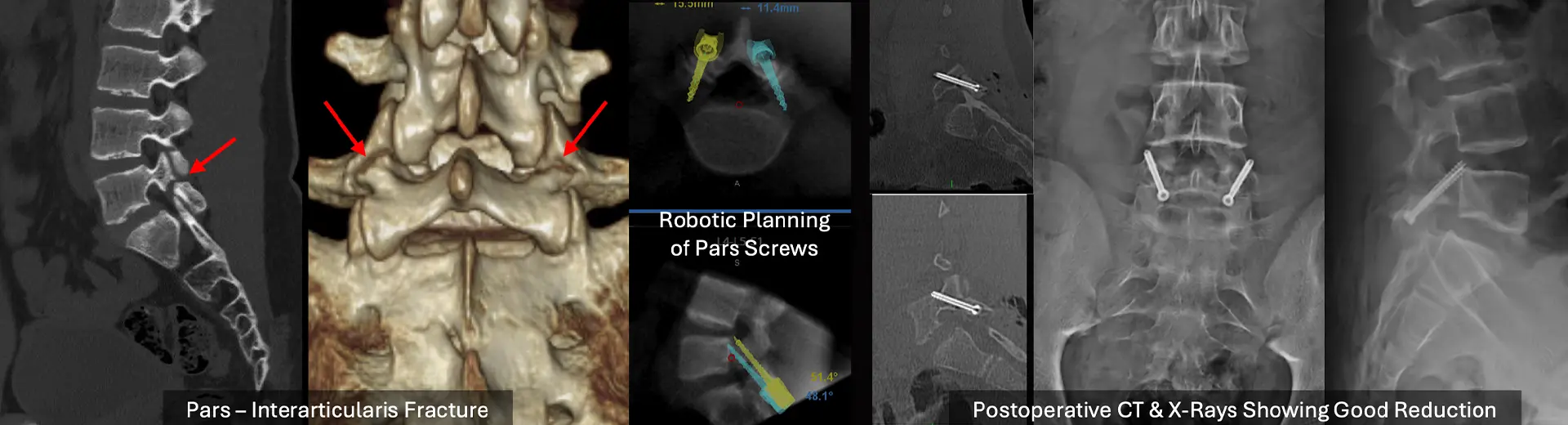
What is Pars Interarticularis Defect?
A minor fracture or weakness occurring in the pars interarticularis segment is spondylolysis or Pars Interarticularis Defect. The lumbar spine is the typical location for this condition, with athletes who do gymnastics, football, or weightlifting commonly developing it due to repetitive strain. Some conditions develop because of genetics or exist since birth. Lower back pain, stiffness, and possibly severe pain that radiates into the legs are the main symptoms.
Mild injuries may heal with rest or physical therapy with bracing, while severe injuries need surgical intervention. Proper treatment and early medical intervention prevent the development of spondylolisthesis, which causes vertebral displacement.
What Is Pars Inter-Articularis Repair Surgery (Buck's Fusion)?
The pars interarticularis defect is a minor vertebral fracture that often appears in L5 of the lower back. Without treatment, it leads to persistent pain, spinal instability, and spondylolisthesis, causing a vertebra to move ahead of another. Buck's Fusion surgical procedure reconstructs the defect by stabilising the spine while bringing pain relief and structural recovery.
Internal fixation alongside bone grafts helps the fractured pars area fuse and prevents progressive breakdown. Spinal fusion repair through Buck's Fusion avoids the extensive approach of traditional surgeries by maintaining natural spinal segment movement. This intervention is a rational choice for people whose conservative treatment approaches have proven unsuccessful.
Through this procedure, you can strengthen affected body parts and decrease pain while preventing persistent issues that compromise spinal stability. Personalised surgical treatment creates optimal results that enable you to perform daily activities with a strengthened spinal structure. The success of spinal fusion depends on having an experienced surgical team for long-lasting pain relief.
What Health Conditions Require Pars Inter-Articularis Repair?
Certain spinal conditions can weaken the pars interarticularis, leading to chronic pain and instability. If left untreated, these conditions may progress, requiring surgical intervention. Understanding these conditions can help you determine whether Buck's Fusion is the right solution for you.
Common Conditions Indicating Buck's Fusion Surgery:
-
Spondylolysis (Stress Fracture of the Pars): A stress fracture in the pars region, often due to repetitive strain or congenital weakness, may fail to heal naturally. This can lead to chronic lower back pain and may require surgical stabilisation.
-
Non-Union Fracture of the Pars: Sometimes, a pars fracture does not heal with conservative treatment. Persistent radiographic evidence of a non-union defect may indicate the need for surgical repair to restore spinal stability.
-
Spondylolisthesis Due to Pars Defect: When a pars defect leads to vertebral slippage (spondylolisthesis), it can cause nerve compression, lower back pain, and leg discomfort. Surgery may be required to stabilise the vertebrae and prevent further misalignment.
-
Persistent Pain Despite Conservative Treatment: If physical therapy, medication, and bracing fail to relieve symptoms and the defect continues to cause discomfort, Buck's Fusion can offer long-term pain relief and improved spinal function.
Indications for Pars Inter-Articularis Repair Surgery
This surgical procedure specifically treats patients with long-term back pain from unhealed pars region stress fractures. Spondylolysis develops from spine-related repetitive stress and natural weak points. If untreated, this condition leads to spondylolisthesis, causing severe pain, restricted movement, and compressed nerves.
Your doctor will recommend Buck's Fusion surgery when other treatments like physical therapy, bracing, and medications don't help your condition.
Another key factor in determining the need for surgery is radiological evidence of an unhealed pars defect. If imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs confirm a non-union fracture with spinal instability, surgical repair may be the most effective solution. In carefully selected cases, early intervention can prevent worsening spinal alignment issues and nerve involvement, allowing you to maintain an active lifestyle without long-term disability.
Key Benefits of Buck's Fusion Surgery:
-
Pain Relief and Functional Recovery: By stabilising the affected vertebra, the surgery reduces mechanical stress on the spine, significantly decreasing pain and improving movement. This allows you to perform daily activities without discomfort.
-
Prevention of Condition Progression: An untreated pars defect may worsen, leading to spondylolisthesis and nerve compression. Surgical repair ensures long-term spinal stability, preventing further complications.
-
Minimally Invasive Approach with Faster Recovery: Compared to traditional spinal fusion, Buck's Fusion is less invasive, preserving mobility in surrounding vertebrae and reducing overall recovery time.
-
Improved Quality of Life: Pain reduction and enhanced spinal function allow you to return to an active lifestyle, including work and physical activities, without limitations.
-
Durable and Long-Lasting Results: The procedure provides a permanent solution for non-healing pars fractures, ensuring strong, stable spinal alignment for years.
Will I Need Any Pre-Procedure Investigations?
Preparing for Pars Inter-Articularis Repair Surgery (Buck's Fusion) is crucial for ensuring a successful outcome and smooth recovery. A structured preoperative plan helps minimise risks and optimise healing. The preparation process includes a comprehensive medical evaluation, diagnostic imaging, and lifestyle adjustments, ensuring that your body is in the best possible condition before surgery.
Medical Evaluation and Diagnostic Imaging: A thorough preoperative medical assessment is essential to evaluate your overall health and identify any factors that could impact the surgery. Your spine specialist will review your medical history, perform a physical examination, and assess existing conditions to ensure you are fit for surgery.
Diagnostic imaging is critical in surgical planning. X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs provide detailed insights into the extent of the pars defect, spinal alignment, and nerve involvement. These scans help the surgeon determine the optimal surgical approach, fixation techniques, and the need for bone grafting. This careful evaluation ensures the procedure is tailored to your specific condition, leading to better surgical outcomes.
Preoperative Counselling and Lifestyle Adjustments - Before undergoing Buck's Fusion, you will receive detailed preoperative counseling to understand the procedure, potential risks, and expected recovery timeline. Your surgeon will explain the surgical steps, postoperative care, and necessary precautions to help you feel prepared.
Lifestyle modifications are often recommended to enhance surgical success. If you smoke, quitting reduces the risk of delayed bone healing. Maintaining a healthy weight alleviates excess pressure on the spine, promoting better recovery outcomes. Your doctor may also advise you to adjust certain medications, such as blood thinners, to minimise surgical complications. Following these preoperative guidelines helps ensure a safe procedure and smooth recovery.
How Does Pars Inter-Articularis Repair Work?
Buck's Fusion is a targeted spinal procedure designed to repair a defect in the pars interarticularis while preserving the mobility of the surrounding vertebrae. The procedure involves bone grafting and internal fixation, ensuring long-term spinal stability.
Surgical Goals and Techniques - The primary goal of Pars Inter-Articularis Repair Surgery (Buck's Fusion) is to eliminate pain, stabilise the spine, and promote healing of the fractured pars region. Unlike traditional spinal fusion, this procedure preserves segmental mobility while ensuring structural integrity.
During surgery, small incisions are made to access the affected vertebra. The fractured area is carefully prepared for fusion, ensuring optimal bone healing. Internal fixation devices such as screws or rods may be used to hold the vertebra in place while the graft heals. The technique aims to provide rigid stabilisation, allowing new bone growth to bridge the fracture site.
The Role of Bone Grafts and Internal Fixation - Bone grafting plays a crucial role in successfully healing a pars defect. A small piece of bone, either from your own body (autograft) or a donor (allograft), is placed at the site of the fracture. This bone graft acts as a scaffold, allowing natural bone regeneration.
Internal fixation devices, such as screws or rods, provide additional support, ensuring that the vertebra remains stable while the bone graft heals. This prevents movement at the fracture site, reducing pain and promoting proper fusion. Over time, the graft integrates with your natural bone, creating a strong, stable connection in the repaired pars region.
Using advanced surgical techniques and personalised treatment approaches, Buck's Fusion offers long-term pain relief, improved spinal function, and a faster return to normal activities.
The Procedure: Step-by-Step
Pars Inter-Articularis Repair Surgery (Buck's Fusion) is a structured, stepwise process designed to restore spinal stability and relieve pain. Each step is carefully executed to ensure optimal healing and fusion of the fractured pars region. The procedure is performed under general anaesthesia and typically lasts two to three hours, depending on the complexity of the defect.
Step 1: Anaesthesia and Patient Positioning - The procedure begins with the administration of general anaesthesia, ensuring you remain comfortable and pain-free throughout the surgery. Once sedated, you will be carefully positioned in a prone (face-down) position on the operating table. This positioning provides optimal access to the lower spine while minimising pressure on surrounding structures. Proper padding and spinal alignment are ensured to reduce any risks associated with prolonged surgical positioning.
Step 2: Incision and Surgical Access - A small incision is made over the affected vertebra to expose the pars interarticularis defect. The surrounding tissues, muscles, and fascia are gently retracted using specialised surgical instruments, allowing direct visualisation of the fractured area. Minimally invasive techniques may be used to reduce surgical trauma and facilitate a faster recovery. The surgeon carefully identifies the pars defect, ensuring precision throughout the procedure.
Step 3: Preparation of the Pars Defect - Once the fractured area is exposed, the surgeon removes any scar tissue or fibrous material that may have formed around the defect. This step is essential to stimulate natural bone healing and create a favourable environment for fusion. The fractured surfaces are prepared by smoothing irregular bone edges, allowing optimal bone graft integration. Ensuring a clean, stable surface is crucial in achieving a successful repair.
Step 4: Bone Grafting and Fixation - A bone graft is placed at the prepared pars defect to promote new bone growth and fusion. The graft may be obtained from your pelvic bone (autograft) or a donor source (allograft). In some cases, synthetic bone substitutes may also be used. Internal fixation devices, such as screws or rods, are then carefully placed to stabilize the vertebra and secure the graft in place. This ensures the repaired pars region remains immobilised, allowing optimal healing and spinal stability.
Step 5: Closure and Post-Surgical Care - Once the bone graft and fixation are in place, the surgeon carefully repositions the muscles and soft tissues before closing the incision with sutures or surgical staples. A sterile dressing is applied to prevent infection, and you are then transferred to the recovery unit for monitoring. Immediate postoperative care focuses on pain management, wound care, and early mobilisation to facilitate a smooth recovery.
How long does it take to recover from the surgery?
The recovery process after Buck's Fusion is structured to ensure optimal healing, pain control, and a gradual return to activity. The initial weeks focus on wound healing and spinal stabilisation, followed by physical therapy and long-term rehabilitation.
Immediate Post-Surgical Care and Monitoring - After surgery, you will be closely monitored in the recovery unit for vital signs, pain levels, and potential complications. Pain management protocols using IV medications or epidural analgesia are initiated to ensure comfort. Early neurological assessments are performed to evaluate spinal function and nerve integrity. Once stable, you will transition to the postoperative care unit, where nurses will assist with gradual mobilisation and breathing exercises to prevent complications such as blood clots or pneumonia.
Pain Management and Early Mobility - Pain control is an integral part of recovery. Oral pain medications, muscle relaxants, and anti-inflammatory drugs help manage discomfort during the initial healing phase. You will be encouraged to begin gentle movements, including sitting and short walks, within 24 to 48 hours. Early mobility promotes blood circulation, prevents stiffness, and accelerates healing. A lumbar brace may be recommended to provide additional support and reduce strain on the surgical site.
Follow-Up and Long-Term Recovery
Physical Rehabilitation and Activity Guidelines - Structured physical therapy begins a few weeks after surgery to restore core strength, flexibility, and spinal stability. Guided exercises focus on gradual weight-bearing activities, posture correction, and strengthening the muscles supporting the spine. High-impact activities should be avoided for at least three to six months to allow complete fusion of the bone graft.
Monitoring Spinal Fusion Progress - Regular follow-up visits with your surgeon are crucial to track healing progress. X-rays or CT scans will be performed periodically to assess bone graft integration and spinal stability. Any delayed healing or implant issues will be addressed proactively to ensure a successful recovery.
How Do I Know If I Am Eligible for Pars Inter-Articularis Repair Surgery (Buck's Fusion)?
You may be eligible for Buck's fusion, a direct repair of the pars interarticularis, if you meet specific clinical and radiological criteria. This surgery is ideal for select individuals with spondylolysis and aims to preserve natural spinal motion, especially in younger, active patients.
You may be a suitable candidate if:
-
You have confirmed spondylolysis (pars defect): Imaging studies (X-ray, CT, or MRI) show a clear defect in the pars interarticularis, typically at L5, without significant disc degeneration or instability.
-
You experience chronic back pain unresponsive to conservative treatment: Persistent low back pain for over 6 months, despite physiotherapy, rest, bracing, or anti-inflammatory medications, suggests a surgical solution may be required.
-
You are young and physically active: Buck's fusion is most successful in adolescents or young adults with high functional demands (e.g., athletes), as it preserves spinal mobility and avoids the limitations of a full spinal fusion.
-
You have minimal or no vertebral slippage: This surgery is generally indicated in patients with Grade 0 or Grade I spondylolisthesis (slippage less than 25%). More advanced slips often require alternative fusion strategies.
-
You have no major disc or facet joint degeneration: An MRI should confirm that adjacent discs and facet joints are healthy. Disc degeneration may reduce the success of a direct repair and instead warrant a different surgical approach.
-
You have good bone quality and are a non-smoker: Healthy bone supports successful fusion and screw fixation. Smoking, poor nutrition, or metabolic bone disease can impair healing and increase complication risk.
Potential Risks and Limitations of Pars Inter-Articularis Repair - While Buck's Fusion is a highly effective procedure, it is essential to understand its potential risks and limitations.
-
Incomplete Fusion (Non-Union) - In some cases, the bone graft may not fully integrate, leading to persistent pain or needing revision surgery.
-
Infection or Wound Healing Issues - Postoperative infections are rare but may require antibiotics or additional interventions.
-
Nerve Irritation or Damage - The proximity of spinal nerves poses a small risk of irritation or temporary weakness, though this is uncommon.
-
Hardware Loosening or Failure - In rare cases, screws or fixation devices may shift, requiring further evaluation.
Why Choose MIRSS for Pars Inter-Articularis Repair Surgery (Buck's Fusion)?
Choosing the right medical centre and surgical team is critical for achieving the best outcomes. MIRSS offers cutting-edge spinal care, experienced specialists, and advanced surgical techniques to ensure the highest standard of treatment.
-
Expert Spine Surgeons - Highly skilled robotic spine surgeons in Bangalore with extensive experience in minimally invasive and complex spinal procedures.
-
State-of-the-Art Facilities - Advanced diagnostic imaging, surgical technology, and post-operative rehabilitation for superior patient care.
-
Comprehensive Post-Surgical Care - Structured pain management, physiotherapy, and long-term follow-ups to ensure optimal recovery.
-
Patient-Centric Approach - Individualised treatment plans tailored to your unique spinal condition, ensuring personalised and effective care.
At MIRSS, your spinal health and recovery are our top priorities, ensuring a safe, successful, and pain-free future.