vertebrae, halting symptom progression and providing long-term therapeutic benefits. Patients seeking spinal fusion at Manipal Hospitals achieve successful outcomes due to the facility's combination of advanced technologies and highly skilled surgical experts.
What is Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF)?
The purpose of PLIF surgery is to stabilise the lumbar spine by connecting two or more vertebrae. The main surgical goals include stopping abnormal segment movement, restoring disc height, and reducing nerve compression caused by damaged tissues and instability.
This surgical treatment uses bone grafts or interbody cages placed within the intervertebral spaces after removing dysfunctional discs. The therapeutic bone regeneration process between vertebrae develops spinal stability. Titanium screws and rods help maintain correct spinal positioning during recovery.
When surgeons restore disc height and decompress nerve structures through PLIF, they achieve significant pain reduction and improved mobility while preventing further spinal deterioration. Patients with lumbar stenosis, spondylolisthesis, recurrent disc herniation, or degenerative disc disease benefit greatly from this procedure, gaining the opportunity to live pain-free with increased activity levels.
What Health Conditions Require Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Canal Stenosis and Instability?
-
Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Age-related disc and facet joint degeneration allows one vertebra to slip forward on the one below, narrowing the spinal canal and causing instability. PLIF both decompresses the neural elements and stabilises the segment.
-
Isthmic Spondylolisthesis: A stress fracture (pars defect) in the vertebral arch allows slippage, leading to central stenosis and back-related leg pain. PLIF restores alignment, fuses the defect, and relieves nerve compression.
-
Degenerative Disc Disease with Instability: Chronic disc height loss and abnormal motion overload the facets, resulting in lumbar canal narrowing and mechanical pain. PLIF replaces the diseased disc with an interbody device and rigid posterior fixation.
-
Post-laminectomy Instability: Extensive decompressive laminectomy can disrupt the posterior tension band, leading to recurrent pain or deformity. PLIF augments decompression with fusion to prevent further instability.
-
Adult Degenerative Scoliosis with Stenosis: Lateral curvature and disc degeneration create asymmetric stenosis on the concave side, causing neurogenic claudication. PLIF corrects alignment and secures the unstable segments.
-
Traumatic Compression Fractures with Instability: Burst fractures or flexion-distraction injuries compromising canal integrity and stability may be managed with PLIF after neural decompression.
-
Neoplastic or Infective Vertebral Body Collapse: Tumour-related lytic lesions or infective spondylodiscitis can destroy vertebral bodies, causing collapse, instability, and stenosis. PLIF following debridement restores stability and decompresses the canal.
Indications for Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF)
Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion is recommended for patients experiencing severe spinal conditions that do not respond to non-surgical treatments. The following conditions are key indications for PLIF:
-
Severe Lumbar Canal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal leading to compression of the spinal cord and nerves, resulting in pain, numbness, and weakness in the lower extremities.
-
Lumbar Instability: Conditions such as spondylolisthesis, where one vertebra slips forward over another, causing severe back pain and difficulty in movement.
-
Failed Conservative Treatments: Patients who do not experience significant relief from physiotherapy, medications, or steroid injections may require PLIF to restore spinal stability.
-
Recurrent Disc Herniation: Repeated herniation of the intervertebral disc, leading to persistent nerve compression and pain that necessitates surgical intervention.
-
Degenerative Disc Disease: Age-related wear-and-tear of spinal discs, causing chronic pain and reduced flexibility, which can be alleviated through fusion surgery.
PLIF is particularly beneficial for patients whose spinal conditions limit daily activities and significantly impact their quality of life. The procedure offers long-term relief by permanently stabilising the affected spinal segments.
Key Aspects of the Surgical Procedure
-
Anaesthesia and Patient Positioning: General anaesthesia with the patient prone on a radiolucent spinal frame. Bolsters support the chest and pelvis, allowing the abdomen to hang free to reduce venous pressure.
-
Posterior Midline Exposure: Subperiosteal dissection of paraspinal muscles exposes the laminae, facets, and transverse processes of the target levels.
-
Neural Decompression: Laminectomy, medial facetectomy, or foraminotomy is performed to relieve pressure on the thecal sac and nerve roots.
-
Discectomy and Endplate Preparation: The intervertebral disc is removed, and cartilaginous endplates are decorticated to expose bleeding bone for fusion.
-
Interbody Cage Insertion: Trial spacers determine the appropriate height and lordosis. A PEEK or titanium cage packed with autograft or bone substitute is inserted to restore disc height and alignment.
-
Pedicle Screw-Rod Fixation: Bilateral pedicle screws are placed in the vertebrae above and below the interbody device. Contoured rods are secured, providing immediate segmental stability.
-
Posterolateral Bone Grafting: Autograft or allograft is laid in the decorticated posterolateral gutters to promote a solid fusion mass.
-
Wound Closure and Drainage: Layered closure of muscle, fascia, and skin is performed. A subfascial drain may be left to prevent hematoma.
-
Postoperative Care: Early mobilisation with physiotherapy, use of a lumbar brace as indicated, multimodal analgesia, and serial radiographs to monitor fusion progress.
Benefits of Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF)
PLIF is effective for long-term treatment of patients requiring spinal stability restoration due to degenerative disc disease combined with nerve compression and spinal instability. While patients benefit from PLIF alone, it delivers lasting functional improvements when combined with nerve decompression procedures.
-
Restores Spinal Stability - Recovering spinal stability is a primary goal of PLIF. Abnormal vertebral movements from spondylolisthesis, degenerative disc disease, and trauma produce pain and progressive spinal misalignment. PLIF resolves this instability by fusing two or more vertebrae using bone grafts, screws, and rods. This stabilisation prevents additional vertebral movement, reduces painful tissue motions, and supports proper long-term spinal alignment.
-
Relieves Nerve Compression - Nerve compression in the lumbar spine causes acute pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness throughout the lower back and legs. PLIF relieves this by creating space around spinal nerves. During the procedure, surgeons remove damaged discs and replace the intervertebral space with bone grafts and fusion cages. This enlarges the space between vertebrae, alleviating nerve compression. PLIF effectively treats symptoms of lumbar radiculopathy (sciatica), cauda equina syndrome, and persistent nerve pain.
-
Improves Posture and Mobility - Severe spinal instability and nerve pressure cause postural problems, stiffness, and reduced mobility. PLIF restores proper spinal alignment, reducing abnormal curves resulting from degenerative changes. Improved spinal mechanics allow patients to perform daily activities without discomfort. Post-surgical rehabilitation and physical therapy enhance patient strength and flexibility, enabling easier, pain-free movement.
-
Enhances Quality of Life - PLIF aims to restore patient independence and improve quality of life. Chronic back pain and nerve symptoms often prevent patients from performing daily activities and sleeping well. By correcting these spinal conditions, PLIF enables patients to resume normal activities with less pain. Patients frequently experience significant pain reduction, improved sleep quality, and better overall physical and psychological well-being.
Advanced surgical techniques, including minimally invasive robotic spine surgery and enhanced rehabilitation protocols, have made PLIF highly successful for maintaining long-term spinal health and function. Patients who follow post-surgical instructions, complete physiotherapy, and make appropriate lifestyle modifications typically achieve a pain-free, active lifestyle after surgery.
Will I Need Any Pre-Procedure Investigations?
Before proceeding with PLIF, patients undergo a series of diagnostic tests to assess their overall health and spinal condition:
-
Spinal Imaging: X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans help visualise spinal degeneration, disc herniation, and nerve compression.
-
Pulmonary Function Tests (if required): Assess lung capacity for safe anaesthesia administration.
-
Neurological Evaluations: Examine nerve function, reflexes, and muscle strength.
-
Blood Tests & General Health Check-up: Routine blood work to assess infection risks, clotting factors, and overall health status.
-
Cardiac & Anaesthesia Clearance: ECG and echocardiograms ensure heart function is stable for surgery.
-
Bone Density Test for Older Patients: Evaluates bone health to determine the feasibility of spinal fusion.
What Happens During the Procedure?
PLIF is a multi-step surgical procedure that involves meticulous planning and execution to ensure optimal results. The key steps include:
Anaesthesia and Positioning: The patient is placed under general anaesthesia and positioned in a prone (face-down) position to allow optimal access to the lumbar spine.
Incision and Exposure: A midline incision is made on the lower back, and the muscles are gently retracted to expose the affected vertebrae.
Nerve Decompression: The surgeon removes portions of the bone (laminectomy) and ligament structures pressing on the spinal nerves, relieving compression and creating space for the fusion process.
Interbody Fusion:
-
The damaged intervertebral disc is carefully removed.
-
A specialised interbody cage filled with bone graft is inserted into the empty disc space to promote fusion between the vertebrae.
-
Titanium screws and rods are placed for additional spinal support and alignment.
Wound Closure and Post-Operative Care: The incision is closed with sutures, and the patient is closely monitored in the recovery unit for pain management and initial rehabilitation.
The entire procedure takes approximately 3-4 hours, and most patients require a hospital stay for post-operative monitoring and physiotherapy.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Surgery
PLIF is performed under general anaesthesia and involves the following steps:
-
Anaesthesia & Patient Positioning: The patient is placed in a prone position to allow access to the lumbar spine.
-
Incision & Exposure of Spine: A midline incision is made, and the muscles are carefully retracted to expose the vertebrae.
-
Nerve Decompression & Disc Removal: The damaged intervertebral disc is removed, alleviating nerve compression and pain.
-
Implantation of Fusion Cage & Screws: A bone graft-filled cage is inserted into the disc space, restoring spinal height and stability.
-
Spinal Alignment and Stability Reinforcement: Screws and rods are placed to hold the vertebrae together while fusion occurs.
-
Closure and Recovery Monitoring: The incision is sutured, and post-surgical monitoring begins.
How long does it take to recover from the surgery?
-
Hospital Stay Duration (5-7 days): Patients are monitored for complications and pain management.
-
Initial Recovery Phase (First 4-6 weeks): Light activities are encouraged, with mobility aids if needed.
-
Long-Term Recovery (6-12 months with physiotherapy): Gradual strengthening exercises improve spinal stability.
-
Follow-up Evaluations for Spinal Fusion Success: Imaging tests confirm fusion and proper healing.
Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion provides long-term relief from lumbar canal stenosis and instability, significantly improving mobility and quality of life. Choosing an experienced surgical team is crucial for a successful outcome. MIRSS offers advanced spinal care with state-of-the-art technology and expert spine specialists. If you experience persistent back pain or neurological symptoms, consulting a specialist at MIRSSls can help determine if PLIF is the right treatment for you.
How do I know if I Am Eligible for PLIF?
Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) is recommended for patients experiencing severe lower back pain and neurological symptoms due to spinal instability. Several factors determine eligibility for this procedure:
-
Cobb Angle and Lumbar Stability Considerations: PLIF is suitable for individuals with a Cobb angle of moderate deformity and spinal instability that may contribute to pain and functional impairment.
-
Progression of Symptoms: Candidates typically experience increasing back pain, leg numbness, or weakness that persists despite conservative treatments such as medication and physical therapy.
-
Impact on Daily Life: Difficulty in walking, prolonged standing, and performing basic activities due to pain or weakness are indicators for surgical intervention.
-
Skeletal Maturity and Age Factors: Adults with fully developed skeletal structures and no age-related contraindications are ideal candidates.
-
Pre-existing Health Conditions: Patients with uncontrolled diabetes, osteoporosis, or cardiovascular conditions require thorough evaluation before surgery.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of PLIF
While PLIF is generally safe, it carries some risks:
-
Infection Risks and Prevention Measures: Antibiotics are administered to prevent post-surgical infections.
-
Bleeding and Blood Clot Risks: Proper monitoring reduces clot formation risk.
-
Nerve Injury and Neurological Considerations: Precision techniques help avoid nerve damage.
-
Implant Failure and Fusion Non-Union Risks: Regular follow-ups ensure proper healing and stability.
-
Post-Surgical Pain and Rehabilitation Needs: Pain management and physiotherapy aid recovery.
Why Choose MIRSS for Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion?
MIRSS is one of the leading spinal surgery hospitals in Bangalore and India, and offers state-of-the-art facilities and a multidisciplinary approach to spine care. Here's why patients trust MIRSS for Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion:
Expert Spine Surgery Team: A highly skilled team of robotic spine surgeons, spine care specialists, and spine anaesthesiologists experienced in complex spinal disorders.
State-of-the-Art Technology:
-
Intraoperative Navigation: Ensures precision and accuracy in implant placement.
-
3D Imaging and Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Enhances surgical precision and minimizes risks.
-
Neuromonitoring: Reduces the risk of nerve damage during surgery.
Comprehensive Pre- and Post-Operative Care:
-
Thorough pre-surgical assessments, including MRI, CT scans, and physical evaluations.
-
Customized rehabilitation plans to promote faster recovery and long-term success.
Proven Success Rate: High patient satisfaction and successful spinal corrections, enabling individuals to return to an active lifestyle with minimal discomfort.
By choosing MIRSS, patients benefit from advanced surgical techniques, compassionate care, and comprehensive support throughout their treatment journey.