Obesity and type 2 diabetes are closely connected health concerns. Obesity significantly raises the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The excess fat deposition in obesity can lead to insulin resistance. As insulin is the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar, resistance to it results in higher blood sugar levels. This can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes. Bariatric surgery, also known as weight loss surgery, is a solution to address both issues.


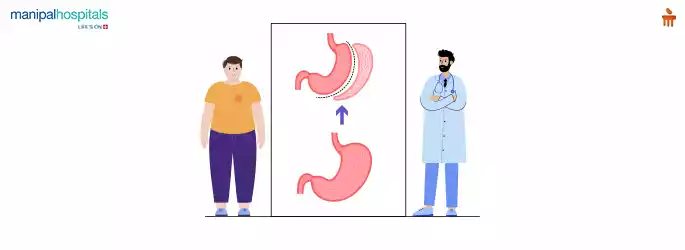
Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery, or obesity surgery, is a medical procedure for weight loss in severely obese individuals when conventional methods like diet and exercise have not yielded results, or obesity-related health issues are severe. It is not just cosmetic but also aims to improve overall health and manage obesity-related complications such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, and joint problems.
How Bariatric Surgery Reverses Type 2 Diabetes?
Bariatric surgery can effectively reverse type 2 diabetes through several mechanisms:
-
Rapid Weight Loss: Significant and sustained weight loss improves insulin sensitivity and reduces resistance, normalizing blood sugar levels.
-
Hormonal Changes: Altering gut hormones enhances insulin production and secretion, as seen in gastric bypass surgery.
-
Reduced Inflammation: Weight loss surgery reduces chronic inflammation, improving insulin sensitivity.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Surgery requires healthier eating habits and increased physical activity, contributing to better control of blood sugar levels.
Is Bariatric Surgery a Permanent Cure for Type 2 Diabetes?
Many individuals experience substantial improvement and even remission of type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery. However, it's essential to understand that weight loss surgery is not a permanent cure. Some may see a return of elevated blood sugar levels or diabetes symptoms later on.
Who is Eligible for Bariatric Surgery?
To be eligible for bariatric surgery, individuals should typically meet these criteria:
-
BMI of 40 or BMI of 35 with obesity-related health issues
-
Failed prior attempts at non-surgical weight loss methods
-
Commitment to lifelong lifestyle changes.
Advantages of Bariatric Surgery
The following are the key advantages that weight loss surgery offers, besides significant loss of weight:
-
Resolution of Health Issues: Often leads to the remission or improvement of obesity-related health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
-
Enhanced Quality of Life: Common benefits include improved mobility, self-esteem, and reduced emotional stress.
-
Long-Term Results: Lasting weight loss is achieved compared to many other weight loss methods.
-
Reduced Medication Dependence: Decreases the need for medications, lowering healthcare costs.
-
Positive Impact on Mental Health: Improved body image, self-confidence, and reduced psychological stress.
-
Reduction in Cardiovascular Risk: Lowers heart disease and stroke risk due to weight loss.
-
Management of Sleep Apnea: Can alleviate sleep apnea symptoms.
-
Enhanced Fertility: Can improve fertility in individuals with obesity-related fertility issues.
Bariatric surgery offers a promising avenue for reversing type 2 diabetes while addressing obesity. At Manipal Hospital Millers Road, we are equipped with 4K ultra HD monitors, 4k optic systems, high-quality Trocars, and tri-stapler technology to improve surgical outcomes. With smooth coordination with a multi-disciplinary team, the surgery and the post-op care aid in fast-tracking the recovery.
Visit Manipal Hospitals Millers Road for any advanced surgical needs or concerns, and consult with the best bariatric surgeon in Bangalore to determine your eligibility for bariatric surgery.
Correlation Between Obesity and Diabetes
Obesity and diabetes, particularly Type 2 diabetes, are linked in a bi-directional manner. The correlation illustrates the importance of integrated care and a holistic approach to managing both conditions. Addressing lifestyle factors, such as diet and physical activity, is often crucial in preventing and managing both obesity and diabetes. Here’s how both are correlated:
|
Obesity Leads to Diabetes |
Diabetes Contributes to Obesity |
|
1. Insulin Resistance: Obesity can lead to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells don’t respond adequately to insulin & more insulin is needed to keep blood glucose levels in check, causing Type 2 diabetes. 2. Inflammation: Excessive fat in individuals with obesity can trigger inflammation, disturbing insulin functionality & subsequently increasing the probability of diabetes. 3. Altered Fat Metabolism: The metabolic processing of fats is modified by obesity, causing fat accumulation in tissues (like the liver & muscles) & hindering the action of insulin. |
1. Insulin Administration: Used as a therapeutic tool in managing diabetes, insulin can potentially induce weight gain. If not carefully counteracted with mindful dietary practices and regular physical activity, this can cause obesity. 2. Hypoglycemia: Individuals managing diabetes may consume excess food as a measure to prevent or address hypoglycemia or low blood sugar. If this becomes a habitual action, it may lead to progressive weight gain. |
Mutual Impact
Both obesity and diabetes share common complications, such as cardiovascular disease, thereby mutually amplifying health risks. Managing one condition can sometimes make the other more difficult to control. For example, some diabetes medications can cause weight gain, complicating the management of obesity.